Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 2- Exposure to neurotoxins and ultra-processed foods
Posted: June 30, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, CBT, digital devices, education, emotions, Evolutionary perspective, health, mindfulness, neurofeedback, Nutrition/diet, Uncategorized | Tags: ADHD, anxiety, depression, diet, glyphosate, herbicide, herbicites, mental-health, neurofeedback, pesticides, supplements', ultraprocessed foods, vitamins 4 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. & Shuford, J. (2024). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 2- Exposure to neurotoxins and ultra-processed foods. NeuroRegulation, 11(2), 219–228. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.11.2.219
Look at your hand and remember that every cell in your body including your brain is constructed out the foods you ingested. If you ingested inferior foods (raw materials to be built your physical structure), then the structure can only be inferior. If you use superior foods, you have the opportunity to create a superior structure which provides the opportunity for superior functioning. -Erik Peper
Summary
Mental health symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Autism, anxiety and depression have increased over the last 15 years. An additional risk factor that may affect mental and physical health is the foods we eat. Even though, our food may look and even taste the same as compared to 50 years ago, it contains herbicide and pesticide residues and often consist of ultra-processed foods. These foods (low in fiber, and high in sugar, animal fats and additives) are a significant part of the American diet and correlate with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in children with ADHD. Due to affluent malnutrition, many children are deficient in essential vitamins and minerals. We recommend that before beginning neurofeedback and behavioral treatments, diet and lifestyle are assessed (we call this Grandmother therapy assessment). If the diet appears low in organic foods and vegetable, high in ultra-processed foods and drinks, then nutritional deficiencies should be assessed. Then the next intervention step is to reduce the nutritional deficiencies and implement diet changes from ultra-processed foods to organic whole foods. Meta-analysis demonstrates that providing supplements such as Vitamin D, etc. and reducing simple carbohydrates and sugars and eating more vegetables, fruits and healthy fats during regular meals can ameliorate the symptoms and promote health.
The previous article and blog, Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms, pointed out how the changes in bonding, screen time and circadian rhythms affected physical and mental health (Peper, 2023a; Peper, 2023b). However, there are many additional factors including genetics that may contribute to the increase is ADHD, autism, anxiety, depression, allergies and autoimmune illnesses (Swatzyna et al., 2018). Genetics contribute to the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD); since, family, twin, and adoption studies have reported that ADHD runs in families (Durukan et al., 2018; Faraone & Larsson, 2019). Genetics is in most cases a risk factor that may or may not be expressed. The concept underlying this blog is that genetics loads the gun and environment and behavior pulls the trigger as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Interaction between Genetics and Environment
The pandemic only escalated trends that already was occurring. For example, Bommersbach et al (2023) analyzed the national trends in mental health-related emergency department visits among USA youth, 2011-2021. They observed that in the USA, Over the last 10 years, the proportion of pediatric ED visits for mental health reasons has approximately doubled, including a 5-fold increase in suicide-related visits. The mental health-related emergency department visits increased an average of 8% per year while suicide related visits increased 23.1% per year. Similar trends have reported by Braghieri et al (2022) from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Mental health trends in the United States by age group in 2008–2019. The data come from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Reproduced with permission from Braghieri, Luca and Levy, Ro’ee and Makarin, Alexey, Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022) https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
The trends reported from this data shows an increase in mental health illnesses for young people ages 18-23 and 24-29 and no changes for the older groups which could be correlated with the release of the first iPhone 2G on June 29, 2007. Thus, the Covid 19 pandemic and social isolation were not THE CAUSE but an escalation of an ongoing trend. For the younger population, the cellphone has become the vehicle for personal communication and social connections, many young people communicate more with texting than in-person and spent hours on screens which impact sleep (Peper, 2023a). At the same time, there are many other concurrent factors that may contributed to increase of ADHD, autism, anxiety, depression, allergies and autoimmune illnesses.
Without ever signing an informed consent form, we all have participated in lifestyle and environmental changes that differ from that evolved through the process of evolutionary natural selection and promoted survival of the human species. Many of those changes in lifestyle are driven by demand for short-term corporate profits over long-term health of the population. As exemplified by the significant increase in vaping in young people as a covert strategy to increase smoking (CDC, 2023) or the marketing of ultra-processed foods (van Tulleken, 2023).
This post focusses how pesticides and herbicides (exposure to neurotoxins) and changes in our food negatively affects our health and well-being and is may be another contributor to the increase risk for developing ADHD, autism, anxiety and depression. Although our food may look and even taste the same compared to 50 years ago, it is now different–more herbicide and pesticide residues and is often ultra-processed. lt contains lower levels of nutrients and vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin B2, Protein, Iron, Calcium and Phosphorus than 50 years ago (Davis et al, 2004; Fernandez-Cornejo et al., 2014). Non-organic foods as compared to organic foods may reduce longevity, fertility and survival after fasting (Chhabra et al., 2013).
Being poisoned by pesticide and herbicide residues in food
Almost all foods, except those labeled organic, are contaminated with pesticides and herbicides. The United States Department of Agriculture reported that “Pesticide use more than tripled between 1960 and 1981. Herbicide use increased more than tenfold (from 35 to 478 million pounds) as more U.S. farmers began to treat their fields with these chemicals” (Fernandez-Cornejo, et al., 2013, p 11). The increase in herbicides and pesticides is correlated with a significant deterioration of health in the United States (Swanson, et al., 2014 as illustrated in the following Figure 3.


Figure 3. Correlation between Disease Prevalence and Glyphosate Applications (reproduced with permission from Swanson et al., 2014.
Although correlation is not causation and similar relationships could be plotted by correlating consumption of ultra-refined foods, antibiotic use, decrease in physical activity, increase in computer, cellphone and social media use, etc.; nevertheless, it may suggest a causal relationship. Most pesticides and herbicides are neurotoxins and can accumulate in the person over time this could affect physical and mental health (Bjørling-Poulsen et al., 2008; Arab & Mostaflou, 2022). Even though the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has determined that the residual concentrations in foods are safe, their long-term safety has not been well established (Leoci & Ruberti, 2021). Other countries, especially those in which agribusiness has less power to affect legislation thorough lobbying, and utilize the research findings from studies not funded by agribusiness, have come to different conclusions…
For example, the USA allows much higher residues of pesticides such as, Round-Up, with a toxic ingredient glyphosate (0.7 parts per million) in foods than European countries (0.01 parts per million) (Wahab et al., 2022; EPA, 2023; European Commission, 2023) as is graphically illustrated in figure 4.

Figure 4: Percent of Crops Sprayed with Glyphosate and Allowable Glyphosate Levels in the USA versus the EU
The USA allows this higher exposure than the European Union even though about half of the human gut microbiota are vulnerable to glyphosate exposure (Puigbo et al., 2022). The negative effects most likely would be more harmful in a rapidly growing infant than for an adult. Most likely, some individuals are more vulnerable than others and are the “canary in mine.” They are the early indicators for possible low-level long-term harm. Research has shown that fetal exposure from the mother (gestational exposure) is associated with an increase in behaviors related to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders and executive function in the child when they are 7 to 12 years old (Sagiv et al., 2021). Also, organophosphate exposure is correlated with ADHD prevalence in children (Bouchard et al., 2010). We hypothesize this exposure is one of the co-factors that have contributed to the decrease in mental health of adults 18 to 29 years.
At the same time as herbicides and pesticides acreage usage has increased, ultra-processed food have become a major part of the American diet (van Tulleken, 2023). Eating a diet high in ultra-processed foods, low in fiber, high sugar, animal fats and additives has been associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in children with ADHD; namely, high consumption of sugar, candy, cola beverages, and non-cola soft drinks and low consumption of fatty fish were also associated with a higher prevalence of ADHD diagnosis (Ríos-Hernández et al., 2017).
In international studies, less nutritional eating behaviors were observed in ADHD risk group as compared to the normal group (Ryu et al., 2022). Artificial food colors and additives are also a public health issue and appear to increase the risk of hyperactive behavior (Arnold et al., 2012). In a randomized double-blinded, placebo controlled trial 3 and 8/9 year old children had an increase in hyperactive behavior for those whose diet included extra additives (McCann et al., 2007). The risk may occur during fetal development since poor prenatal maternal is a critical factor in the infants neurodevelopment and is associated with an increased probability of developing ADHD and autism (Zhong et al., 2020; Mengying et al., 2016).
Poor nutrition even affects your unborn grandchild
Poor nutrition not only affects the mother and the developing fetus through epigenetic changes, it also impacts the developing eggs in the ovary of the fetus that can become the future granddaughter (Wilson, 2015). At birth, the baby has all of her eggs. Thus, there is a scientific basis for the old wives tale that curses may skip a generation. Providing maternal support is even more important since it affects the new born and the future grandchild. The risk may even begin a generation earlier since the grandmother’s poor nutrition as well as stress causes epigenetic changes in the fetus eggs. Thus 50% of the chromosomes of the grandchild were impacted epigenetically by the mother’s and grandmother’s dietary and health status .
Highly processed foods
Highly refined foods have been processed to remove many of their nutrients. These foods includes white bread, white rice, pasta, and sugary drinks and almost all the fast foods and snacks. These foods are low in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they are high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and calories. In addition, additives may have been added to maximize taste and mouth feel and implicitly encourage addiction to these foods. A diet high in refined sugars and carbohydrates increases the risk of diabetes and can worsen the symptoms of ADHD, autism, depression, anxiety and increase metabolic disease and diabetes (Woo et al., 2014; Lustig, 2021; van Tulleken, 2023). Del-Ponte et al. (2019) noted that a diet high in refined sugar and saturated fat increased the risk of symptoms of ADHD, whereas a healthy diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits and vegetables, would protect against the symptoms.
Most likely, a diet of highly refined foods may cause blood sugar to spike and crash, which can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression and cognitive decline and often labeled as “hangryness” (the combination of anger and hunger) (Gomes et al., 2023; Barr et al., 2019). At the same time a Mediterranean diet improves depression significantly more than the befriending control group (Bayles et al., 2022). In addition, refined foods are low in essential vitamins and minerals as well as fiber. Not enough fiber can slow down digestion, affect the human biome, and makes it harder for the body to absorb nutrients. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can contribute to the symptoms of ADHD, autism, depression, and anxiety. Foods do impact our mental and physical health as illustrated by foods that tend to reduce depression (LaChance & Ramsey, 2018; MacInerney et al., 2017). By providing appropriate micronutrients such as minerals (Iron, Magnesium Zinc), vitamins (B6, B12, B9 and D), Omega 3s (Phosphatidylserine) and changing our diet, ADHD symptoms can be ameliorated.
Many children with ADHD, anxiety, depression are low on essential vitamins and minerals. For example, low levels of Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D may be caused by eating ultra-refined foods, fast foods, and drinking soft drink. At the same time, the children are sitting more in indoors in front of the screen and thereby have lower sun exposure that is necessary for the vitamin D production.
“Because of lifestyle changes and sunscreen use, about 42% of Americans are deficient in vitamin D. Among children between 1 to 11 years old, an estimated 15% have vitamin D deficiency. And researchers have found that 17% of adolescents and 32% of young adults were deficient in vitamin D.” (Porto and Abu-Alreesh, 2022).
Reduced sun exposure is even more relevant for people of color (and older people); since, their darker skin (increased melanin) protects them from ultraviolet light damage but at the same time reduces the skins production of vitamin D. Northern Europeans were aware of the link between sun exposure and vitamin D production. To prevent rickets (a disease caused by vitamin D deficiency) and reduce upper respiratory tract infections the children were given a tablespoon of cod liver oil to swallow (Linday, 2010). Cod liver oil, although not always liked by children, is more nutritious than just taking a Vitamin D supplements. It is a whole food and a rich source of vitamin A and D as well as containing a variety of Omega 3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (USDA, 2019).
Research studies suggest that ADHD can be ameliorated with nutrients, and herbs supplements (Henry & CNS, 2023). Table 1 summarizes some of the nutritional deficits observed and the reduction of ADHD symptoms when nutritional supplements were given (adapted from Henry, 2023; Henry & CNS, 2023).
| Nutritional deficits observed in people with ADHD | Decrease in ADHD symptoms with nutritional supplements |
| Vitamin D: In meta-analysis with a total number of 11,324 children, all eight trials reported significantly lower serum concentrations of 25(OH)D in patients diagnosed with ADHD compared to healthy controls. (Kotsi et al, 2019) | After 8 weeks children receiving vitamin D (50,000 IU/week) plus magnesium (6 mg/kg/day) showed a significant reduction in emotional problems as observed in a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Hemamy et al., 2021). |
| Iron: In meta-analysis lower serum ferritin was associated with ADHD in children (Wang et al., 2017) and the mean serum ferritin levels are lower in the children with ADHD than in the controls (Konofal et al., 2004). | After 12 weeks of supplementation with Iron (ferrous sulfate) in double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, clinical trials symptoms of in children with ADHD as compared to controls were reduced (Tohidi et al., 2021; Pongpitakdamrong et all, 2022). |
| Omega 3’s: Children with ADHD are more likely to be deficient in omega 3’s than children without ADHD (Chang et al., 2017). | Adding Omega-3 supplements to their diet resulted in an improvement in hyperactivity, impulsivity, learning, reading and short term memory as compared to controls in 16 randomized controlled trials including 1514 children and young adults with ADHD (Derbyshire, 2017) |
| Magnesium: In meta-analysis, subjects with ADHD had lower serum magnesium levels compared with to their healthy controls (Effatpahah et al., 2019) | 8 weeks of supplementation with Vitamin D and magnesium caused a significant decrease in children with conduct problems, social problems, and anxiety/shy scores (Hemamy et al., 2020). |
| Vitamin B2, B6, B9 and B12deficiency has been found in many patients with Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder (Landaas et al, 2016; Unal et al., 2019). | Vitamin therapy appears to reduce symptoms of ADHD and ASD (Poudineh et al., 2023; Unal et al., 2019). An 8 weeks supplementing with Vitamin B6 and magnesium decreased hyperactivity and hyperemotivity/aggressiveness. When supplementation was stopped, clinical symptoms of the disease reappeared in few weeks (Mousain-Bosc et al., 2006). |
Table 1. Examples of vitamin and mineral deficiencies associated with symptoms of ADHD and supplementation to reduction of ADHD symptoms.
Supplementation of vitamins and minerals in many cases consisted of more than one single vitamin or mineral. For an in-depth analysis and presentation, see the superb webinar by Henry & CNS (2023): https://divcom-events.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/divcom-events/recording/e29cefcae6c1103bb7f3aa780efee435/playback? (Henry & CNS, 2023).
Whole foods are more than the sum of individual parts (the identified individual constituents/nutrients). The process of digestion is much more complicated than ingesting simple foods with added vitamins or minerals. Digestion is the interaction of many food components (many of which we have not identified) which interact and affect the human biome. A simple added nutrient can help; however, eating whole organic foods it most likely be healthier. For example, whole-wheat flour is much more nutritious. Whole wheat is rich in vitamins B-1, B-3, B-5, riboflavin, folate well as fiber while refined white flour has been bleached and stripped of fiber and nutrients to which some added vitamins and iron are added.
Recommendation
When working with clients, follow Talib’s principles as outlined in Part 1 by Peper (2023) which suggests that to improve health first remove the unnatural which in this case are the ultra-processed foods, simple carbohydrates, exposure to pesticides and herbicides (Taleb, 2014). The approach is beneficial for prevention and treatment. This recommendation to optimize health is both very simple and very challenging. The simple recommendation is to eat only organic foods and as much variety as possible as recommended by Professor Michael Pollan in his books, Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and Food Rules (Pollan, 2006; Pollan, 2011).
Do not eat foods that contain herbicides and pesticide residues or are ultra-processed. Although organic foods especially vegetable and fruits are often much more expensive, you have choice: You can pay more now to optimize health or pay later to treat disease. Be safe and not sorry. This recommendation is similar to the quote, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food,” that has been attributed falsely since the 1970s to Hippocrates, the Greek founder of western medicine (5th Century, BC) (Cardenas, 2013).
There are many factors that interfere with implementing these suggestions; since, numerous people live in food deserts (no easy access to healthy unprocessed foods ) or food swamps (a plethora of fast food outlets) and 54 million Americans are food insecure (Ney, 2022). In addition, we and our parents have been programmed by the food industry advertising to eat the ultra- processed foods and may no longer know how to prepare healthy foods such as exemplified by a Mediterranean diet. Recent research by Bayles et al (2022) has shown that eating a Mediterranean diet improves depression significantly more than the befriending control group. In addition, highly processed foods and snacks are omnipresent, often addictive and more economical.
Remember that clients are individuals and almost all research findings are based upon group averages. Even when the data implies that a certain intervention is highly successful, there are always some participants for whom it is very beneficial and some for whom it is ineffective or even harmful. Thus, interventions need to be individualized for which there is usually only very limited data. In most cases, the original studies did not identify the characteristics of those who were highly successful or those who were unsuccessful. In addition, when working with specific individuals with ADHD, anxiety, depression, etc. there are multiple possible causes.
Before beginning specific clinical treatment such as neurofeedback and/or medication, we recommend the following:
- “Grandmother assessment” that includes and assessment of screen time, physical activity, outdoor sun exposure, sleep rhythm as outlined in Part 1 by Peper (2023). Then follow-up with a dietary assessment that investigates the prevalence of organic/non organic foods, ingestion of fast foods, ultra-processed foods, soft drinks, high simple carbohydrate and sugar, salty/sugary/fatty snacks, fruits, vegetables, and eating patterns (eating with family or by themselves in front of screens). Be sure to include an assessment of emotional reactivity and frequency of irritability and “hangryness”.
- If the assessment suggest low level of organic whole foods and predominance of ultra- refined foods, it may be possible that the person is deficient in vitamins and minerals. Recommend that the child is tested for the vitamin deficiencies. If vitamin deficiencies identified, recommend to supplement the diet with the necessary vitamins and mineral and encourage eating foods that naturally include these substances (Henry & CNS, 2023). If there is a high level of emotional reactivity and “hangryness,” a possible contributing factor could be hypoglycemic rebound from a high simple carbohydrate (sugar) intake or not eating breakfast combined with hyperventilation (Engel et al., 1947; Barr et al., 2019). Recommend eliminating simple carbohydrate breakfast and fast food snacks and substitute organic foods that include complex carbohydrates, protein, fats, vegetables and fruit. Be sure to eat breakfast.
- Implement “Grandmother Therapy”. Encourage the family and child to change their diet to eating a whide variety of organic foods (vegetables, fruits, some fish, meat and possibly dairy) and eliminate simple carbohydrates and sugars. This diet will tend to reduce nutritional deficits and may eliminate the need for supplements.
- Concurrent with the stabilization of the physiology begin psychophysiological treatment strategies such as neurofeedback biofeedback and cognitive behavior therapy.
Relevant blogs
Author Disclosure
Authors have no grants, financial interests, or conflicts to disclose.
References
Arnold, L, Lofthouse, N., & Hurt, E. (2012). Artificial food colors and attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms: conclusions to dye for. Neurotherapeutics, 9(3), 599-609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-012-0133-x
Arab, A. & Mostafalou, S. (2022). Neurotoxicity of pesticides in the context of CNS chronic diseases. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 32(12), 2718-2755. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2021.1987396
Barr, E.A., Peper, E., & Swatzyna, R.J. (2019). Slouched Posture, Sleep Deprivation, and Mood Disorders: Interconnection and Modulation by Theta Brain Waves. NeuroRegulation, 6(4), 181–189. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.4.181
Bayes. J., Schloss, J., Sibbritt, D. (2022). The effect of a Mediterranean diet on the symptoms of depression in young males (the “AMMEND: A Mediterranean Diet in MEN with Depression” study): a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 116(2), 572-580. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqac106
Bjørling-Poulsen, M., Andersen, H.R. & Grandjean, P. Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ Health 7, 50 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-7-50
Bommersbach, T.J., McKean, A.J., Olfson, M., Rhee, T.G. (2023). National Trends in Mental Health–Related Emergency Department Visits Among Youth, 2011-2020. JAMA, 329(17):1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.4809
Bouchard, M.F., Bellinger, D.C., Wright, R.O., & Weisskopf, M.G. (2010). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and urinary metabolites of organophosphate pesticides. Pediatrics, 125(6), e1270-7. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-3058
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Cardenas, D. (2013). Let not thy food be confused with thy medicine: The Hippocratic misquotation. e-Spen Journal, 8(6), 3260-3262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnme.2013.10.002
CDC, (2023). Quick Facts on the Risks of E-cigarettes for Kids, Teens, and Young Adults. CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 23, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/Quick-Facts-on-the-Risks-of-E-cigarettes-for-Kids-Teens-and-Young-Adults.html
Chang, J.C., Su, K.P., Mondelli, V. et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Youths with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials and Biological Studies. Neuropsychopharmacol. 43, 534–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.160
Chhabra, R., Kolli, S., & Bauer, J.H. (2013). Organically Grown Food Provides Health Benefits to Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE, 8(1): e52988. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052988
Davis, D. R., Epp, M. D., & Riordan, H. D. (2004). Changes in USDA food composition data for 43 garden crops, 1950 to 1999. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 23(6), 669-682. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719409
Derbyshire, E. (2017). Do Omega-3/6 Fatty Acids Have a Therapeutic Role in Children and Young People with ADHD? J Lipids. 6285218. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6285218
Del-Ponte, B., Quinte, G.C., Cruz, S., Grellert, M., & Santos, I. S. Dietary patterns and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 252, 160-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.04.061
Durukan, İ., Kara, K., Almbaideen, M., Karaman, D., & Gül, H. (2018). Alexithymia, depression and anxiety in parents of children with neurodevelopmental disorder: Comparative study of autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics International, 60(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.13510
Effatpanah, M., Rezaei, M., Effatpanah, H., Effatpanah, Z., Varkaneh, H.K., Mousavi. S.M., Fatahi, S., Rinaldi, G., & Hashemi, R. (2019). Magnesium status and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res, 274, 228-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.02.043
Engel, G.L., Ferris, E.B., & Logan, M. (1947). Hyperventilation; analysis of clinical symptomatology. Ann Intern Med, 27(5), 683-704. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-27-5-683
EPA. (2023). Glyphosate. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/glyphosate
European Commission. (2023). EU legislation on MRLs.Food Safety. Assessed April 1, 2023. https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/maximum-residue-levels/eu-legislation-mrls_en#:~:text=A%20general%20default%20MRL%20of,e.g.%20babies%2C%20children%20and%20vegetarians
Faraone, S.V. & Larsson, H. (2019). Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry, 24(4), 562-575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0
Fernandez-Cornejo, J. Nehring, R, Osteen, C., Wechsler, S., Martin, A., & Vialou, A. (2014). Pesticide use in the U.S. Agriculture: 21 Selected Crops, 1960-2008. Economic Information Bulletin Number 123, United State Department of Agriculture. https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/43854/46734_eib124.pdf
Gomes, G. N., Vidal, F. N., Khandpur. N., et al. (2023). Association Between Consumption of Ultraprocessed Foods and Cognitive Decline. JAMA Neurol, 80(2),142–150. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.4397
Hemamy, M., Heidari-Beni, M., Askari, G., Karahmadi, M., & Maracy, M. (2020). Effect of Vitamin D and Magnesium Supplementation on Behavior Problems in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Int J Prev Med, 11(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_546_17
Henry, K. (2023). An Integrative Medicine Approach to ADHD. Rupa Health. Accessed September 30, 2023. https://www.rupahealth.com/post/an-integrative-medicine-approach-to-adhd
Henry, K. & CNS, L.A. (2023). Natural treatments for ADHD. Webinar Presentation by IntegrativePractitioner.com and sponsored by Rupa Health, June 6, 2023 https://divcom-events.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/divcom-events/recording/e29cefcae6c1103bb7f3aa780efee435/playback?
Hemamy, M., Pahlavani, N., Amanollahi, A. et al. (2021). The effect of vitamin D and magnesium supplementation on the mental health status of attention-deficit hyperactive children: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr, 21, 178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-021-02631-1
Konofal, E., Lecendreux, M., Arnulf, I., & Mouren, M. (2004). Iron Deficiency in Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 158(12), 1113–1115. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.158.12.1113
Kotsi, E., Kotsi, E. & Perrea, D.N. (2019). Vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a meta-analysis. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord, 11, 221–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-018-0276-7
LaChance, L.R. & Ramsey, D. (2018). Antidepressant foods: An evidence-based nutrient profiling system for depression. World J Psychiatr, 8(3): 97-104. World J Psychiatr., 8(3): 97-104. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v8.i3.97
Landaas, E.T., Aarsland, T.I., Ulvik, A., Halmøy, A., Ueland. P.M., & Haavik, J. (20166). Vitamin levels in adults with ADHD. BJPsych Open, 2(6), 377-384. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjpo.bp.116.003491
Linday, L.A. (2010). Cod liver oil, young children, and upper respiratory tract infections. J Am Coll Nutr, 29(6), 559-62. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2010.10719894
Leoci, R. & Ruberti, M. (2021) Pesticides: An Overview of the Current Health Problems of Their Use. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 9, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2021.98001
Lustig, R.H. (2021). Metaboical: The lure and the lies of processed food, nutrition, and modern medicine. New York: Harper Wave. https://www.amazon.com/Metabolical-processed-poisons-people-planet/dp/1529350077
MacInerney, E. K., Swatzyna, R. J., Roark, A. J., Gonzalez, B. C., & Kozlowski, G. P. (2017). Breakfast choices influence brainwave activity: Single case study of a 12-year-old female. NeuroRegulation, 4(1), 56–62. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.4.1.56
McCann, D., Barrett, A., Cooper, A., Crumpler, D., Dalen, L., Grimshaw, K., et al. (2007). Food additives and hyperactive behavior in 3-year old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet, 370(9598), 1560-1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3
Mengying, L.I, Fallin, A, D., Riley,A., Landa, R., Walker, S.O., Silverstein, M., Caruso, D., et al. (2016). The Association of Maternal Obesity and Diabetes With Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities. Pediatrics, 137(2), e20152206. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-2206
Mousain-Bosc, M., Roche, M., Polge, A., Pradal-Prat, D., Rapin, J., & Bali, J.P. (2006). Improvement of neurobehavioral disorders in children supplemented with magnesium-vitamin B6. I. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders. Magnes Res. 19(1), 46-52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16846100/#:~:text=In%20almost%20all%20cases%20of,increase%20in%20Erc%2DMg%20values.
Ney, J. (2022). Food Deserts and Inequality. Social Policy Data Lab. Updated: Jan 24, 2022. Accessed September, 23, 2023. https://www.socialpolicylab.org/post/grow-your-blog-community
Peper, E. (2023a). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. the peperperspective July 2, 2023. Accessed august 8, 2024, https://peperperspective.com/2023/07/04/reflections-on-the-increase-in-autism-adhd-anxiety-and-depression-part-1-bonding-screen-time-and-circadian-rhythms/
Peper, E. (2023b). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. NeuroRegulation, 10(2), 134-138. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.10.2.134
Pollan, M. (2006). Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and Food Rules. New York Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Omnivores-Dilemma-Natural-History-Meals/dp/1594200823/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?_
Pollan, M. (2011). Food rules. New York Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Food-Rules-Eaters-Michael-Pollan/dp/B00VSBILFG/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?
Pongpitakdamrong, A., Chirdkiatgumchai, V., Ruangdaraganon, N., Roongpraiwan, R., Sirachainan, N., Soongprasit, M., & Udomsubpayakul, U. (2022). Effect of Iron Supplementation in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Iron Deficiency: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, 43(2), 80-86., https://doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0000000000000993
Porto, A. & Abu-Alreesh, S. (2022). Vitamin D for babies, children & adolescents. Health Living. Healthychildren.org. Accessed September 24, 2023. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/nutrition/Pages/vitamin-d-on-the-double.aspx#
Poudineh, M., Parvin, S., Omidali, M., Nikzad, F., Mohammadyari, F., Sadeghi Poor Ranjbar, F., F., Nanbakhsh, S., & Olangian-Tehrani, S. (2023). The Effects of Vitamin Therapy on ASD and ADHD: A Narrative Review. CNS & Neurological Disorders – Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets – CNS & Neurological Disorders), (22), 5, 2023, 711-735. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527321666220517205813
Puigbò, P., Leino, L. I., Rainio, M. J., Saikkonen, K., Saloniemi, I., & Helander, M. (2022). Does Glyphosate Affect the Human Microbiota?. Life, 12(5), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050707
Ríos-Hernández, A., Alda, J.A., Farran-Codina, A., Ferreira-García, E., & Izquierdo-Pulido, M. (2017). The Mediterranean Diet and ADHD in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics, 139(2):e20162027. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2027
Ryu, S.A., Choi, Y.J., An, H., Kwon, H.J., Ha, M., Hong, Y.C., Hong, S.J., & Hwang, H.J. (2022). Associations between Dietary Intake and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Scores by Repeated Measurements in School-Age Children. Nutrients, 14(14), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142919
Sagiv, S.K., Kogut, K., Harley, K., Bradman, A., Morga, N., & Eskenazi, B. (2021). Gestational Exposure to Organophosphate Pesticides and Longitudinally Assessed Behaviors Related to Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Executive Function, American Journal of Epidemiology, 190(11), 2420–2431. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwab173
Swanson, N.L., Leu, A., Abrahamson, J., & Wallet, B. (2014). Genetically engineered crops, glyphosate and the deterioration of health in the United States of America. Journal of Organic Systems, 9(2), 6-17. https://www.organic-systems.org/journal/92/JOS_Volume-9_Number-2_Nov_2014-Swanson-et-al.pdf
Swatzyna, R. J., Boutros, N. N., Genovese, A. C., MacInerney, E. K., Roark, A. J., & Kozlowski, G. P. (2018). Electroencephalogram (EEG) for children with autism spectrum disorder: Evidential considerations for routine screening. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 28(5), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-018-1225-x
Taleb, N. N. (2014). Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder (Incerto). New York: Random House Publishing Group. https://www.amazon.com/Antifragile-Things-That-Disorder-Incerto/dp/0812979680/ref=tmm_pap_swatch_0
Tohidi, S., Bidabadi, E., Khosousi, M.J., Amoukhteh, M., Kousha, M., Mashouf, P., Shahraki, T. (2021). Effects of Iron Supplementation on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children Treated with Methylphenidate. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci, 19(4), 712-720. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2021.19.4.712
Unal, D. Çelebi, F., Bildik,H.N., Koyuncu, A., & Karahan, S. (2019). Vitamin B12 and haemoglobin levels may be related with ADHD symptoms: a study in Turkish children with ADHD, Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 29(4), 515-519. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750573.2018.1459005
USDA. (2019). Fish oil, cod liver. FoodData Central. USDA U.S> Department of Agriculture. Published 4/1/2019. Accessed September 24, 2024. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173577/nutrients
Van Tulleken, C. (2023). Ultra-Processed People. The Science Behind Food That Isn’t Food. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. https://www.amazon.com/Ultra-Processed-People-Science-Behind-Food/dp/1324036729/ref=asc_df_1324036729/?
Wahab, S., Muzammil, K., Nasir, N., Khan, M.S., Ahmad, M.F., Khalid, M., Ahmad, W., Dawria, A., Reddy, L.K.V., & Busayli, A.M. (2022). Advancement and New Trends in Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Food: A Comprehensive Review. Plants (Basel), 11(9), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091106
Wang. Y., Huang, L., Zhang, L., Qu, Y., & Mu, D. (2017). Iron Status in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One, 12(1):e0169145. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169145
Wilson, L. (2015). Mothers, beware: Your lifestyle choices will even affect your grandkids.
News Corp Australia Network. Accessed Jun 24, 2024. https://www.news.com.au/lifestyle/parenting/kids/mothers-beware-your-lifestyle-choices-will-even-affect-your-grandkids/news-story/3f326f457546cfb32af5c409f335fb56
Woo, H.D.,; Kim, D.W., Hong, Y.-S., Kim, Y.-M.,Seo, J.-H.,; Choe, B.M., Park, J.H.,; Kang, J.-W., Yoo, J.-H.,; Chueh, H.W., et al. (2014). Dietary Patterns in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Nutrients, 6, 1539-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6041539
Zhong, C., Tessing, J., Lee, B.K., Lyall, K. Maternal Dietary Factors and the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review of Existing Evidence. Autism Res,13(10),1634-1658. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2402
What to eat? Low fat foods, high fat foods…..?
Posted: July 12, 2014 Filed under: Evolutionary perspective, Nutrition/diet, Uncategorized | Tags: cancer, diet, evolution, health, heart disease, vitamins 4 CommentsMeat for sale (tongue and liver) at a traditional market (photo by Erik Peper).
Should I eat vegetables or meats? Should it be steaks or organ meats such as liver, heart, sweet breads? What foods contributes most to heart disease or cancer? Should I change my diet or take medications to lower my cholesterol?
Despite the many years of research the data is not clear. Many public health dietary guidelines and recommendations were based upon flawed research, researchers’ bias and promoted by agribusiness. Starting in the 1950s there has been a significant change in the dietary habits from eating animal fats to plant based oils and fats. It is so much cheaper to produce plant based polyunsaturated salad or cooking oils (e.g. Wesson and Mazola) and hydrogenated hardened oils (e.g. margarine and Crisco) than animal fats (e.g., butter, beef tallow, and lard). Despite the many claims that lowering animal fat intake would reduce heart disease and possibly cancer, the claims are not supported by research data. It is true that consuming liquid plant based oils lowers the cholesterol, but with the possible exception of olive oil, polyunsaturated oils are associated with an increased cancer and death rates in large population studies (Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group,1982; Shaten, 1997).
 We assume that lowering cholesterol is healthy; however, it is usually a surrogate marker representing a hypothesized improvement in health. A short term apparent reduction in cholesterol levels or other illness markers may mask the long term harm. Only long term outcome studies which measure the total death rate– not just from one disease being studied but from all causes of death–provides the objective results. When looking at the results over a longer time period, there appears to be no correlation between fat intake and heart disease. In fact lowering fat intake seems to be associated with poorer long term health as described in the outstanding book, The Big Fat Surprise–Why Butter, Meat & Cheese Belong in a Healthy Diet, by the science writer, Nina Teichol. Her superb investigative reporting describes in detail the flawed and biased research that underpinned the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the American Heart Association (AHA) recommendations to reduce animal fats and use more plant based oils.
We assume that lowering cholesterol is healthy; however, it is usually a surrogate marker representing a hypothesized improvement in health. A short term apparent reduction in cholesterol levels or other illness markers may mask the long term harm. Only long term outcome studies which measure the total death rate– not just from one disease being studied but from all causes of death–provides the objective results. When looking at the results over a longer time period, there appears to be no correlation between fat intake and heart disease. In fact lowering fat intake seems to be associated with poorer long term health as described in the outstanding book, The Big Fat Surprise–Why Butter, Meat & Cheese Belong in a Healthy Diet, by the science writer, Nina Teichol. Her superb investigative reporting describes in detail the flawed and biased research that underpinned the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the American Heart Association (AHA) recommendations to reduce animal fats and use more plant based oils.
What should I eat now?
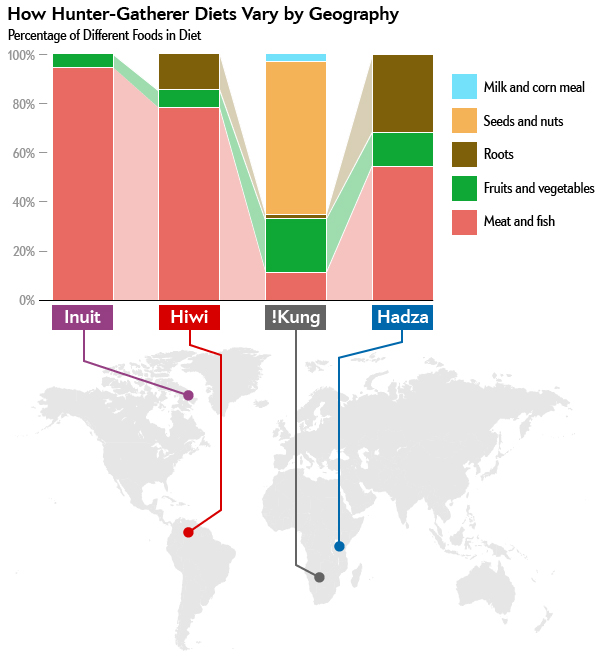
Diet recommendations used to be simple: Reduce animal fat intake and eat more plants. Now, there are no simple recommendations because they may depend upon your genetics (e.g., digestion of milk depends whether you are lactose tolerant or intolerant), your epigenetics (e.g., maternal malnutrition during your embryological development is a major risk for developing heart disease in later life), your physical and social activities (e.g., exercise reduces the risk for many diseases), and environment. The recent popularity of the hunter and gatherer diet, often known as the paleo diet, is challenging–it may depends on your ancestors. What hunter and gatherers ate depended upon geography and availability of food sources. The Inuit’s diet in the Arctic consisted of 90% meat/fish diet while the !Kung Bushman’ diet from the Kalahari desert in Africa consisted of less than a 15% meat/fish diet as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. The food content of hunter gatherers varied highly depending on geography. From: Jabr, F. (2013). How to Really Eat Like a Hunter-Gatherer: Why the Paleo Diet Is Half-Baked. Scientific American, June 3.
Use common sense to make food choices.
- Eat only those foods which in the course of evolution have been identified as foods. This means eating a variety of plants based foods (fruits, tubers, leaves, stems, nuts, etc.) and more organ meats. Ask yourself what foods did your forefathers/mothers ate that supported survival and reproductive success. Carnivores usually ate the internal organs first and often would leave the muscles for scavengers.
- Eat like your great, great grandparents. They were not yet brainwashed by the profit incentives of agribusiness and pharmaceutical industry. For more information, read the outstanding books by Michael Pollan, The Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and In Defense of Food: An Eater’s Manifesto.
- If possible eat only organically grown/raised foods. Non organic foods usually contain low levels of pesticides, insecticides, antibiotics and hormones which increases the risk of cancer (Reuben, 2010). They may also also contain fewer nutrients such as essential minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants (Barański et al, 2014). The beneficial effects of organic foods have been challenging to demonstrate because it may take many years to show a difference. Preliminary data strongly suggests that organic foods as compared to non organic foods increases longevity, improves fertility and enhances survival during starvation (Chhabra, Kolli, & Bauer, 2013). For more information, see my blog, Live longer, enhance fertility and increase stress resistance: Eat Organic foods.
- Adapt the precautionary principle and assume that any new and artificially produced additives or chemically processed foods–most of the foods in boxes and cans in the central section of the supermarket–contain novel materials which have not been part of our historical dietary experience. These foods may be harmful over the long term and our bodies not yet know how to appropriately digest such foods such as trans fats (Kummerow, 2009).
- Be doubtful of dietary recommendations especially if you know of counter examples and exceptions. For example, the low fat diet recommendations could not explain the French or Swiss paradox (high butter and cheese intake and low heart disease rates). If examples exist, the popular dogma is incomplete or possibly wrong. Be skeptical about any health food claims. Ask who has funded the research, who decides whether a food can have a label that states “it is heart health” and can prevent a disease, and who would benefit if more of this food is sold.
My final comments on nutrition (source unknown).
- The Japanese eat very little fat and suffer fewer heart attacks than us.
- The Mexicans eat a lot of fat and suffer fewer heart attacks than us.
- The French eat lots of butter and drink alcohol and suffer fewer heart attacks than us.
- The Chinese drink very little red wine and suffer fewer heart attacks than us.
- The Italians drink a lot of red wine and suffer fewer heart attacks than us.
- The Germans drink a lot of beer and eat lots of sausages and fats and suffer fewer heart attacks than us.
Conclusion
Eat and drink what you like especially if you enjoy it with company…speaking English is apparently what kills you!
References:
Jabr, F. (2013). How to Really Eat Like a Hunter-Gatherer: Why the Paleo Diet Is Half-Baked. Scientific American, June 3.http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-paleo-diet-half-baked-how-hunter-gatherer-really-eat/
Kummerow, F. A. (2009). The negative effects of hydrogenated trans fats and what to do about them. Atherosclerosis, 205(2), 458-465.http://www.atherosclerosis-journal.com/article/S0021-9150%2809%2900208-1/abstract
Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group. (1982). Multiple risk factor intervention trial. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 248(12), 1465-1477. http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=377969
Pollan, M. (2006). The Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals. New York: Penguin Press. ISBN: 1594200823
Pollan, M. (2009). In Defense of Food: An Eater’s Manifesto. New York: Penguin Press. ISBN: 978-0143114963
Reuben, S. H. (2010). Reducing environmental cancer risk: what we can do now. DIANE Publishing. http://deainfo.nci.nih.gov/advisory/pcp/annualReports/pcp08-09rpt/PCP_Report_08-09_508.pdf
Shaten, B. J., Kuller, L. H., Kjelsberg, M. O., Stamler, J., Ockene, J. K., Cutler, J. A., & Cohen, J. D. (1997). Lung cancer mortality after 16 years in MRFIT participants in intervention and usual-care groups. Annals of epidemiology, 7(2), 125-136. http://www.annalsofepidemiology.org/article/S1047-2797%2896%2900123-8/abstract
Teicholz, N. (2014). The big fat surprise-Why butter, meat & cheese belong in a healthy diet. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBM 978-1-4516-2442-7 http://www.thebigfatsurprise.com/
Can multivitamins prevent cancer?
Posted: October 20, 2012 Filed under: Uncategorized | Tags: cancer, diet, nutrition, vitamins Leave a commentA multivitamin a day keeps the doctor away to prevent nutritional deficiency and indirectly reduce cancer risks. Although most previous research studies have not demonstrated whether vitamin supplements are useful in the prevention or the treatment of cancer, the recently published randomized control trial of 14,641 male physicians in the Journal of the American Medical Association demonstrated that a multivitamin a day significantly reduced the incidence of cancer. The participants started taking the vitamin or placebo at about age 50 and continued for eleven years. This study, Multivitamins in the Prevention of Cancer in Men- The Physicians’ Health Study II Randomized Controlled Trial, is different from most previous studies. It is one of the first randomized controlled trial in which the participants did not know whether they took a multivitamin or placebo daily. Even though the effect is small, the study finds that taking a multivitamin daily reduces cancer risk.
To promote health, take a multivitamin a day; however, the benefits gained by taking a multivitamin imply that:
- We are affluently malnutritioned as our daily western industrialized processed diet is deficient in nutrients that support our immune system and health. It would be better to eat an organic food diet with lots of vegetables and fruits. Even The President’s Cancer Panel Report, Reducing Environmental Cancer Risk: What We Can Do Now, published by the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, recommends to consume to the “extent possible, food grown without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.” Eating an organic hunter and gatherer diet would include many other essential vitamins and minerals –some which we do not yet know—that are not included in a single multivitamin.
- Start eating a healthy diet from birth since it will have more impact to prevent cancer than adding a multivitamin a day at age 50. Most epidemiological studies have shown that a predominantly vegetable and fruit diet is associated with lower cancer rates.
- Implement a health promoting life style to support the immune system. Begin now by practicing stress management, incorporating exercise, performing self-healing strategies, and eating organic vegetable, fruits (no processed foods). For more suggestions see our book, Fighting Cancer-A Nontoxic Approach to Treatment.
Food for thought- Is my “healthy diet” harming me?
Posted: March 16, 2012 Filed under: Uncategorized | Tags: ADHD, Alzheimer, diet, multiple sclerosis, Spina bivada, vitamins 3 CommentsHow can you imply that I have malnutrition! I eat a full, balanced diet including meats, vegetables, fruits, dairy, etc. I take a multiple vitamin every day and even shop for organic foods at my local farmer’s market. In fact, I shifted my diet to follow the American Heart Disease Association and USDA Food Plate and Pyramid guidelines!
Evolution optimized human genetics for a hunter-gatherer diet but in the last few centuries our diet has radically changed and is totally different from the ideal diet of our ancestors. We now eat many foods that were not part of our diet five to ten thousand years ago such as corn, wheat, milk and all packaged and processed foods. We eat on the average 160 lbs of sugar instead of less than two pounds of honey a year, and steaks instead of the organ meats such as liver which would have provided essential vitamin A, D, etc.
A healthy diet is much more than a nutritionally poor high caloric foods (e.g., cereals, hamburgers, white rice or flour) with some vitamins and minerals added. A healthy diet mirrors our evolutionary past —a hunter gatherer diet–which supports the growth and maintenance of our body and brain. This diet would consist of natural, non industrialized produced foods such as vegetables, leaves, fruits, berries, nuts, roots, tubers, wild fish and meats from animals. This type of diet significantly exceeds the FDA’s recommended Daily Intake (RDI) guidelines which are the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy individuals in the United States.
These minimum RDI for vitamins and minerals are often too low and do not include the myriad of micro and macro nutrients necessary to achieve and maintain optimum health. Nutrients do not act in alone but in concert with each other as Michael Pollan pointed out in his superb book, In Defense of Food.
Dietary guidelines from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) My Plate and Food Pyramid and organizations such as the American Heart Association are more the result of successful lobbying by large agribusiness than from research findings. By following USDA and FDA guidelines, we may set the stage for long term subclinical malnutrition which reduces our resilience to fight disease.
If the recommended modern Western diet was sufficient then there would be no need to take additional vitamin or mineral supplements to prevent illnesses. This is not the case! Controlled research studies have shown that numerous illnesses can be ameliorated or prevented by taking specific supplements.
- The risk of having a baby with Spina bivida (neural tube defect) can be reduced by 71% when women before becoming pregnant take 400 µg of folic acid (vitamin B9) per day. Taking the folic acid supplement may not have been necessary if the woman had eating foods naturally high in folic acid such as leafy vegetable (spinach, asparagus, turnip greens), egg yolks, sun flower seeds and liver.
- Pregnant women can reduce the risk of their babies having eczema by 42 percent and egg allergies by 40 percent when they take fish oil capsules (1000 mg of Omega 3s) daily during pregnancy as compared to the women whoonly took vegetable capsule. Taking Omega 3s may not have been necessary if the woman had eating foods naturally high in Omega 3s such as cold water oily fish, flax seed, eggs produced by free ranging hens who are not fed corn or soy, and brains from mammals.
- Teenage girls who took vitamin D supplements had significantly lower bone fractures than girls who did not take vitamin D supplements. Is it possible that chronic low levels of vitamin D (chronic malnutrition caused by our industrialized agribusiness diet) and use of sunscreen are significant co-factor in the increasing epidemic of osteoporosis in older women? Taking vitamin D may not have been necessary if the girls had eating foods naturally high in vitamin D such as alfalfa shoots, fatty fish, beef liver and whole eggs produced by free ranging hens and enough sun exposure.
Eating the industrialized produced western diet may also increase the risk developing neurological degenerative diseases. Adults with low omega-3 blood levels had significantly lower total cerebral brain volume than adults who had the highest levels of omega-3s. More importantly, adults with low levels of omega-3 levels did significantly worse on abstract memory, visual memory and executive function than the adults who had high omega-3 levels.
These research findings are worrisome; since, shrinking brains are a feature associated with neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Is it possible that our diet contributes to the expanding epidemics of Alzheimer’s disease and ADHD?
If some illness can be prevented by taking supplements, would it not be wiser to eat a diet which provides sufficiently nutrients for the brain and body?
Watch the inspirational presentation by Dr. Terry Wahls, MD, Minding Your Mitochondria, who cured her multiple sclerosis which was untreatable by western medicine. She reversed her illness by eating a hunter and gathers diet which provided the optimum nutrition for her brain. Over a period of three to a year, she got out of herwheel chair, started to ride a bicycle, and eventually rode horseback as shown in her Youtube video.
Experience the benefits of eating a hunter gatherer diet. For one month eat as a hunter and gatherer. Eat nine cups of organic vegetables, leaves, berries, roots, fruit as well as tubers, some fish, and some organ meat from free ranging animals. Do not eat corn products, sugar and processed foods. In four weeks, you may notice a difference: more energy, less inflammation and improved cognition. For dietary guidelines see chapter 9 in the book, Fighting Cancer-A Nontoxic Approach to Treatment.