Pragmatic techniques for monitoring and coaching breathing
Posted: December 14, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, emotions, meditation, mindfulness, neurofeedback, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, Uncategorized | Tags: art, books, Breathing rate, coaching, FlowMD app, nasal breathing, personal-development, self-monitoring, writing 4 CommentsDaniella Matto, MA, BCIA BCB-HRV , Erik Peper, PhD, BCB, and Richard Harvey, PhD
Adapted from: Matto, D., Peper, E., & Harvey, R. (2025). Monitoring and coaching breathing patterns and rate. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. https://townsendletter.com/monitoring-and-coaching-breathing-patterns-and-rate/
This blog aims to describe several practical strategies to observe and monitor breathing patterns to promote effortless diaphragmatic breathing. The goal of these strategies is to foster effortless, whole-body diaphragmatic breathing that promote health.
Breathing is usually covert and people are not usually aware of their breathing rate (breaths per minute) or pattern (abdominal or thoracic, breath holding or shallow breathing) unless they have an illness such as asthma, emphysema or are performing physical activity (Boulding et al, 2015)). Observing breathing is challenging; awareness of respiration often leads to unaware changes in the breath pattern or to an attempt to breathe perfectly (van Dixhoorn, 2021). Ideally breathing patterns should be observed/monitored when the person is unaware of their breathing pattern and the whole body participates (van Dixhoorn, 2008). A useful strategy is to have the person perform a task and then ask, “What happened to your breathing?”. For example, ask a person to simulate putting a thread through the eye of a needle or quickly look to the extreme right and left while keeping their head still. In almost all cases, the person holds their breath (Peper et al., 2002).
Teaching effortless slow diaphragmatic breathing is a precursor of Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback and is based on slow paced breathing (Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014; Steffen et al., 2017; Shaffer and Meehan, 2020). Mastering effortless diaphragmatic breathing is a powerful tool in the treatment of a variety of physical, behavioural, and cognitive conditions; however, to integrate this method into clinical or educational practice is easier said than done. Clients with dysfunctional breathing patterns often have difficulty following a breath pacer or mastering effortless breathing at a slower pace.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a few simple strategies that can be used to observe and monitor breathing patterns, provide economic strategies for observation and training, and suggestions to facilitate effortless diaphragmatic breathing.
Strategies to observe and monitor breathing pattern
Observation of the breathing patterns
- Is the breathing through the nose or mouth? Nose is usually better (Watso et al., 2023; Nestor, 2020).
- Does the abdomen expand during inhalation and constricts during exhalation or does the chest expand and rise during inhalation and fall during exhalation? Abdominal movement is usually better.
- Is exhalation flow softly or explosively like a sigh? Slow flow exhalation is preferred.
- Is the breath held or continues during activities? In most cases continued breathing is usually better.
- Does the person gasp before speaking or allows to speak while normally exhaling?
- What is the breathing rate (breaths per minute)? When sitting peacefully less than 14 breaths/minute is usually better and about 6 breaths per minute to optimize HRV
Physiological monitoring.
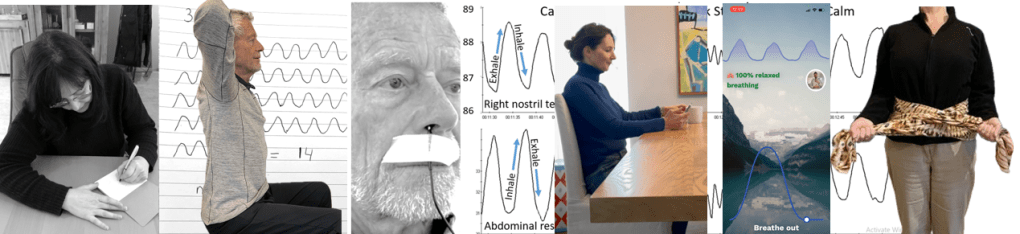
- Monitoring breathing with strain gauges around the abdomen and chest, and heart rate is the most common approach to identify the location of breath, the breathing pattern and heart rate variability. The strain gauges are placed around the chest and abdomen and heart rate is monitored with a blood volume pulse amplitude sensor from the finger. representative recording shows the effect of thoughts on breathing, heartrate and pulse amplitude of which the participant is totally unaware as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Physiological recording of breathing patterns with strain gauges.
- Monitoring breathing with a thermistor placed at the entrance of the nostril that has the most airflow (nasal patency) (Jovanov et al., 2001; Lerman et al., 2016). When the person exhales through the nose, the thermistor temperature increases and decreases when they inhale. A representative recording of a person being calm, thinking a stressful thought. and being calm. Although there were significant changes as indicated by the change in breathing patterns, the person was unaware of the changes as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Use of a thermistor to monitor breathing from the dominant nostril compared to the abdominal expansion as monitored by a strain gauge around the abdomen.
- Additional physiological monitoring approaches. There are many other physiological measures can be monitored to such as end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2), a non-invasive measurement of the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhaled breath (Meuret et al., 2008; Meckley, 2013); scalene/trapezius EMG to identify thoracic breathing (Peper & Tibbett, 1992; Peper & Tibbets, 1994); low abdominal EMG to identify transfers and oblique tightening during exhalation and relaxation during inhalation (Peper et al., 2016; and heart rate to monitor cardiorespiratory synchrony (Shaffer & Meehan, 2020). Physiological monitoring is useful; since, the clinician and the participant can observe the actual breathing pattern in real time, how the pattern changes in response the cognitive and physical tasks, and used for feedback training. The recorded data can document breathing problems and evidence of mastery.
The challenges of using physiological monitoring arethat the equipment may be expensive, takes skill to operate and interpret the data, and is usually located in the office and not at home.
Economic strategies for observation and training breathing
To complement the physiological monitoring and allow observations outside the office and at home, some of the following strategies may be used to observe breathing pattern (rate and expansion of the breath in the body), and suggestion to facilitate effortless diaphragmatic breathing. These exercises make excellent homework for the client. Practicing awareness and internal self-regulation by the client outside the clinic contributes enormously to the effect of biofeedback training (Wilson et al., 2023),
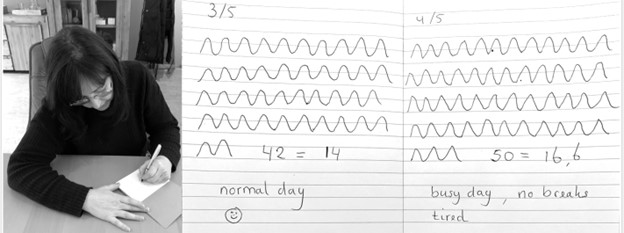
Observe breathing rate: Draw the breathing pattern
Take a piece of paper, a pen and a timer, set to 3 minutes. Start the timer. Upon inhalation draw the line up and upon exhalation draw the line down, creating a wave. When the timer stops, after 3 minutes, calculate the breathing rate per minute by dividing the number of waves by 3 as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Drawing the breathing pattern for three minutes during two different days.
From these drawings, the breathing rate become evident. Many individuals are often surprised to discover that their breathing rate increased during periods of stress, such as a busy day with no breaks, compared to their normal days.
Monitoring and training diaphragmatic breathing
The scarf technique for abdominal feedback
Many participants are unaware that they are predominantly breathing in their chest and their abdomen expansion is very limited during inhalation. Before beginning, have participant loosen their belt and or stand upright since sitting collapsed/slouched or having the waist constriction such as a belt of tight constrictive clothing that inhibits abdominal expansion during inhalation.
Place the middle part of a long scarf or shawl on your lower back, take the ends in both hands and cross the ends: your left hand is holding the right part of the scarf, and the right hand is holding the left end of the scarf. Give a bit of a pull, so you can feel any movement of the scarf. When breathing more abdominally you will feel a pull at the ends of the scarf as you lower back, and flanks will expand as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Using a scarf as feedback.
FlowMD app
A recent cellphone app, FlowMD, is unique because it uses the cellphone camera to detect the subtle movements of the chest and abdomen (FlowMD, 2024). It provides real time feedback of the persons breathing pattern. Using this app, the person sits in front of their cellphone camera and after calibration, the breathing pattern is displayed as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5. Training breathing with FlowMD,.
Suggestions to optimize abdominal breathing that may lead to a slower breath rate when the client practices the technique
Beach pose
By locking the upper chest and sitting up straight it is often easier to breathe so that the abdomen can expand and constrict. Place your hands behind your head and Interlock your finger of both hands, pull your elbows back and up. The person can practice this either laying down on their back or sitting straight up at the edge of the chair as shown in Figure 6.
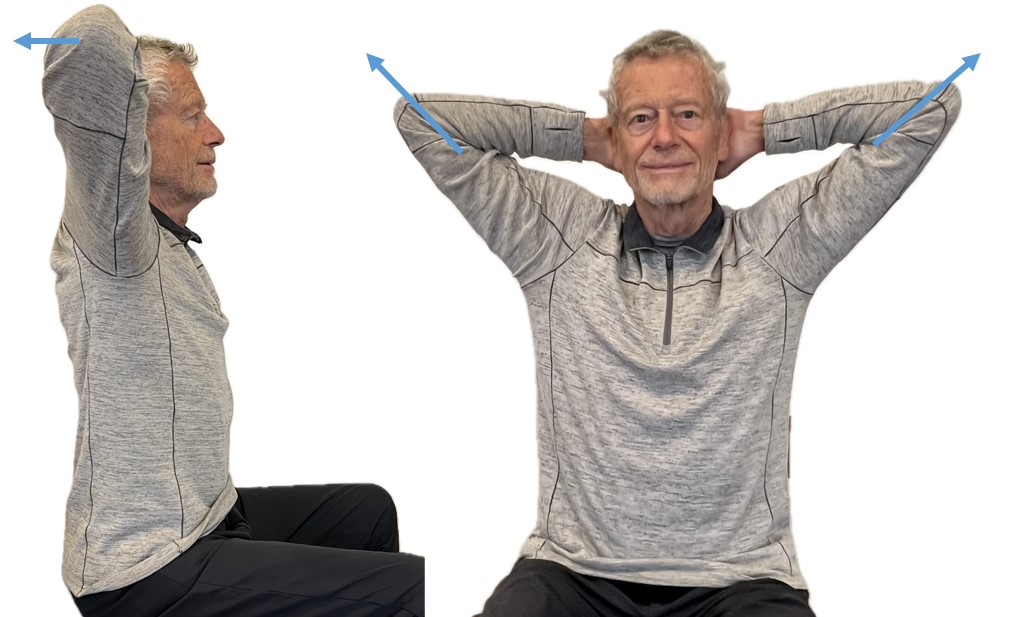

Figure 6. Sitting erect with the shoulders pulled back and up to allow abdominal expansion and constriction as the breathing pattern.
Observe the effect of posture on breathing
Have the person sit slouched/collapsed like a letter C and take a few slow breath, then have them sit up in a tall and erect position and take a few slow breaths. Usually they will observe that it is easier to breathe slower and lower and tall and erect.
Using your hands for feedback to guide natural breathing
Holding your hands with index fingers and thumbs touching the lower abdomen. When inhaling the fingers and thumbs separate and when exhaling they touch again (ensuring a full exhale and avoiding over breathing). The slight increase in lower abdominal muscle tension during the exhalation and relaxation during inhalation and the abdominal wall expands can also be felt with fingertips as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Using your hands and finger for feedback to guide the natural breathing of expansion and constriction of the abdomen. Reproduced by permission from Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49.
Coaching suggestions
There are many strategies to observe, teach and implement effortless breathing (Peper et al., 2024).. Even though breathing is natural and babies and young children breathe diaphragmatically as their large belly expands and constricts. Yet, in many cases the natural breathing shifts to dysfunctional breathing for multiple reasons such as chronic triggering defense reactions to avoiding pain following abdominal surgery (Peper et al, 2015). When participants initially attempt to relearn this natural pattern, it can be challenging especially, if the person habitually breathes shallowly, rapidly and predominantly in their chest.
When initially teaching effortless breathing, have the person exhale more air than normal without the upper chest compressing down and instead allow the abdomen comes in and up thereby exhaling all the air. If the person is upright then allow inhalation to occur without effort by letting the abdominal wall relaxes and expands. Initially inhale more than normal by expanding the abdomen without lifting the chest. Then exhale very slowly and continue to breathe so that the abdomen expands in 360 degrees during inhalation and constricts during exhalation. Let the breathing go slower with less and less effort. Usually, the person can feel the anus dropping and relaxing during inhalation.
Another technique is to ask the person to breathe in more air than normal and then breathe in a little extra air to completely fill the lungs, before exhaling fully. Clients often report that it teaches them to use the full capacity of the lungs.
The goal is to breath without effort. Indirectly this can be monitored by finger temperature. If the finger temperature decreases, the participant most likely is over-breathing or breathing with too much effort, creating sympathetic activity; if the finger temperature increases, breathing occurs slower and usually with less effort indicating that the person’s sympathetic activation is reduced.
Conclusion
There are many strategies to monitor and coach breathing. Relearning diaphragmatic breathing can be difficult due to habitual shallow chest breathing or post-surgical adaptations. Initial coaching may involve extended exhalations, conscious abdominal expansion, and gentle inhalation without chest movement. Progress can be monitored through indirect physiological markers like finger temperature, which reflects changes in sympathetic activity. The integration of these techniques into clinical or educational practice enhances self-regulation, contributing significantly to therapeutic outcomes. In this article we provided a few strategies which may be useful for some clients.
Additional blogs on breathing
https://peperperspective.com/2015/09/25/resolving-pelvic-floor-pain-a-case-report/
REFERENCES
Boulding, R., Stacey, R., & Niven, N. (2016). Dysfunctional breathing: a review of the literature and proposal for classification. European Respiratory Review, 25(141),: 287-294. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0088-2015
FlowMD. (2024). FlowMD app. Accessed December 13, 2024. https://desktop.flowmd.co/
Jovanov, E., Raskovic, D., & Hormigo, R. (2001). Thermistor-based breathing sensor for circadian rhythm evaluation. Biomedical sciences instrumentation, 37, 493–497. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11347441/
Lehrer, P. & Gevirtz R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work? Front Psychol, 5,756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
Lerman, J., Feldman, D., Feldman, R. et al. Linshom respiratory monitoring device: a novel temperature-based respiratory monitor. (2016). Can J Anesth/J Can Anesth, 63, 1154–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-016-0694-y
Meckley, A. (2013). Balancing Unbalanced Breathing: The Clinical Use of Capnographic Biofeedback. Biofeedback, 41(4), 183–187. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-41.4.02
Meuret, A. E., Wilhelm, F. H., Ritz, T., & Roth, W. T. (2008). Feedback of end-tidal pCO2 as a therapeutic approach for panic disorder. Journal of psychiatric research, 42(7), 560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.06.005
Nestor, J. (2020). Breath: The New Science of a Lost Art. New York: Riverhead Books. https://www.amazon.com/Breath-New-Science-Lost-Art/dp/0735213615/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Peper, E., Gibney, K.H., & Holt, C.F. (2002). Make Health Happen. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. https://he.kendallhunt.com/product/make-health-happen-training-yourself-create-wellness
Peper, E., Oded, Y., Harvey, R., Hughes, P., Ingram, H., & Martinez, E. (2024). Breathing for health: Mastering and generalizing breathing skills. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. November 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/suggestions-for-mastering-and-generalizing-breathing-skills/
Peper, E., & Tibbetts, V. (1992). Fifteen-month follow-up with asthmatics utilizing EMG/incentive inspirometer feedback. Biofeedback and self-regulation, 17(2), 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000104
Peper, E. & Tibbetts, V. (1994). Effortless diaphragmatic breathing. Physical Therapy Products. 6(2), 67-71. https://biofeedbackhealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/peper-and-tibbets-effortless-diaphragmatic.pdf
Shaffer, F. and Meehan, Z.M. (2020). A Practical Guide to Resonance Frequency Assessment for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.570400
Steffen, P.R., Austin, T., DeBarros, A., and Brown, T. (2017). The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood. Front Public Health, 5, 222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2017.00222
van Dixhoorn, J.V. (2008). Whole-body breathing. Biofeedback, 36,54–58. https://www.euronet.nl/users/dixhoorn/L.513.pdf
van Dixhoorn, J.V. (2021). Functioneel ademen-Adem-en ontspannings oefeningen voor gevorderden. Amersfoort: Uiteveriy Van Dixhoorn. https://www.bol.com/nl/nl/p/functioneel-ademen/9300000132165255/
Watso, J. C., Cuba, J.N., Boutwell, S.L, Moss, J…(2023). Acute nasal breathing lowers diastolic blood pressure and increases parasympathetic contributions to heart rate variability in young adults. American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology.
325I(6), R797-R80. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00148.2023
Wilson, V., Somers, K. & Peper, E. (2023). Differentiating Successful from Less Successful Males and Females in a Group Relaxation/Biofeedback Stress Management Program. Biofeedback, 51(3), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.5298/608570
[1] Correspondence should be addressed to:
Erik Peper, Ph.D., Institute for Holistic Health Studies, San Francisco State University, 1600 Holloway Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94132 Tel: 415 338 7683 Email: epeper@sfsu.edu web: www.biofeedbackhealth.org blog: www.peperperspective.com
Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 2- Exposure to neurotoxins and ultra-processed foods
Posted: June 30, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, CBT, digital devices, education, emotions, Evolutionary perspective, health, mindfulness, neurofeedback, Nutrition/diet, Uncategorized | Tags: ADHD, anxiety, depression, diet, glyphosate, herbicide, herbicites, mental-health, neurofeedback, pesticides, supplements', ultraprocessed foods, vitamins 4 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. & Shuford, J. (2024). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 2- Exposure to neurotoxins and ultra-processed foods. NeuroRegulation, 11(2), 219–228. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.11.2.219
Look at your hand and remember that every cell in your body including your brain is constructed out the foods you ingested. If you ingested inferior foods (raw materials to be built your physical structure), then the structure can only be inferior. If you use superior foods, you have the opportunity to create a superior structure which provides the opportunity for superior functioning. -Erik Peper
Summary
Mental health symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Autism, anxiety and depression have increased over the last 15 years. An additional risk factor that may affect mental and physical health is the foods we eat. Even though, our food may look and even taste the same as compared to 50 years ago, it contains herbicide and pesticide residues and often consist of ultra-processed foods. These foods (low in fiber, and high in sugar, animal fats and additives) are a significant part of the American diet and correlate with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in children with ADHD. Due to affluent malnutrition, many children are deficient in essential vitamins and minerals. We recommend that before beginning neurofeedback and behavioral treatments, diet and lifestyle are assessed (we call this Grandmother therapy assessment). If the diet appears low in organic foods and vegetable, high in ultra-processed foods and drinks, then nutritional deficiencies should be assessed. Then the next intervention step is to reduce the nutritional deficiencies and implement diet changes from ultra-processed foods to organic whole foods. Meta-analysis demonstrates that providing supplements such as Vitamin D, etc. and reducing simple carbohydrates and sugars and eating more vegetables, fruits and healthy fats during regular meals can ameliorate the symptoms and promote health.
The previous article and blog, Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms, pointed out how the changes in bonding, screen time and circadian rhythms affected physical and mental health (Peper, 2023a; Peper, 2023b). However, there are many additional factors including genetics that may contribute to the increase is ADHD, autism, anxiety, depression, allergies and autoimmune illnesses (Swatzyna et al., 2018). Genetics contribute to the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD); since, family, twin, and adoption studies have reported that ADHD runs in families (Durukan et al., 2018; Faraone & Larsson, 2019). Genetics is in most cases a risk factor that may or may not be expressed. The concept underlying this blog is that genetics loads the gun and environment and behavior pulls the trigger as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Interaction between Genetics and Environment
The pandemic only escalated trends that already was occurring. For example, Bommersbach et al (2023) analyzed the national trends in mental health-related emergency department visits among USA youth, 2011-2021. They observed that in the USA, Over the last 10 years, the proportion of pediatric ED visits for mental health reasons has approximately doubled, including a 5-fold increase in suicide-related visits. The mental health-related emergency department visits increased an average of 8% per year while suicide related visits increased 23.1% per year. Similar trends have reported by Braghieri et al (2022) from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Mental health trends in the United States by age group in 2008–2019. The data come from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Reproduced with permission from Braghieri, Luca and Levy, Ro’ee and Makarin, Alexey, Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022) https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
The trends reported from this data shows an increase in mental health illnesses for young people ages 18-23 and 24-29 and no changes for the older groups which could be correlated with the release of the first iPhone 2G on June 29, 2007. Thus, the Covid 19 pandemic and social isolation were not THE CAUSE but an escalation of an ongoing trend. For the younger population, the cellphone has become the vehicle for personal communication and social connections, many young people communicate more with texting than in-person and spent hours on screens which impact sleep (Peper, 2023a). At the same time, there are many other concurrent factors that may contributed to increase of ADHD, autism, anxiety, depression, allergies and autoimmune illnesses.
Without ever signing an informed consent form, we all have participated in lifestyle and environmental changes that differ from that evolved through the process of evolutionary natural selection and promoted survival of the human species. Many of those changes in lifestyle are driven by demand for short-term corporate profits over long-term health of the population. As exemplified by the significant increase in vaping in young people as a covert strategy to increase smoking (CDC, 2023) or the marketing of ultra-processed foods (van Tulleken, 2023).
This post focusses how pesticides and herbicides (exposure to neurotoxins) and changes in our food negatively affects our health and well-being and is may be another contributor to the increase risk for developing ADHD, autism, anxiety and depression. Although our food may look and even taste the same compared to 50 years ago, it is now different–more herbicide and pesticide residues and is often ultra-processed. lt contains lower levels of nutrients and vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin B2, Protein, Iron, Calcium and Phosphorus than 50 years ago (Davis et al, 2004; Fernandez-Cornejo et al., 2014). Non-organic foods as compared to organic foods may reduce longevity, fertility and survival after fasting (Chhabra et al., 2013).
Being poisoned by pesticide and herbicide residues in food
Almost all foods, except those labeled organic, are contaminated with pesticides and herbicides. The United States Department of Agriculture reported that “Pesticide use more than tripled between 1960 and 1981. Herbicide use increased more than tenfold (from 35 to 478 million pounds) as more U.S. farmers began to treat their fields with these chemicals” (Fernandez-Cornejo, et al., 2013, p 11). The increase in herbicides and pesticides is correlated with a significant deterioration of health in the United States (Swanson, et al., 2014 as illustrated in the following Figure 3.


Figure 3. Correlation between Disease Prevalence and Glyphosate Applications (reproduced with permission from Swanson et al., 2014.
Although correlation is not causation and similar relationships could be plotted by correlating consumption of ultra-refined foods, antibiotic use, decrease in physical activity, increase in computer, cellphone and social media use, etc.; nevertheless, it may suggest a causal relationship. Most pesticides and herbicides are neurotoxins and can accumulate in the person over time this could affect physical and mental health (Bjørling-Poulsen et al., 2008; Arab & Mostaflou, 2022). Even though the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has determined that the residual concentrations in foods are safe, their long-term safety has not been well established (Leoci & Ruberti, 2021). Other countries, especially those in which agribusiness has less power to affect legislation thorough lobbying, and utilize the research findings from studies not funded by agribusiness, have come to different conclusions…
For example, the USA allows much higher residues of pesticides such as, Round-Up, with a toxic ingredient glyphosate (0.7 parts per million) in foods than European countries (0.01 parts per million) (Wahab et al., 2022; EPA, 2023; European Commission, 2023) as is graphically illustrated in figure 4.

Figure 4: Percent of Crops Sprayed with Glyphosate and Allowable Glyphosate Levels in the USA versus the EU
The USA allows this higher exposure than the European Union even though about half of the human gut microbiota are vulnerable to glyphosate exposure (Puigbo et al., 2022). The negative effects most likely would be more harmful in a rapidly growing infant than for an adult. Most likely, some individuals are more vulnerable than others and are the “canary in mine.” They are the early indicators for possible low-level long-term harm. Research has shown that fetal exposure from the mother (gestational exposure) is associated with an increase in behaviors related to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders and executive function in the child when they are 7 to 12 years old (Sagiv et al., 2021). Also, organophosphate exposure is correlated with ADHD prevalence in children (Bouchard et al., 2010). We hypothesize this exposure is one of the co-factors that have contributed to the decrease in mental health of adults 18 to 29 years.
At the same time as herbicides and pesticides acreage usage has increased, ultra-processed food have become a major part of the American diet (van Tulleken, 2023). Eating a diet high in ultra-processed foods, low in fiber, high sugar, animal fats and additives has been associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in children with ADHD; namely, high consumption of sugar, candy, cola beverages, and non-cola soft drinks and low consumption of fatty fish were also associated with a higher prevalence of ADHD diagnosis (Ríos-Hernández et al., 2017).
In international studies, less nutritional eating behaviors were observed in ADHD risk group as compared to the normal group (Ryu et al., 2022). Artificial food colors and additives are also a public health issue and appear to increase the risk of hyperactive behavior (Arnold et al., 2012). In a randomized double-blinded, placebo controlled trial 3 and 8/9 year old children had an increase in hyperactive behavior for those whose diet included extra additives (McCann et al., 2007). The risk may occur during fetal development since poor prenatal maternal is a critical factor in the infants neurodevelopment and is associated with an increased probability of developing ADHD and autism (Zhong et al., 2020; Mengying et al., 2016).
Poor nutrition even affects your unborn grandchild
Poor nutrition not only affects the mother and the developing fetus through epigenetic changes, it also impacts the developing eggs in the ovary of the fetus that can become the future granddaughter (Wilson, 2015). At birth, the baby has all of her eggs. Thus, there is a scientific basis for the old wives tale that curses may skip a generation. Providing maternal support is even more important since it affects the new born and the future grandchild. The risk may even begin a generation earlier since the grandmother’s poor nutrition as well as stress causes epigenetic changes in the fetus eggs. Thus 50% of the chromosomes of the grandchild were impacted epigenetically by the mother’s and grandmother’s dietary and health status .
Highly processed foods
Highly refined foods have been processed to remove many of their nutrients. These foods includes white bread, white rice, pasta, and sugary drinks and almost all the fast foods and snacks. These foods are low in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they are high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and calories. In addition, additives may have been added to maximize taste and mouth feel and implicitly encourage addiction to these foods. A diet high in refined sugars and carbohydrates increases the risk of diabetes and can worsen the symptoms of ADHD, autism, depression, anxiety and increase metabolic disease and diabetes (Woo et al., 2014; Lustig, 2021; van Tulleken, 2023). Del-Ponte et al. (2019) noted that a diet high in refined sugar and saturated fat increased the risk of symptoms of ADHD, whereas a healthy diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits and vegetables, would protect against the symptoms.
Most likely, a diet of highly refined foods may cause blood sugar to spike and crash, which can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression and cognitive decline and often labeled as “hangryness” (the combination of anger and hunger) (Gomes et al., 2023; Barr et al., 2019). At the same time a Mediterranean diet improves depression significantly more than the befriending control group (Bayles et al., 2022). In addition, refined foods are low in essential vitamins and minerals as well as fiber. Not enough fiber can slow down digestion, affect the human biome, and makes it harder for the body to absorb nutrients. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can contribute to the symptoms of ADHD, autism, depression, and anxiety. Foods do impact our mental and physical health as illustrated by foods that tend to reduce depression (LaChance & Ramsey, 2018; MacInerney et al., 2017). By providing appropriate micronutrients such as minerals (Iron, Magnesium Zinc), vitamins (B6, B12, B9 and D), Omega 3s (Phosphatidylserine) and changing our diet, ADHD symptoms can be ameliorated.
Many children with ADHD, anxiety, depression are low on essential vitamins and minerals. For example, low levels of Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D may be caused by eating ultra-refined foods, fast foods, and drinking soft drink. At the same time, the children are sitting more in indoors in front of the screen and thereby have lower sun exposure that is necessary for the vitamin D production.
“Because of lifestyle changes and sunscreen use, about 42% of Americans are deficient in vitamin D. Among children between 1 to 11 years old, an estimated 15% have vitamin D deficiency. And researchers have found that 17% of adolescents and 32% of young adults were deficient in vitamin D.” (Porto and Abu-Alreesh, 2022).
Reduced sun exposure is even more relevant for people of color (and older people); since, their darker skin (increased melanin) protects them from ultraviolet light damage but at the same time reduces the skins production of vitamin D. Northern Europeans were aware of the link between sun exposure and vitamin D production. To prevent rickets (a disease caused by vitamin D deficiency) and reduce upper respiratory tract infections the children were given a tablespoon of cod liver oil to swallow (Linday, 2010). Cod liver oil, although not always liked by children, is more nutritious than just taking a Vitamin D supplements. It is a whole food and a rich source of vitamin A and D as well as containing a variety of Omega 3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (USDA, 2019).
Research studies suggest that ADHD can be ameliorated with nutrients, and herbs supplements (Henry & CNS, 2023). Table 1 summarizes some of the nutritional deficits observed and the reduction of ADHD symptoms when nutritional supplements were given (adapted from Henry, 2023; Henry & CNS, 2023).
| Nutritional deficits observed in people with ADHD | Decrease in ADHD symptoms with nutritional supplements |
| Vitamin D: In meta-analysis with a total number of 11,324 children, all eight trials reported significantly lower serum concentrations of 25(OH)D in patients diagnosed with ADHD compared to healthy controls. (Kotsi et al, 2019) | After 8 weeks children receiving vitamin D (50,000 IU/week) plus magnesium (6 mg/kg/day) showed a significant reduction in emotional problems as observed in a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Hemamy et al., 2021). |
| Iron: In meta-analysis lower serum ferritin was associated with ADHD in children (Wang et al., 2017) and the mean serum ferritin levels are lower in the children with ADHD than in the controls (Konofal et al., 2004). | After 12 weeks of supplementation with Iron (ferrous sulfate) in double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, clinical trials symptoms of in children with ADHD as compared to controls were reduced (Tohidi et al., 2021; Pongpitakdamrong et all, 2022). |
| Omega 3’s: Children with ADHD are more likely to be deficient in omega 3’s than children without ADHD (Chang et al., 2017). | Adding Omega-3 supplements to their diet resulted in an improvement in hyperactivity, impulsivity, learning, reading and short term memory as compared to controls in 16 randomized controlled trials including 1514 children and young adults with ADHD (Derbyshire, 2017) |
| Magnesium: In meta-analysis, subjects with ADHD had lower serum magnesium levels compared with to their healthy controls (Effatpahah et al., 2019) | 8 weeks of supplementation with Vitamin D and magnesium caused a significant decrease in children with conduct problems, social problems, and anxiety/shy scores (Hemamy et al., 2020). |
| Vitamin B2, B6, B9 and B12deficiency has been found in many patients with Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder (Landaas et al, 2016; Unal et al., 2019). | Vitamin therapy appears to reduce symptoms of ADHD and ASD (Poudineh et al., 2023; Unal et al., 2019). An 8 weeks supplementing with Vitamin B6 and magnesium decreased hyperactivity and hyperemotivity/aggressiveness. When supplementation was stopped, clinical symptoms of the disease reappeared in few weeks (Mousain-Bosc et al., 2006). |
Table 1. Examples of vitamin and mineral deficiencies associated with symptoms of ADHD and supplementation to reduction of ADHD symptoms.
Supplementation of vitamins and minerals in many cases consisted of more than one single vitamin or mineral. For an in-depth analysis and presentation, see the superb webinar by Henry & CNS (2023): https://divcom-events.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/divcom-events/recording/e29cefcae6c1103bb7f3aa780efee435/playback? (Henry & CNS, 2023).
Whole foods are more than the sum of individual parts (the identified individual constituents/nutrients). The process of digestion is much more complicated than ingesting simple foods with added vitamins or minerals. Digestion is the interaction of many food components (many of which we have not identified) which interact and affect the human biome. A simple added nutrient can help; however, eating whole organic foods it most likely be healthier. For example, whole-wheat flour is much more nutritious. Whole wheat is rich in vitamins B-1, B-3, B-5, riboflavin, folate well as fiber while refined white flour has been bleached and stripped of fiber and nutrients to which some added vitamins and iron are added.
Recommendation
When working with clients, follow Talib’s principles as outlined in Part 1 by Peper (2023) which suggests that to improve health first remove the unnatural which in this case are the ultra-processed foods, simple carbohydrates, exposure to pesticides and herbicides (Taleb, 2014). The approach is beneficial for prevention and treatment. This recommendation to optimize health is both very simple and very challenging. The simple recommendation is to eat only organic foods and as much variety as possible as recommended by Professor Michael Pollan in his books, Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and Food Rules (Pollan, 2006; Pollan, 2011).
Do not eat foods that contain herbicides and pesticide residues or are ultra-processed. Although organic foods especially vegetable and fruits are often much more expensive, you have choice: You can pay more now to optimize health or pay later to treat disease. Be safe and not sorry. This recommendation is similar to the quote, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food,” that has been attributed falsely since the 1970s to Hippocrates, the Greek founder of western medicine (5th Century, BC) (Cardenas, 2013).
There are many factors that interfere with implementing these suggestions; since, numerous people live in food deserts (no easy access to healthy unprocessed foods ) or food swamps (a plethora of fast food outlets) and 54 million Americans are food insecure (Ney, 2022). In addition, we and our parents have been programmed by the food industry advertising to eat the ultra- processed foods and may no longer know how to prepare healthy foods such as exemplified by a Mediterranean diet. Recent research by Bayles et al (2022) has shown that eating a Mediterranean diet improves depression significantly more than the befriending control group. In addition, highly processed foods and snacks are omnipresent, often addictive and more economical.
Remember that clients are individuals and almost all research findings are based upon group averages. Even when the data implies that a certain intervention is highly successful, there are always some participants for whom it is very beneficial and some for whom it is ineffective or even harmful. Thus, interventions need to be individualized for which there is usually only very limited data. In most cases, the original studies did not identify the characteristics of those who were highly successful or those who were unsuccessful. In addition, when working with specific individuals with ADHD, anxiety, depression, etc. there are multiple possible causes.
Before beginning specific clinical treatment such as neurofeedback and/or medication, we recommend the following:
- “Grandmother assessment” that includes and assessment of screen time, physical activity, outdoor sun exposure, sleep rhythm as outlined in Part 1 by Peper (2023). Then follow-up with a dietary assessment that investigates the prevalence of organic/non organic foods, ingestion of fast foods, ultra-processed foods, soft drinks, high simple carbohydrate and sugar, salty/sugary/fatty snacks, fruits, vegetables, and eating patterns (eating with family or by themselves in front of screens). Be sure to include an assessment of emotional reactivity and frequency of irritability and “hangryness”.
- If the assessment suggest low level of organic whole foods and predominance of ultra- refined foods, it may be possible that the person is deficient in vitamins and minerals. Recommend that the child is tested for the vitamin deficiencies. If vitamin deficiencies identified, recommend to supplement the diet with the necessary vitamins and mineral and encourage eating foods that naturally include these substances (Henry & CNS, 2023). If there is a high level of emotional reactivity and “hangryness,” a possible contributing factor could be hypoglycemic rebound from a high simple carbohydrate (sugar) intake or not eating breakfast combined with hyperventilation (Engel et al., 1947; Barr et al., 2019). Recommend eliminating simple carbohydrate breakfast and fast food snacks and substitute organic foods that include complex carbohydrates, protein, fats, vegetables and fruit. Be sure to eat breakfast.
- Implement “Grandmother Therapy”. Encourage the family and child to change their diet to eating a whide variety of organic foods (vegetables, fruits, some fish, meat and possibly dairy) and eliminate simple carbohydrates and sugars. This diet will tend to reduce nutritional deficits and may eliminate the need for supplements.
- Concurrent with the stabilization of the physiology begin psychophysiological treatment strategies such as neurofeedback biofeedback and cognitive behavior therapy.
Relevant blogs
Author Disclosure
Authors have no grants, financial interests, or conflicts to disclose.
References
Arnold, L, Lofthouse, N., & Hurt, E. (2012). Artificial food colors and attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms: conclusions to dye for. Neurotherapeutics, 9(3), 599-609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-012-0133-x
Arab, A. & Mostafalou, S. (2022). Neurotoxicity of pesticides in the context of CNS chronic diseases. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 32(12), 2718-2755. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2021.1987396
Barr, E.A., Peper, E., & Swatzyna, R.J. (2019). Slouched Posture, Sleep Deprivation, and Mood Disorders: Interconnection and Modulation by Theta Brain Waves. NeuroRegulation, 6(4), 181–189. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.4.181
Bayes. J., Schloss, J., Sibbritt, D. (2022). The effect of a Mediterranean diet on the symptoms of depression in young males (the “AMMEND: A Mediterranean Diet in MEN with Depression” study): a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 116(2), 572-580. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqac106
Bjørling-Poulsen, M., Andersen, H.R. & Grandjean, P. Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ Health 7, 50 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-7-50
Bommersbach, T.J., McKean, A.J., Olfson, M., Rhee, T.G. (2023). National Trends in Mental Health–Related Emergency Department Visits Among Youth, 2011-2020. JAMA, 329(17):1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.4809
Bouchard, M.F., Bellinger, D.C., Wright, R.O., & Weisskopf, M.G. (2010). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and urinary metabolites of organophosphate pesticides. Pediatrics, 125(6), e1270-7. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-3058
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Cardenas, D. (2013). Let not thy food be confused with thy medicine: The Hippocratic misquotation. e-Spen Journal, 8(6), 3260-3262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnme.2013.10.002
CDC, (2023). Quick Facts on the Risks of E-cigarettes for Kids, Teens, and Young Adults. CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 23, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/Quick-Facts-on-the-Risks-of-E-cigarettes-for-Kids-Teens-and-Young-Adults.html
Chang, J.C., Su, K.P., Mondelli, V. et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Youths with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials and Biological Studies. Neuropsychopharmacol. 43, 534–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.160
Chhabra, R., Kolli, S., & Bauer, J.H. (2013). Organically Grown Food Provides Health Benefits to Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE, 8(1): e52988. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052988
Davis, D. R., Epp, M. D., & Riordan, H. D. (2004). Changes in USDA food composition data for 43 garden crops, 1950 to 1999. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 23(6), 669-682. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719409
Derbyshire, E. (2017). Do Omega-3/6 Fatty Acids Have a Therapeutic Role in Children and Young People with ADHD? J Lipids. 6285218. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6285218
Del-Ponte, B., Quinte, G.C., Cruz, S., Grellert, M., & Santos, I. S. Dietary patterns and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 252, 160-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.04.061
Durukan, İ., Kara, K., Almbaideen, M., Karaman, D., & Gül, H. (2018). Alexithymia, depression and anxiety in parents of children with neurodevelopmental disorder: Comparative study of autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics International, 60(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.13510
Effatpanah, M., Rezaei, M., Effatpanah, H., Effatpanah, Z., Varkaneh, H.K., Mousavi. S.M., Fatahi, S., Rinaldi, G., & Hashemi, R. (2019). Magnesium status and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res, 274, 228-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.02.043
Engel, G.L., Ferris, E.B., & Logan, M. (1947). Hyperventilation; analysis of clinical symptomatology. Ann Intern Med, 27(5), 683-704. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-27-5-683
EPA. (2023). Glyphosate. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/glyphosate
European Commission. (2023). EU legislation on MRLs.Food Safety. Assessed April 1, 2023. https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/maximum-residue-levels/eu-legislation-mrls_en#:~:text=A%20general%20default%20MRL%20of,e.g.%20babies%2C%20children%20and%20vegetarians
Faraone, S.V. & Larsson, H. (2019). Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry, 24(4), 562-575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0
Fernandez-Cornejo, J. Nehring, R, Osteen, C., Wechsler, S., Martin, A., & Vialou, A. (2014). Pesticide use in the U.S. Agriculture: 21 Selected Crops, 1960-2008. Economic Information Bulletin Number 123, United State Department of Agriculture. https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/43854/46734_eib124.pdf
Gomes, G. N., Vidal, F. N., Khandpur. N., et al. (2023). Association Between Consumption of Ultraprocessed Foods and Cognitive Decline. JAMA Neurol, 80(2),142–150. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.4397
Hemamy, M., Heidari-Beni, M., Askari, G., Karahmadi, M., & Maracy, M. (2020). Effect of Vitamin D and Magnesium Supplementation on Behavior Problems in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Int J Prev Med, 11(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_546_17
Henry, K. (2023). An Integrative Medicine Approach to ADHD. Rupa Health. Accessed September 30, 2023. https://www.rupahealth.com/post/an-integrative-medicine-approach-to-adhd
Henry, K. & CNS, L.A. (2023). Natural treatments for ADHD. Webinar Presentation by IntegrativePractitioner.com and sponsored by Rupa Health, June 6, 2023 https://divcom-events.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/divcom-events/recording/e29cefcae6c1103bb7f3aa780efee435/playback?
Hemamy, M., Pahlavani, N., Amanollahi, A. et al. (2021). The effect of vitamin D and magnesium supplementation on the mental health status of attention-deficit hyperactive children: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr, 21, 178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-021-02631-1
Konofal, E., Lecendreux, M., Arnulf, I., & Mouren, M. (2004). Iron Deficiency in Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 158(12), 1113–1115. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.158.12.1113
Kotsi, E., Kotsi, E. & Perrea, D.N. (2019). Vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a meta-analysis. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord, 11, 221–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-018-0276-7
LaChance, L.R. & Ramsey, D. (2018). Antidepressant foods: An evidence-based nutrient profiling system for depression. World J Psychiatr, 8(3): 97-104. World J Psychiatr., 8(3): 97-104. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v8.i3.97
Landaas, E.T., Aarsland, T.I., Ulvik, A., Halmøy, A., Ueland. P.M., & Haavik, J. (20166). Vitamin levels in adults with ADHD. BJPsych Open, 2(6), 377-384. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjpo.bp.116.003491
Linday, L.A. (2010). Cod liver oil, young children, and upper respiratory tract infections. J Am Coll Nutr, 29(6), 559-62. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2010.10719894
Leoci, R. & Ruberti, M. (2021) Pesticides: An Overview of the Current Health Problems of Their Use. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 9, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2021.98001
Lustig, R.H. (2021). Metaboical: The lure and the lies of processed food, nutrition, and modern medicine. New York: Harper Wave. https://www.amazon.com/Metabolical-processed-poisons-people-planet/dp/1529350077
MacInerney, E. K., Swatzyna, R. J., Roark, A. J., Gonzalez, B. C., & Kozlowski, G. P. (2017). Breakfast choices influence brainwave activity: Single case study of a 12-year-old female. NeuroRegulation, 4(1), 56–62. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.4.1.56
McCann, D., Barrett, A., Cooper, A., Crumpler, D., Dalen, L., Grimshaw, K., et al. (2007). Food additives and hyperactive behavior in 3-year old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet, 370(9598), 1560-1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3
Mengying, L.I, Fallin, A, D., Riley,A., Landa, R., Walker, S.O., Silverstein, M., Caruso, D., et al. (2016). The Association of Maternal Obesity and Diabetes With Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities. Pediatrics, 137(2), e20152206. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-2206
Mousain-Bosc, M., Roche, M., Polge, A., Pradal-Prat, D., Rapin, J., & Bali, J.P. (2006). Improvement of neurobehavioral disorders in children supplemented with magnesium-vitamin B6. I. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders. Magnes Res. 19(1), 46-52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16846100/#:~:text=In%20almost%20all%20cases%20of,increase%20in%20Erc%2DMg%20values.
Ney, J. (2022). Food Deserts and Inequality. Social Policy Data Lab. Updated: Jan 24, 2022. Accessed September, 23, 2023. https://www.socialpolicylab.org/post/grow-your-blog-community
Peper, E. (2023a). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. the peperperspective July 2, 2023. Accessed august 8, 2024, https://peperperspective.com/2023/07/04/reflections-on-the-increase-in-autism-adhd-anxiety-and-depression-part-1-bonding-screen-time-and-circadian-rhythms/
Peper, E. (2023b). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. NeuroRegulation, 10(2), 134-138. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.10.2.134
Pollan, M. (2006). Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and Food Rules. New York Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Omnivores-Dilemma-Natural-History-Meals/dp/1594200823/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?_
Pollan, M. (2011). Food rules. New York Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Food-Rules-Eaters-Michael-Pollan/dp/B00VSBILFG/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?
Pongpitakdamrong, A., Chirdkiatgumchai, V., Ruangdaraganon, N., Roongpraiwan, R., Sirachainan, N., Soongprasit, M., & Udomsubpayakul, U. (2022). Effect of Iron Supplementation in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Iron Deficiency: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, 43(2), 80-86., https://doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0000000000000993
Porto, A. & Abu-Alreesh, S. (2022). Vitamin D for babies, children & adolescents. Health Living. Healthychildren.org. Accessed September 24, 2023. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/nutrition/Pages/vitamin-d-on-the-double.aspx#
Poudineh, M., Parvin, S., Omidali, M., Nikzad, F., Mohammadyari, F., Sadeghi Poor Ranjbar, F., F., Nanbakhsh, S., & Olangian-Tehrani, S. (2023). The Effects of Vitamin Therapy on ASD and ADHD: A Narrative Review. CNS & Neurological Disorders – Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets – CNS & Neurological Disorders), (22), 5, 2023, 711-735. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527321666220517205813
Puigbò, P., Leino, L. I., Rainio, M. J., Saikkonen, K., Saloniemi, I., & Helander, M. (2022). Does Glyphosate Affect the Human Microbiota?. Life, 12(5), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050707
Ríos-Hernández, A., Alda, J.A., Farran-Codina, A., Ferreira-García, E., & Izquierdo-Pulido, M. (2017). The Mediterranean Diet and ADHD in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics, 139(2):e20162027. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2027
Ryu, S.A., Choi, Y.J., An, H., Kwon, H.J., Ha, M., Hong, Y.C., Hong, S.J., & Hwang, H.J. (2022). Associations between Dietary Intake and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Scores by Repeated Measurements in School-Age Children. Nutrients, 14(14), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142919
Sagiv, S.K., Kogut, K., Harley, K., Bradman, A., Morga, N., & Eskenazi, B. (2021). Gestational Exposure to Organophosphate Pesticides and Longitudinally Assessed Behaviors Related to Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Executive Function, American Journal of Epidemiology, 190(11), 2420–2431. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwab173
Swanson, N.L., Leu, A., Abrahamson, J., & Wallet, B. (2014). Genetically engineered crops, glyphosate and the deterioration of health in the United States of America. Journal of Organic Systems, 9(2), 6-17. https://www.organic-systems.org/journal/92/JOS_Volume-9_Number-2_Nov_2014-Swanson-et-al.pdf
Swatzyna, R. J., Boutros, N. N., Genovese, A. C., MacInerney, E. K., Roark, A. J., & Kozlowski, G. P. (2018). Electroencephalogram (EEG) for children with autism spectrum disorder: Evidential considerations for routine screening. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 28(5), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-018-1225-x
Taleb, N. N. (2014). Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder (Incerto). New York: Random House Publishing Group. https://www.amazon.com/Antifragile-Things-That-Disorder-Incerto/dp/0812979680/ref=tmm_pap_swatch_0
Tohidi, S., Bidabadi, E., Khosousi, M.J., Amoukhteh, M., Kousha, M., Mashouf, P., Shahraki, T. (2021). Effects of Iron Supplementation on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children Treated with Methylphenidate. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci, 19(4), 712-720. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2021.19.4.712
Unal, D. Çelebi, F., Bildik,H.N., Koyuncu, A., & Karahan, S. (2019). Vitamin B12 and haemoglobin levels may be related with ADHD symptoms: a study in Turkish children with ADHD, Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 29(4), 515-519. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750573.2018.1459005
USDA. (2019). Fish oil, cod liver. FoodData Central. USDA U.S> Department of Agriculture. Published 4/1/2019. Accessed September 24, 2024. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173577/nutrients
Van Tulleken, C. (2023). Ultra-Processed People. The Science Behind Food That Isn’t Food. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. https://www.amazon.com/Ultra-Processed-People-Science-Behind-Food/dp/1324036729/ref=asc_df_1324036729/?
Wahab, S., Muzammil, K., Nasir, N., Khan, M.S., Ahmad, M.F., Khalid, M., Ahmad, W., Dawria, A., Reddy, L.K.V., & Busayli, A.M. (2022). Advancement and New Trends in Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Food: A Comprehensive Review. Plants (Basel), 11(9), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091106
Wang. Y., Huang, L., Zhang, L., Qu, Y., & Mu, D. (2017). Iron Status in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One, 12(1):e0169145. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169145
Wilson, L. (2015). Mothers, beware: Your lifestyle choices will even affect your grandkids.
News Corp Australia Network. Accessed Jun 24, 2024. https://www.news.com.au/lifestyle/parenting/kids/mothers-beware-your-lifestyle-choices-will-even-affect-your-grandkids/news-story/3f326f457546cfb32af5c409f335fb56
Woo, H.D.,; Kim, D.W., Hong, Y.-S., Kim, Y.-M.,Seo, J.-H.,; Choe, B.M., Park, J.H.,; Kang, J.-W., Yoo, J.-H.,; Chueh, H.W., et al. (2014). Dietary Patterns in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Nutrients, 6, 1539-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6041539
Zhong, C., Tessing, J., Lee, B.K., Lyall, K. Maternal Dietary Factors and the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review of Existing Evidence. Autism Res,13(10),1634-1658. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2402