Reduce Interpersonal Stress*
Posted: December 4, 2025 Filed under: attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, CBT, emotions, Exercise/movement, healing, health, meditation, mindfulness, Pain/discomfort, stress management | Tags: health, mental-health, nutrition, wellness 2 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. & Harvey, R. Adjunctive techniques to reduce interpersonal stress at home. Biofeedback. 53(3), 54-57. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt

Stress often triggers defensive reactions—manifesting as anger, frustration, or anxiety that may mirror fight-or-flight responses. These reactions can reduce rational thinking, increase long-term health risks, and contribute to psychological and physiological disorders. and complicate the management of specific symptoms. Outlined are some pragmatic techniques that can be implemented during the day to interrupt and reduce stress.
After we had been living in our house for a few years, a new neighbor moved in next door. Within months, she accused us of moving things in her yard, blamed us when there was a leak in her house, claimed we were blowing leaves from her property onto other neighbors’ properties, and even screamed at her tenants to the extent that the police were called numerous times. Just looking at her house through the window was enough to make my shoulders tighten and leave me feeling upset.
When I drove home and saw her standing in front of her house, I would drive around the block one more time to avoid her while . . . feeling my body contract. Often, when I woke up in the morning, I would already anticipate conflict with my neighbor. I would share stories of my disturbing neighbor and her antics with my friends. They were very supportive and agreed with me that she was crazy. However, the acknowledgment and validation from my friends did not resolve my anger or indignation or the anxiety that was triggered whenever I saw my neighbor or thought of her. I spent far too much time anticipating and thinking about her, which resulted in tension in my own body—my heart rate would increase, and my neck and shoulders would tighten.
I decided to change. I knew I could not change her; however, I could change my reactivity and perspective. Thus, I practiced a “pause and recenter” technique. At the first moment of awareness that I was thinking about her or her actions, I would change my posture by sitting up straight, begin looking upward, breathe lower and slower, and then, in my mind’s eye, send a thought of goodwill streaming to her like an ocean wave flowing through and around her in the distance. I chose to do this series of steps because I believe that within every person, no matter how crazy or cruel, there is a part that is good, and it is that part I want to support.
I repeated this pause and recenter technique many times, especially whenever I looked in the direction of her house or saw her in her yard. I also reframed and reappraised her aggressive, negative behavior as her way of coping with her own demons. Three months later, I no longer reacted defensively. When I see her, I can say hello and discuss the weather without triggering my defensive reaction. I feel so much more at peace living where I am.
When stressed, angry, rejected, frustrated, or hurt, we so often blame the other person (Leary, 2015). The moment we think about that person or event, our anger, indignation, resentment, and frustration are triggered. We keep rehashing what happened. As we relive the experiences in our mind, we are unaware that we are also reliving bodily reactions to past events.
We are often unaware of the harm we are doing to ourselves until we experience physical symptoms such as high blood pressure, gastrointestinal distress, and muscle tightness along with behavioral and psychological symptoms such as insomnia, anxiety, or depression (Carney et al., 2006; Gerin et al., 2012). As we think of past events or interact again with a person involved in those past events, our body automatically responds with a defense reaction as if we were being threatened again in the present moment.
This defense reaction to memory of past threats from a “crazy” neighbor activates our fight-or-flight responses and increases sympathetic activation so that we can run faster and fight more ferociously to survive; however, this reaction also reduces blood flow through the frontal cortex—a process that reduces our ability to think rationally (van Dinther et al., 2024; Willeumier, et al., 2011). When we become so upset and stressed that our mind is captured by the other person, this reaction contributes to symptoms of chronic stress such as an increase in hypertension, myofascial pain, depression, insomnia, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic disorders (Duan et al., 2022; Russell et al., 2015; Suls, 2013).
Sharing our frustrations with friends and others is normal. It feels good to blame people for their personal limitations or mental illness; however, over time, blaming others avoids building adaptive capacity in strengthening skills that reduce chronic stress reactions (Fast & Tiedens, 2010; Lou et al., 2023). The time spent rehashing and justifying our feelings diminishes the time we spend in the present moment and our focus on upcoming opportunities.
In the moment of an encounter with a difficult neighbor, we may not realize that we have a choice. Some people keep living and reacting to past hurts or losses perpetually. Some people can learn to let go and/or forgive and make space in favor of considering new opportunities for learning and growth. Although the choice is ours, it is often very challenging to implement—even with the best intentions—because we react automatically when reminded of past hurts (seeing that person, anticipating meeting or actually meeting that person who caused the hurt, or being triggered by other events that evoke memories of the pain).
What Can You Do
Choose to change your response. Choose to reduce reactivity. Choosing adaptive reactions does not mean you condone what happened or agree that the other person was right. You are just choosing to live your life and not continue to be captured by nor react to the previous triggers. Many people report that after implementing some of the practices described below along with many other stress management techniques, their automatic reactivity was noticeably decreased. They report that their chronic stress symptoms were reduced and they have the freedom to live in present instead of being captured by the painful past.
Pause and Recenter by Sending Goodwill
Our automatic reaction to the trigger elicits a defense reaction that reduces our ability to think rationally. Therefore, the moment you anticipate or begin to react, take three very slow diaphragmatic breaths, inhaling for approximately 4–5 seconds and exhaling for about 5–6 seconds, where one in-and-out breath takes about 10 seconds to complete. As you inhale, allow your abdomen to expand; then as you exhale, slowly make yourself tall and look up. Looking up allows easier access to empowering and positive memories (Peper et al., 2017).
Continue looking up, inhaling slowly to allow the abdomen to expand. Repeat this slow breath again. On the third long, slow breath, while looking up, evoke a memory of someone in whose presence you felt at peace and who loves you, such as your grandmother, aunt, uncle, or even a pet. Reawaken positive feelings associated with memories of being loved. Allow a smile inwardly or outwardly and soften your eyes as you experience the loving memory.
Next, put your hands on your chest, take another long slow breath as your abdomen expands, and as you exhale bring your hands away from your chest and stretch them out in front of you. At the same time in your mind’s eye, imagine sending goodwill to that person involved in the interpersonal conflict that previously evoked your stress response. As if you are sending an ocean wave that is streaming outward to the person.
As you do the pause and recenter technique, remember you are not condoning what happened; instead, you are sending goodwill to that person’s positive aspect. From this perspective, everyone has an intrinsic component—however small—that some label as the individual’s human potential, Christ nature or Buddha nature.

Why would this be effective? This practice short-circuits the automatic stress response and provides time to recenter, interrupting ongoing rumination by shifting the mind away from thoughts about the person or event that induced stress toward a positive memory. By evoking a loving memory from the past, we facilitate a reduction in arousal, evoke a positive mood, and decrease sympathetic nervous system activation (Speer & Delgado, 2017). Slower diaphragmatic breathing also reduces sympathetic activation (Birdee et al., 2023; Siedlecki et al., 2022). By combining body-centered and mind-centered techniques, we can pause and create the opportunity to respond positively rather than reacting with anger and hurt.
Practice Sending Goodwill the Moment You Wake Up
So often when we wake up, we anticipate the challenges, and even the prospect of interacting with a person or event heightens our defense reaction. Therefore, as soon as you wake up, sit at the edge of the bed, repeat the previous practice, pause, and center. Then, as you sit at the edge of the bed, slightly smile with soft eyes, look up, and inhale as your abdomen expands. Then, stamp a foot into the floor while saying, “Today is a new day.” Next, inhale, allowing your abdomen to expand; as you look up, stamp the opposite foot on the floor while saying, “Today is a new day.” Finally, send goodwill to the person who previously triggered your defensive reaction.
Why would this be effective? Looking up makes it easier to access positive memories and thoughts. Stamping your foot on the ground is a nonverbal expression of determination and anchors the thought of a new day, thereby focusing on new opportunities (Feldman, 2022).
Interrupt the Stress Response with the ABCs
The moment you notice discomfort, pain, stress, or negative thoughts, interrupt the cycle with a simple ABC strategy (Peper, 2025):
- Adjust posture and look up
- Breathe by allowing your abdomen to relax and expand while inhaling
- Change your internal dialogue, smile and focus on what you want to do
Why would this be effective? By shifting your posture and gently looking upward, you make it easier to access positive and empowering memories and thoughts (Peper et al., 2019). This simple change in body position can interrupt habitual stress responses and open the doorway to more constructive states.
Slow, diaphragmatic breathing further supports this process by reducing sympathetic arousal and restoring a sense of calm. As your breathing deepens, clarity of mind increases, allowing you to respond rather than react (Peper et al, 2024b; Matto et al, 2025).
Equally important is transforming critical, judgmental, or negative self-talk into affirmative, supportive statements. Describe what you want to do—rather than what you want to avoid. This reframing creates a clear internal guide and significantly increases the likelihood that you will achieve your desired goals.
Complete the Alarm Reaction a Burst of Physical Activity
When you feel overwhelmed and fully captured by a stress reaction, one of the most effective strategies is to complete the fight-flight response with a brief burst of intense physical activity. This momentary action such as running in place, vigorously shaking your arms, or doing a few rapid push-offs from a wall (Peper et al., 2024a). After completing the physical activity implement your stress management strategies such as breathing, cognitive reframing, meditation, etc.
Why would this be effective? The intense physical activity discharges the excessive physiological arousal and interrupts the cycle of rumination. For practical examples and step-by-step guidance, see the article Quick Rescue Techniques When Stressed (Peper et al., 2024a) or the accompanying blog post: https://peperperspective.com/2024/02/04/quick-rescue-techniques-when-stressed/
Discuss Your Issue from the Third-Person Perspective
When thinking, ruminating, talking, texting, or writing about the event, discuss it from the third-person perspective. Replace the first-person pronoun “I” with “she” or “he.” For example, instead of saying “I was really pissed off when my boss criticized my work without giving any positive suggestions for improvement,” say “He was really pissed off when his boss criticized his work without offering any positive suggestions for improvement.”
Why would this be effective? The act of substituting the third-person pronoun for the first-person pronoun interrupts our automatic reactivity because it requires us to observe and change our language, which activates parts of the frontal cortex. This third-person/first-person process creates a psychological distance from our feelings, allowing for a more objective and calmer perspective on the situation, effectively reducing stress by stepping back from the immediate emotional response (Moser et al., 2017). This process can be interpreted as meaning that you are no longer fully captured by the emotions, as you are simultaneously the observer of your own inner language and speech.
Compare Yourself with Others Who are less Fortunate
When you feel sorry for yourself or hurt, take a breath, look upward, and compare yourself with others who are suffering much more. In that moment, consider yourself incredibly lucky compared with people enduring extreme poverty, bombings, or severe disfigurement. Be grateful for what you have.
Why would this be effective? Research shows that when we compare ourselves with people who are more successful, we tend to feel worse—especially when we have low self-esteem. However, when we compare ourselves with others who are suffering more, we tend to feel better (Aspinwall, & Taylor, 1993). This comparison relativizes our perspective on suffering, making our own hardships and suffering seem less significant compared with the severe suffering of others.
Conclusion
It is much easier to write and talk about these practices than to implement them. Reminding yourself to implement them can be very challenging. It requires significant effort and commitment. In some cases, the benefits are not experienced immediately; however, when practiced many times during the day for six to eight weeks, many people report feeling less resentment and experience a reduction in symptoms and improvements in health and relationships.
*This blog was inspired by the podcast “No Hard Feelings,” an episode on Hidden Brain produced by Shankar Vedantam (2025) that featured psychologist Fred Luskin, and the wisdom taught by Dora Kunz (Kunz & Peper, 1983, 1984a, 1984b, 1987).
See the following posts for more relevant information
References
Aspinwall, L. G., & Taylor, S. E. (1993). Effects of social comparison direction, threat, and self-esteem on affect, self-evaluation, and expected success. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 64(5), 708–722. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.64.5.708
Birdee, G., Nelson, K.,Wallston, K., Nian, H., Diedrich, A., Paranjape, S., Abraham, R., & Gamboa, A. (2023). Slow breathing for reducing stress: The effect of extending exhale. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2023.102937
Carney, C. E., Edinger, J. D., Meyer, B., Lindman, L., & Istre, T. (2006). Symptom-focused rumination and sleep disturbance. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 4(4), 228–241. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15402010bsm0404_3
Defayette, A. B., Esposito-Smythers, C., Cero, I., Harris, K. M.,Whitmyre, E. D., & López, R. (2023). Interpersonal stress and proinflammatory activity in emerging adults with a history of suicide risk: A pilot study. Journal of Mood and Anxiety Disorders, 2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xjmad.2023.100016
Dienstbier, R. A. (1989). Arousal and physiological toughness: Implications for mental and physical health. Psychological Review, 96(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-95x.96.1.84
Duan, S., Lawrence, A., Valmaggia, L., Moll, J., & Zahn, R. (2022). Maladaptive blame-related action tendencies are associated with vulnerability to major depressive disorder. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 145, 70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.11.043
Fast, N. J., & Tiedens, L. Z. (2010). Blame contagion: The automatic transmission of self-serving attributions. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46(1), 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2009.10.007
Feldman, Y. (2022). The dialogical dance–A relational embodied approach to supervision. In C. Butte & T. Colbert (Eds.), Embodied approaches to supervision: The listening body (chap. 2). Routledge. https://www.amazon.com/Embodied-Approaches-Supervision-C%C3%A9line-Butt%C3%A9/dp/0367473348
Gerin,W., Zawadzki,M. J., Brosschot, J. F., Thayer, J. F., Christenfeld, N. J., Campbell, T. S., & Smyth, J. M. (2012). Rumination as a mediator of chronic stress effects on hypertension: A causal model. International Journal of Hypertension, 2012, 453465. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/453465
Hase, A., O’Brien, J., Moore, L. J., & Freeman, P. (2019). The relationship between challenge and threat states and performance: A systematic review. Sport, Exercise, and Performance Psychology, 8(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.1037/spy0000132
Hassamal, S. (2023). Chronic stress, neuroinflammation, and depression: An overview of pathophysiological mechanisms and emerging anti-inflammatories. Frontiers in Psychiatry,
14, 1130989. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1130989
Kunz, D., & Peper, E. (1983). Fields and their clinical implications—Part III: Anger and how it affects human interactions. The American Theosophist, 71(6), 199–203. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280777019_Fields_and_their_clinical_implications-Part_III_Anger_and_how_it_affects_human_interactions
Kunz, D., & Peper, E. (1984a). Fields and their clinical implications IV: Depression from the energetic perspective: Etiological underpinnings. The American Theosophist, 72(8), 268–275. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280884054_Fields_and_their_clinical_implications_Part_IV_Depression_from_the_energetic_perspective-Etiological_underpinnings
Kunz, D., & Peper, E. (1984b). Fields and their clinical implications V: Depression from the energetic perspective: Treatment strategies. The American Theosophist, 72(9), 299–306. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280884158_Fields_and_their_clinical_implications_Part_V_Depression_from_the_energetic_perspective-Treatment_strategies
Kunz, D., & Peper, E. (1987). Resentment: A poisonous undercurrent. The Theosophical Research Journal, IV(3), 54–59. Also in: Cooperative Connection, IX(1), 1–5. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/387030905_Resentment_Continued_from_page_4
Leary, M. R. (2015). Emotional responses to interpersonal rejection. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 17(4), 435–441. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2015.17.4/mleary
Lou, Y., Wang, T., Li, H., Hu, T. Y., & Xie, X. (2023). Blame others but hurt yourself: Blaming or sympathetic attitudes toward victims of COVID-19 and how it alters one’s health status. Psychology & Health, 39(13), 1877–1898. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2023.2269400
Matto, D., Peper, E., & Harvey, R. (2025). Monitoring and coaching breathing patterns and rate. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. https://townsendletter.com/monitoring-and-coaching-breathing-patterns-and-rate/
Moser, J. S., Dougherty, A., Mattson, W. I., Katz, B., Moran, T. P.,Guevarra, D., Shablack, H.,Ayduk,O., Jonides, J., Berman, M. G., & Kross, E. (2017). Third-person self-talk facilitates emotion regulation without engaging cognitive control: Converging evidence from ERP and fMRI. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 4519. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04047-3
Peper, E. (2025). Breathe Away Menstrual Pain- A Simple Practice That Brings Relief. the peper perspective-ideas on illness, health and well-being from Erik Peper. https://peperperspective.com/2025/11/22/6825/
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3), 153-169. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.1533-1
Peper, E., Lin, I.-M., Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback, 45(2), 36–41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E., Oded, Y., & Harvey, R. (2024a). Quick somatic rescue techniques when stressed. Biofeedback, 52(1), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.5298/982312
Peper, E., Oded, Y., Harvey, R., Hughes, P., Ingram, H., & Martinez, E. (2024b). Breathing for health: Mastering and generalizing breathing skills. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. November 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/suggestions-for-mastering-and-generalizing-breathing-skills/
Russell, M. A., Smith, T. W., & Smyth, J. M. (2015). Anger expression, momentary anger, and symptom severity in patients with chronic disease. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 50(2), 259–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-015-9747-7
Siedlecki, P., Ivanova, T. D., Shoemaker, J. K., & Garland, S. J. (2022). The effects of slow breathing on postural muscles during standing perturbations in young adults. Experimental Brain Research, 240, 2623–2631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-022-06437-0
Speer, M. E., & Delgado, M. R. (2017). Reminiscing about positive memories buffers acute stress responses. Nature Human Behaviour, 1, 0093. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-017-0093
Suls, J. (2013). Anger and the heart: Perspectives on cardiac risk, mechanisms and interventions. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 55(6), 538–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2013.03.002
van Dinther, M., Hooghiemstra, A. M., Bron, E. E., Versteeg, A., et al. (2024). Lower cerebral blood flow predicts cognitive decline in patients with vascular cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, 20(1), 136–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.13408
Vedantam, S. (2025). No hard feelings. Hidden brain. Accessed February 5, 2025. https://hiddenbrain.org/podcast/no-hard-feelings/
Willeumier, K., Taylor, D. V., & Amen, D. G. (2011). Decreased cerebral blood flow in the limbic and prefrontal cortex using SPECT imaging in a cohort of completed suicides. Translational Psychiatry, 1(8), e28. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2011.28
Zannas, A. S., & West, A. E. (2014). Epigenetics and the regulation of stress vulnerability and resilience. Neuroscience, 264, 157–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.003
Breathe Away Menstrual Pain- A Simple Practice That Brings Relief *
Posted: November 22, 2025 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, cognitive behavior therapy, education, emotions, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: dysmenorrhea, health, meditation, menstrual cramps, mental-health, mindfulness, wellness 2 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. Harvey, R., Chen, & Heinz, N. (2025). Practicing diaphragmatic breathing reduces menstrual symptoms both during in-person and synchronous online teaching. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, Published online: 25 October 2025. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09745-7
“Once again, the pain starts—sharp, deep, and overwhelming—until all I can do is curl up and wait for it to pass. There’s no way I can function like this, so I call in sick. The meds take the edge off, but they don’t really fix anything—they just mask it for a little while. I usually don’t tell anyone it’s menstrual pain; I just say I’m not feeling well. For the next couple of days, I’m completely drained, struggling just to make it through.
Many women experience discomfort during menstruation, from mild cramps to intense, even disabling pain. When the pain becomes severe, the body instinctively responds by slowing down—encouraging rest, curling up to protect the abdomen, and often reaching for medication in hopes of relief. For most, the symptoms ease within a day or two, occasionally stretching into three, before the body gradually returns to balance.
Another helpful approach is to practice slow abdominal breathing, guided by a breathing app FlowMD. In our study led by Mattia Nesse, PhD, in Italy, the response of one 22-year-old woman illustrated the power of this simple practice.
“Last night my period started, so I was a bit discouraged because I knew I’d get stomach pain, etc. On the other hand, I said, “Okay, let’s see if the breathing works,” and it was like magic — incredible. I’ll need to try it more times to understand whether it consistently has the same effect, but right now it truly felt magical. Just 3 minutes of deep breathing with the app were enough, and I’m not saying I don’t feel any pain anymore, but it has decreased a lot, so thank you! Thank you again for this tool… I’m really happy!”
The Silent Burden of Menstrual Pain
Menstrual pain, or dysmenorrhea, affects most women at some point in their lives — often silently. For many, the monthly cycle brings not only physical discomfort but also shame, fatigue, and interruptions to work or school. It is one of the leading causes of absenteeism and reduced productivity worldwide (Itani et al., 2022; Thakur & Pathania, 2022). In addition, the estimated health cost ranged from US $1367 to US$ 7043 per year (Huang et al., 2021). Yet, despite its prevalence, most women are never taught how to use their own physiology to ease these symptoms.
The Study (Peper et al, 2025)
Seventy-five university women participated across two upper-division Holistic Health courses. Forty-nine practiced 30 minutes per day of breathing and relaxation over five weeks as well as practicing the moment they anticipated or felt discomfort; twenty-six served as a comparison group without a specific daily self-care routine. Students rated change in menstrual symptoms on a scale from –5 (“much worse”) to +5 (“much better”). For the detailed steps in training, see the blog: https://peperperspective.com/2023/04/22/hope-for-menstrual-cramps-dysmenorrhea-with-breathing/ (Peper et al., 2023).
What changed
The results were striking. Women who practiced breathing and relaxation showed significant decrease in menstrual symptoms compared to the non-intervention group (p = 0.0008) as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Decrease in menstrual symptoms as compared to the control group after implementing slow diaphragmatic breathing.
Why does breathing and posture change have a beneficial effect?
When you stay curled up, your abdomen becomes compressed, leaving little room for the lower belly to relax or for the diaphragm to move freely. The result? Tension builds, and pain often increases.
To reverse this, create space for relaxation. Gently loosen your waist and let your abdomen expand as you inhale. Uncurl your body—lengthen your spine and open your chest, as shown in Figure 2. With each easy breath, you invite calm and allow your body to shift from tension to ease.
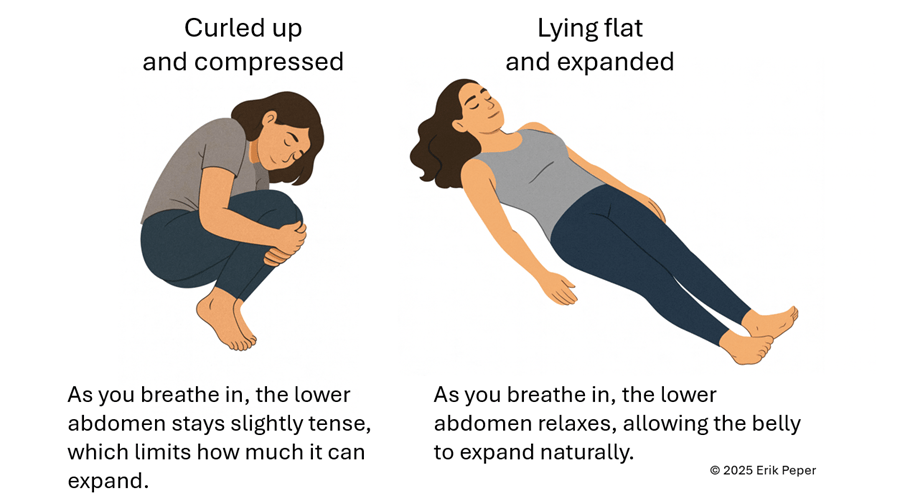
Figure 2. Curling up compresses the abdomen and prevents relaxation of the lower belly. In contrast, lying flat with the body gently expanded allows the abdomen to move freely with each breath, which can help reduce menstrual discomfort.
In contrast, slow abdominal or diaphragmatic breathing activates the body’s natural relaxation response. It quiets the stress-driven sympathetic nervous system, calms the mind, and improves circulation in the abdominal area. With each slow breath in, the abdomen gently expands while the pelvic floor and abdominal muscles relax. As you exhale, these muscles naturally tighten slightly, helping to massage and move blood and lymph through the abdominal region. This rhythmic movement supports healing and ease, as illustrated in Figure 3.
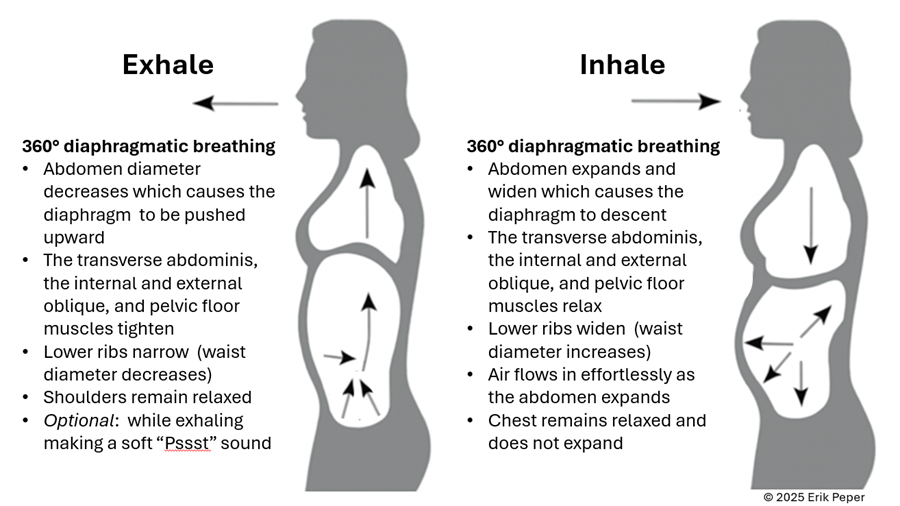
Figure 3. The dynamic process of diaphragmatic breathing.
The process of slower, lower diaphragmatic breathing
When lying down, rest comfortably on your back with your legs slightly apart. Allow your abdomen to rise naturally as you inhale and fall as you exhale. As you breathe out, imagine the air flowing through your abdomen, down your legs, and out through your feet. To deepen this sensation, you can ask a partner to gently stroke from your abdomen down your legs as you exhale—helping you sense the flow of release through your body.
Gently focus on slow, effortless diaphragmatic breathing. With each inhalation, your abdomen expands, and the lower belly softens. As you exhale, the abdomen gently goes down pushing the diaphragm upward and allowing the air to leave easily. Breathing slowly—about six breaths per minute—helps engage the body’s natural relaxation response.
If you notice that your breath is staying high in your chest instead of expanding through the abdomen, your symptoms may not improve and can even increase. One participant experienced this at first. After learning to let her abdomen expand with each inhalation while keeping her shoulders and chest relaxed, her next menstrual cycle was markedly easier and far less uncomfortable. The lesson is clear: technique matters.
“During times of pain, I practiced lying down and breathing through my stomach… and my cramps went away within ten minutes. It was awesome.” — 22-year-old college student
“Whenever I felt my cramps worsening, I practiced slow deep breathing for five to ten minutes. The pain became less debilitating, and I didn’t need as many painkillers.” — 18-year-old college student
These successes point out that it’s not just breathing — it’s how you breathe by providing space for the abdomen to expand during inhalation.
Practice: How to Do Diaphragmatic Breathing
- Find a quiet space. Lie on your back or sit comfortably erect with your shoulders relaxed.
- Place one hand on your chest and one on your abdomen.
- Inhale slowly through your nose for about 3–4 seconds. Let your abdomen expand as you breathe in — your chest should remain relaxed.
- Exhale gently through your mouth for 4—6 seconds, allowing the abdomen to fall or constrict naturally.
- As you exhale imagine the air moving down your arms, through your abdomen, down your legs, and out your feet
- Practice daily for 20 minutes and also for 5–10 minutes during the day when menstrual discomfort begins.
- Add warmth. Placing a warm towel or heating pad over your abdomen can enhance relaxation while lying on your back and breathing slowly.
With regular practice and implementing it during the day when stressed, this simple method can reduce cramps, promote calm, and reconnect you with your body’s natural rhythm.
Implement the ABCs during the day
The ABC sequence—adapted from the work of Dr. Charles Stroebel, who developed The Quieting Reflex (Stroebel, 1982)—teaches a simple way to interrupt stress reactions in real time. The moment you notice discomfort, pain, stress, or negative thoughts, interrupt the cycle with a simple ABC strategy:
A — Adjust your posture
Sit or stand tall, slightly arch your lower back and allowing the abdomen to expand while you inhale and look up. This immediately shifts your body out of the collapsed “defense posture’ and increases access to positive thoughts (Tsai et all, 2016; Peper et al., 2019)
B — Breathe
Allow your abdomen to expand as you inhale slowly and deeply. Let it get smaller as you exhale. Gently make a soft hissing sound as you exhale while helps the abdomen and pelvic floor to tighten. Then allow the abdomen to relax and widen which without effort draws the air in during inhalation. As you exhale, stay tall and imagine the air flowing through you and down your legs and out your feet.
C — Concentrate
Refocus your attention on what you want to do and add a gentle smile. This engages positive emotions, the smile helps downshift tension.
The video clip guides you through the ABCs process.
Integrate the breathing during the day by implementing your ABCs
When students practice relaxation technique and this method, they reported greater reductions in symptoms compared with a control group. By learning to notice tension and apply the ABC steps as soon as stress arises, they could shift their bodies and minds toward calm more quickly, as shown in Figure 4.
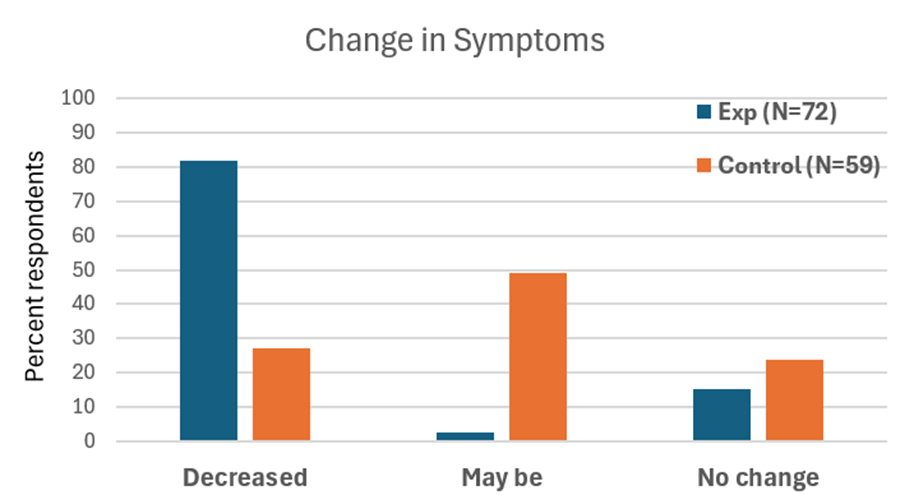
Figure 4. Change in symptoms after practicing a sequential relaxation and breathing techniques for four weeks.
Takeaway
Menstrual pain doesn’t have to be endured in silence or masked by medication alone. By practicing 30 minutes of slow diaphragmatic breathing daily and many times during the day, women may be able to reduce pain, stress, and discomfort — while building self-awareness and confidence in their body’s natural rhythms thereby having the opportunity to be more productive.
We recommend that schools and universities include self-care education—especially breathing and relaxation practices—as part of basic health curricula as this approach is scalable. Teaching young women to understand their bodies, manage stress, and talk openly about menstruation can profoundly improve well-being. It not only reduces physical discomfort but also helps dissolve the stigma that still surrounds this natural process,
Remember: Breathing is free—available anytime, anywhere and is helpful in reducing pain and discomfort. (Peper et al., 2025; Joseph et al., 2022)
See the following blogs for more in-depth information and practical tips on how to learn and apply diaphragmatic breathing:
REFERENCES
Itani, R., Soubra, L., Karout, S., Rahme, D., Karout, L., & Khojah, H.M.J. (2022). Primary Dysmenorrhea: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Updates. Korean J Fam Med, 43(2), 101-108. https://doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.21.0103
Huang, G., Le, A. L., Goddard, Y., James, D., Thavorn, K., Payne, M., & Chen, I. (2022). A systematic review of the cost of chronic pelvic pain in women. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada, 44(3), 286–293.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogc.2021.08.011
Joseph, A. E., Moman, R. N., Barman, R. A., Kleppel, D. J., Eberhart, N. D., Gerberi, D. J., Murad, M. H., & Hooten, W. M. (2022). Effects of slow deep breathing on acute clinical pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, 27, 2515690X221078006. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515690X221078006
Peper, E., Booiman, A. & Harvey, R. (2025). Pain-There is Hope. Biofeedback, 53(1), 1-9. http://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-53.01.16
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N., & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Chen, S., & Heinz, N. (2025). Practicing diaphragmatic breathing reduces menstrual symptoms both during in-person and synchronous online teaching. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. Published online: 25 October 2025. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09745-7
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153-169. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.1533-1
Stroebel, C. (1982). The Quieting Reflex. New York: Putnam Pub Group. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-Quieting-Charles-M-D-Stroebel/dp/0399126570/
Thakur, P. & Pathania, A.R. (2022). Relief of dysmenorrhea – A review of different types of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. MaterialsToday: Proceedings.18, Part 5, 1157-1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.207
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I. M. (2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23-27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
*Edited with the help of ChatGPT 5
Use the power of your mind to transform health and aging
Posted: February 18, 2025 Filed under: attention, behavior, cancer, CBT, cognitive behavior therapy, COVID, education, health, meditation, mindfulness, Pain/discomfort, placebo, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: health, imimune function, longevity, mental-health, mind-body, nutrition, Reframing, wellness Leave a commentMost of the time when I drive or commute by BART, I listen to podcasts (e.g., Freakonomics, Hidden Brain, this podcast will kill you, Science VS, Huberman Lab). although many of the podcasts are highly informative; , rarely do I think that everyone could benefit from it. The recent podcast, Using your mind to control your health and longevity, is an exception. In this podcast, neuroscientist Andrew Huberman interviews Professor Ellen Langer. Although it is three hours and twenty-two minute long, every minute is worth it (just skip the advertisements by Huberman which interrupts the flow). Dr. Langer delves into how our thoughts, perceptions, and mindfulness practices can profoundly influence our physical well-being.
She presents compelling evidence that our mental states are intricately linked to our physical health. She discusses how our perceptions of time and control can significantly impact healing rates, hormonal balance, immune function, and overall longevity. By reframing our understanding of mindfulness—not merely as a meditative practice but as an active, moment-to-moment engagement with our environment—we can harness our mental faculties to foster better health outcomes. The episode also highlights practical applications of Dr. Langer’s research, offering insights into how adopting a mindful approach to daily life can lead to remarkable health benefits. By noticing new things and embracing uncertainty, individuals can break free from mindless routines, reduce stress, and enhance their overall quality of life. This podcast is a must-listen for anyone interested in the profound connection between mind and body. It provides valuable tools and perspectives for those seeking to take an active role in their health and well-being through the power of mindful thinking. It will change your perspective and improve your health. Listen to or watch the interview:
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QYAgf_lfio4

Useful blogs to reduce stress
Is mindfulness training old wine in new bottles?
Posted: January 11, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, CBT, cognitive behavior therapy, healing, health, meditation, self-healing, stress management | Tags: anxiety, autogenic training, biofeedback, health, meditation, mental-health, mindfulness, pain, passive attention, progressive muscle relaxation, wellness, yoga 2 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Lin, I-M. (2019). Mindfulness training has themes common to other technique. Biofeedback. 47(3), 50-57. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-47.3.02

This extensive blog discusses the benefits of mindfulness-based meditation (MM) techniques and explores how similar beneficial outcomes occur with other mind-centered practices such as transcendental meditation, and body-centered practices such as progressive muscle relaxation (PMR), autogenic training (AT), and yoga. For example, many standardized mind-body techniques such as mindfulness-based stress reduction and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (a) are associated with a reduction in symptoms of symptoms such as anxiety, pain and depression. This article explores the efficacy of mindfulness based techniques to that of other self-regulation techniques and identifies components shared between mindfulness based techniques and several previous self-regulation techniques, including PMR, AT, and transcendental meditation. The authors conclude that most of the commonly used self-regulation strategies have comparable efficacy and share many elements.
Mindfulness-based strategies are based in ancient Buddhist practices and have found acceptance as one of the major contemporary behavioral medicine techniques (Hilton et al, 2016; Khazan, 2013). Throughout this blog the term mindfulness will refer broadly to a mental state of paying total attention to the present moment, with a non-judgmental awareness of the inner and/ or outer experiences (Baer et al., 2004; Kabat-Zinn, 1994).
In 1979, Jon Kabat-Zinn introduced a manual for a standardized Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center (Kabat-Zinn, 1994, 2003). The eight-week program combined mindfulness as a form of insight meditation with specific types of yoga breathing and movements exercises designed to focus on awareness of the mind and body, as well as thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
There is a substantial body of evidence that mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT); Teasdale et al., 1995) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) (Kabat-Zinn, 1994, 2003) have combined with skills of cognitive therapy for ameliorating stress symptoms such as negative thinking, anxiety and depression. For example, MBSR and MBCT has been confirmed to be clinical beneficial in alleviating a variety of mental and physical conditions, for people dealing with anxiety, depression, cancer-related pain and anxiety, pain disorder, or high blood pressure (The following are only a few of the hundred studies published: Andersen et al., 2013; Carlson et al., 2003; Fjorback et al., 2011; Greeson, & Eisenlohr-Moul, 2014; Hoffman et al., 2012; Marchand, 2012; Baer, 2015; Demarzo et al., 2015; Khoury et al, 2013; Khoury et al, 2015; Chapin et al., 2014; Witek Janusek et al., 2019). Currently, MBSR and MBCT techniques that are more standardized are widely applied in schools, hospitals, companies, prisons, and other environments.
The Relationship Between Mindfulness and Other Self-Regulation Techniques
This section addresses two questions: First, how do mindfulness-based interventions compare in efficacy to older self-regulation techniques? Second, and perhaps more basically, how new and different are mindfulness-based therapies from other self-regulation-oriented practices and therapies?
Is mindfulness more effective than other mind/body body/mind approaches?
Although mindfulness-based meditation (MM) techniques are effective, it does not mean that is is more effective than other traditional meditation or self-regulation approaches. To be able to conclude that MM is superior, it needs to be compared to equivalent well-coached control groups where the participants were taught other approaches such as progressive relaxation, autogenic training, transcendental meditation, or biofeedback training. In these control groups, the participants would be taught by practitioners who were self-experienced and had mastered the skills and not merely received training from a short audio or video clip (Cherkin et al, 2016). The most recent assessment by the National Centere for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institutes of Health (NCCIH-NIH, 2024) concluded that generally “the effects of mindfulness meditation approaches were no different than those of evidence-based treatments such as cognitive behavioral therapy and exercise especially when they include how to generalize the skills during the day” (NCCIH, 2024). Generalizing the learned skills into daily life contributes to the successful outcome of Autogenic Training, Progressive Relaxation, integrated biofeedback stress management training, or the Quieting Response (Luthe, 1979; Davis et al., 2019; Wilson et al., 2023; Stroebel, 1982).
Unfortunately, there are few studies that compare the effective of mindfulness meditation to other sitting mental techniques such as Autogenic Training, Transcendental Meditation or similar meditative practices that are used therapeutically. When the few randomized control studies of MBSR versus autogenic training (AT) was done, no conclusions could be drawn as to the superior stress reduction technique among German medical students (Kuhlmann et al., 2016).
Interestingly, Tanner, et al (2009) in a waitlist study of students in Washington, D.C. area universities practicing TM used the concept of mindfulness, as measured by the Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Skills (KIM) (Baer et al, 2004) as a dependent variable, where TM practice resulted in greater degrees of ‘mindfulness.’ More direct comparisons of MM with body-focused techniques, such as progressive relaxation, or Autogenic training mindfulness-based approaches, have not found superior benefit. For example, Agee et al (2009) compared the stress management effects of a five-week Mindfulness Meditation (MM) to a five-week Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) course and found no meaningful reports of superiority of one over the other program; both MM and PMR were effective in reducing symptoms of stress.
In a persuasive meta-analysis comparing MBSR with other similar stress management techniques used among military service members, Crawford, et al (2013) described various multimodal programs for addressing post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other military or combat-related stress reactions. Of note, Crawford, et al (2013) suggest that all of the multi-modal approaches that include Autogenic Training, Progressive Muscle Relaxation, movement practices including Yoga and Tai Chi, as well as Mindfulness Meditation, and various types of imagery, visualization and prayer-based contemplative practices ALL provide some benefit to service members experiencing PTSD.
An important observation by Crawford et al (2013) pointed out that when military service members had more physical symptoms of stress, the meditative techniques appeared to work best, and when the chief complaints were about cognitive ruminations, the body techniques such as Yoga or Tai Chi worked best to reduce symptoms. Whereas it may not be possible to say that mindfulness meditation practices are clearly superior to other mind-body techniques, it may be possible to raise questions about mechanisms that unite the mind-body approaches used in therapeutic settings.
Could there be negative side effects?
Another point to consider is the limited discussion of the possible absence of benefit or even harms that may be associated with mind-body therapies. For example, for some people, meditation does not promote prosocial behavior (Kreplin et al, 2018). For other people, meditation can evoke negative physical and/or psychological outcomes (Lindahl et al, 2017; Britton et al., 2021). There are other struggles with mind-body techniques when people only find benefit in the presence of a skilled clinician, practitioner, or guru, suggesting a type of psychological dependency or transference, rather than the ability to generalize the benefits outside of a set of conditions (e.g. four to eight weeks of one to four hour trainings) or a particular setting (e.g. in a natural and/or quiet space).
Whereas the detailed instructions for many mindfulness meditation trainings, along with many other types of mind-body practices (e.g. Transcendental Meditation, Autogenic Training, Progressive Muscle Relaxation, Yoga, Tai Chi…) create conditions that are laudable because they are standardized, a question is raised as to ‘critical ingredients’, using the metaphor of baking. The difference between a chocolate and a vanilla cake is not ingredients such as flour, or sugar, etc., which are common to all cakes, but rather the essential or critical ingredient of the chocolate or vanilla flavoring. So what are the essential or critical ingredients in mind-body techniques? Extending the metaphor, Crawford, et al (2013, p. 20) might say the critical ingredient common to the mind-body techniques they studied was that people “can change the way their body and mind react to stress by changing their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors…” with techniques that, relatively speaking, “involve minimal cost and training time.”
The skeptical view suggested here is that MM techniques share similar strategies with other mind-body approaches that encouraging learners to ‘pay attention and shift intention.’ This strategy is part of the instructions when learning Progressive Relaxation, Autogenic Training, Transcendental Meditation, movement meditation of Yoga and Tai Chi and, with instrumented self-regulation techniques such as bio/neurofeedback. In this sense, MM training repackages techniques that have been available for millennia and thus becomes ‘old wine sold in new bottles.’
We wonder if a control group for compassionate mindfulness training would report more benefits if they were asked not only to meditate on compassionate acts, but actually performed compassionate tasks such as taking care of person in pain, helping a homeless person, or actually writing and delivering a letter of gratitude to a person who has helped them in the past? The suggestion is to titrate the effects of MM techniques, moving from a more basic level of benefit to a more fully actualized level of benefit, generalizing their skill beyond a training setting, as measured by the Baer et al (2004) Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Skills.
Each generation of clinicians and educators rediscover principles without always recognizing that the similar principles were part of the previous clinical interventions. The analogies and language has changed; however, the underlying concepts may be the same. Mindfulness interventions are now the new, current and popular approach. Some of the underlying ‘mindfulness’ concepts that are shared in common with successfully other mind-body and self-regulation approaches include:
The practitioner must be self-experienced in mindfulness practice. This means that the practitioners do not merely believe the practice is effective; they know it is effective from self-experience. Inner confidence conveyed to clients and patients enhances the healing/placebo effect. It is similar to having sympathy or empathy for clients and patients that occurs from have similar life experiences, such as when a clinician speaks to a patient. For example, a male physician speaking to a female patient who has had a mastectomy may be compassionate; however, empathy occurs more easily when another mastectomy patient (who may also be a physician) shares how she struggled overcame her doubts and can still be loved by her partner.
There may also be a continuum of strengthening beliefs about the benefits of mindfulness techniques that leads to increase benefits for the approach. Knowing there are some kinds of benefits from initiating a practice of mindfulness increases empathy/compassion for others as they learn. Proving that mindfulness techniques are causing benefits after systematically comparing their effectiveness with other approaches strengthens the belief in the mindfulness approaches. Note that a similar process of strengthening one’s belief in an approach occurs gradually, over time as clients and patients progress through beginner, intermediate and advanced levels of mind-body practices.
Observing thoughts without being captured. Being a witness to the thoughts, emotions, and external events results in a type of covert global desensitization and skill mastery of NOT being captured by those thoughts and emotions. This same process of non-attachment and being a witness is one of the underpinnings of techniques that tacitly and sometime covertly support learning ways of controlling attention, such as with Autogenic Training; namely how to passively attend to a specific body part without judgment and, report on the subjective experience without comparison or judgment.
Ongoing daily practice. Participants take an active role in their own healing process as they learn to control and focus their attention. Participants are often asked to practice up to one hour a day and apply the practices during the day as mini-practices or awareness cues to interrupt the dysfunctional behavior. For example in Autogenic training, trainees are taught to practice partial formula (such my “neck and shoulders are heavy”) during the day to bring the body/mind back to balance. While with Progressive Relaxation, the trainee learns to identify when they tighten inappropriate muscles (dysponesis) and then inhibit this observed tension.
Peer support by being in a group. Peer support is a major factor for success as people can share their challenges and successes. Peer support tends to promote acceptance of self-and others and provides role modeling how to cope with stressors. It is possible that some peer support groups may counter the benefits of a mind-body technique, especially when the peers do not provide support or may in fact impede progress when they complain of the obstacles or difficulties in their process.
These concepts are not unique to Mindfulness Meditation (MM) training. Similar instructions have been part of the successful/educational intervention of Progressive Relaxation, Autogenic Training, Yogic practices, and Transcendental Meditation. These approaches have been most successful when the originators, and their initial students, taught their new and evolving techniques to clients and patients; however, they became less successful as later followers and practitioners used these approaches without learning an in-depth skill mastery. For example, Progressive relaxation as taught by Edmund Jacobson consisted of advanced skill mastery by developing subtle awareness of different muscle tension that was taught over 100 sessions (Mackereth & Tomlinson, 2010). It was not simply listening once to a 20-minute audio recording about tightening and relaxing muscles. Similarly, Autogenic training is very specific and teaches passive attention over a three to six-month time-period while the participant practices multiple times daily. Stating the obvious, learning Autogenic Training, Mindfulness, Progressive Relaxation, Bio/Neurofeedback or any other mind-body technique is much more than listening to a 20-minute audio recording.
The same instructions are also part of many movement practices. For many participants focusing on the movement automatically evoked a shift in attention. Their attention is with the task and they are instructed to be present in the movement.
Areas to explore.
Although Mindfulness training with clients and patients has resulted in remarkable beneficial outcomes for the participants, it is not clear whether mindfulness training is better than well taught PR, AT, TM or other mind/body or body/mind approaches. There are also numerous question to explore such as: 1) Who drops out, 2) Is physical exercise to counter sitting disease and complete the alarm reaction more beneficial, and 3) Strategies to cope with wandering attention.
- Who drops out?
We wonder if mindfulness is appropriate for all participants as sometimes participants drop out or experience negative abreactions. It not clear who those participants are. Interestingly, hints for whom the techniques may be challenging can be found in the observations of Autogenic Training that lists specific guidelines for contra-, relative- and non-indications (Luthe, 1970).
- Physical movement to counter sitting disease and complete the alarm reaction.
Although many mindfulness meditation practices may include yoga practices, most participants practice it in a sitting position. It may be possible that for some people somatic movement practices such as a slow Zen walk may quiet the inner dialogue more quickly. In our experience, when participants are upset and highly stressed, it is much easier to let go of agitation by first completing the triggered fight/flight response with vigorous physical activity such as rapidly walking up and downs stairs while focusing on the burning sensations of the thigh muscles. Once the physical stress reaction has been completed and the person feels physically calmer then the mind is quieter. Then have the person begin their meditative practice.
- Strategies to cope with wandering attention.
Some participants have difficulty staying on task, become sleepy, worry, and/or are preoccupied. We observed that first beginning with physical movement practices or Progressive Relaxation appears to be a helpful strategy to reduce wandering thoughts. If one has many active thoughts, progressive relaxation continuously pulls your attention to your body as you are directed to tighten and let go of muscle groups. Being guided supports developing the passive focus of attention to bring awareness back to the task at hand. Once internally quieter, it is easier hold their attention while doing Autogenic Training, breathing or Mindfullness Meditation.
By integrating somatic components with the mindfulness such as done in Progressive Relaxation or yoga practices facilitates the person staying present. Similarly, when teaching slower breathing, if a person has a weight on their abdomen while practicing breathing, it is easier to keep attending to the task: allow the weight to upward when inhaling and feeling the exhalation flowing out through the arms and legs.
Therapeutic and education strategies that implicitly incorporate mindfulness
Progressive relaxation
In the United States during the 1920 progressive relaxation (PR) was developed and taught by Edmund Jacobson (1938). This approach was clinically very successful for numerous illnesses ranging from hypertension, back pain, gastrointestinal discomfort, and anxiety; it included 50 year follow-ups. Patients were active participants and practiced the skills at home and at work and interrupt their dysfunctional patterns during the day such as becoming aware of unnecessary muscle tension (dyponetic activity) and then release the unnecessary muscle tension (Whatmore & Kohli, 1968). This structured approach is totally different than providing an audio recording that guides clients and patients through a series of tightening and relaxing of their muscles. The clinical outcome of PR when taught using the original specific procedures described by Jacobson (1938) was remarkable. The incorporation of Progressive Relaxation as the homework practice was an important cofactor in the successful outcome in the treatment of muscle tension headache using electromyography (EMG) biofeedback by Budzynski, Stoyva and Adler (1970).
Autogenic Training
In 1932 Johannes Schultz in Germany published a book about Autogenic Training describing the basic training procedure. The basic autogenic procedure, the standard exercises, were taught over a minimum period of three month in which the person practiced daily. In this practice they directed theri passive attention to the following cascading sequence: heaviness of their arms, warmth of their arms, heart beat calm and regular, breathing calm and regular or it breathes me, solar plexus is warm, forehead is cool, and I am at peace (Luthe, 1979). Three main principles of autonomic training mentioned by Luthe (1979) are: (1) mental repetition of topographically oriented verbal formulae for brief periods; (2) passive concentration; and (3) reduction of exteroceptive and proprioceptive afferent stimulation. The underlying concepts of Autogenic Therapy include as described by Peper and Williams (1980):
The body has an innate capacity for self-healing and it is this capacity that is allowed to become operative in the autogenic state. Neither the trainer nor trainee has the wisdom necessary to direct the course of the self-balancing process; hence, the capacity is allowed to occur and not be directed.
- Homeostatic self-regulation is encouraged.
- Much of the learning is done by the trainee at home; hence, the responsibility for the training lies primarily with the trainee.
- The trainer/teacher must be self-experience in the practice.
- The attitude necessary for successful practice is one of passive attention; active striving and concern with results impedes the learning process. An attitude of acceptance is cultivated, letting be whatever comes up. This quality of attention is known as “mindfulness’ in meditative traditions.
The clinical outcome for autogenic therapy is very promising. The detailed guided self-awareness training and uncontrolled studies showed benefits across a wide variety of psychosomatic illness such as asthma, cancer, hypertension, anxiety, pain irritable bowel disease, depression (Luthe & Schultz, 1970a; Luthe & Schultz, 1970b). Autogenic training components have also been integrated in biofeedback training. Elmer and Alice Green included the incorporation of autogenic training phrases with temperature biofeedback for the very successful treatment of migraines (Green & Green, 1989). Autonomic training combine with biofeedback in clinical practices produced better results than control group for headache population (Luthe, 1979). Empirical research found that autonomic training was applied efficiently in emotional and behavioral problems, and physical disorder (Klott, 2013), such as skin disorder (Klein & Peper, 2013), insomnia (Bowden et al., 2012), Meniere’s disease (Goto, Nakai, & Ogawa, 2011) and the multitude of stress related symptoms (Wilson et al., 2023).
Bio/neurofeedback training
Starting in the late 1960s, biofeedback procedures have been developed as a successful treatment approach for numerous illnesses ranging from headaches, hypertension, to ADHD (Peper et al., 1979; Peper & Shaffer, 2010; Khazan, 2013). In most cases, the similar instructions that are part of mindfulness meditation are also embedded in the bio/neurofeedback instructions. The participants are instructed to learn control over some physiological parameter and then practice the same skill during daily life. This means that during the learning process, the person learn passive attention and is not be captured by marauding thoughts and feeling. and during the day develop awareness Whenever they become aware of dysfunctional patterns, thoughts, emotions, they initiated their newly learned skill. The ongoing biological feedback signals continuously reminds them to focus.
Transcendental meditation
The next fad to hit the American shore was Transcendental Meditation (TM)– a meditation practice from the ancient Vedic tradition in India. The participant were given a mantra that they mentally repeated and if their attention wanders, they go back to repeating the mantra internally. The first study that captured the media’s attention was by Wallace (1970) published in the Journal Science which reported that “During meditation, oxygen consumption and heart rate decreased, skin resistance increased, and the electroencephalogram showed specific changes in certain frequencies. These results seem to distinguish the state produced by Transcendental Meditation from commonly encountered states of consciousness and suggest that it may have practical applications.” (Wallace, 1970).
The participants were to practice the mantra meditation twice a day for about 20 minutes. Meta-analysis studies have reported that those who practiced TM as compared to the control group experienced significant improved of numerous disorders such as CVD risk factors, anxiety, metabolic syndrome, drug abuse and hypertension (Paul-Labrador et al, 2006; Rainforth et al., 2007; Hawkins, 2003).
To make it more acceptable for the western audience, Herbert Benson, MD, adapted and simplified techniques from TM training and then labelled a core element, the ‘relaxation response’ (Benson et al., 1974) Instead of giving people a secret mantra and part of a spiritual tradition, he recommend using the word “one” as the mantra. Numerous studies have demonstrated that when patients practice the relaxation response, many clinical symptoms were reduced. The empirical research found that practiced transcendental meditation caused increasing prefrontal low alpha power (8-10Hz) and theta power of EEG; as well as higher prefrontal alpha coherence than other locations at both hemispheres. Moreover, some individuals also showed lower sympathetic activation and higher parasympathetic activation, increased respiratory sinus arrhythmic and frontal blood flow, and decreased breathing rate (Travis, 2001, 2014). Although TM and Benson’s relaxation response continues to be practiced, mindfulness has taking it place.
Conclusion
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) and Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) are very beneficial and yet may be considered ‘old wine in new bottles’ where the metaphor refers to millennia old meditation techniques as ‘old wine’ and the acronyms such as MBSR or MBCT as ‘new bottles’. Like many other ‘new’ therapeutic approaches or for that matter, many other ‘new’ medications, use it now before it becomes stale and loses part of its placebo power. As long as the application of a new technique is taught with the intensity and dedication of the promotors of the approach, and as long as the participants are required to practice while receiving support, the outcomes will be very beneficial, and most likely similar in effect to other mind-body approaches.
The challenge facing mindfulness practices just as those from Autogenic Training, Progressive Relaxation and Transcendental Meditation, is that familiarity breeds contempt and that clients and therapists are continuously looking for a new technique that promises better outcome. Thus as Mindfulness training is taught to more and more people, it may become less promising. In addition, as mindfulness training is taught in less time, (e.g. fewer minutes and/or fewer sessions), and with less well-trained instructors, who may offer less support and supervision for people experiencing possible negative effects, the overall benefits may decrease. Thus, mindfulness practice, Autogenic training, progressive relaxation, Transcendental Meditation, movement practices, meditation, breathing practices as well as the many spiritual practices all appear to share common fate of fading over time. Whereas the core principles of mind-body techniques are ageless, the execution is not always assured.
References
Agee, J. D., Danoff-Burg, S., & Grant, C. A. (2009). Comparing brief stress management courses in a community sample: Mindfulness skills and progressive muscle relaxation. Explore: The Journal of Science and Healing, 5(2), 104-109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2008.12.004
Andersen, S. R., Würtzen, H., Steding-Jessen, M., Christensen, J., Andersen, K. K., Flyger, H., … & Dalton, S. O. (2013). Effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction on sleep quality: Results of a randomized trial among Danish breast cancer patients. Acta Oncologica, 52(2), 336-344. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2012.745948
Alvarez-Jimenez, M., Gleeson, J. F., Bendall, S., Penn, D. L., Yung, A. R., Ryan, R. M., … Nelson, B. (2018). Enhancing social functioning in young people at Ultra High Risk (UHR) for psychosis: A pilot study of a novel strengths and mindfulness-based online social therapy. Schizophrenia Research, 202, 369-377 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2018.07.022
Baer, R. A. (2003). Mindfulness training as a clinical intervention: A conceptual and empirical review. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 10, 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bpg015
Baer, R. A.. (2015). Mindfulness-based treatment approaches: Clinician’s guide to evidence base and applications. New York: Elsevier. https://www.elsevier.com/books/mindfulness-based-treatment-approaches/baer/978-0-12-416031-6
Baer, R., Smith, G., & Allen, K. (2004). Assessment of mindfulness by self-report: The Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Skills. Assessment, 11, 191–206. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191104268029
Benson, H., Beary, J. F., & Carol, M. P. (1974).The Relaxation Response. Psychiatry, 37(1), 37-46. https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/upsy20
Bowden, A., Lorenc, A., & Robinson, N. (2012). Autogenic Training as a behavioural approach to insomnia: A prospective cohort study. Primary Health Care Research & Development, 13, 175-185. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1463423611000181
Britton, W.B., Lindahl, J.R., Coope, D.J., Canby, N.K., & Palitsky, R. (2021). Defining and Measuring Meditation-Related Adverse Effects in Mindfulness-Based Programs. Clinical Psychological Science, 9(6), 1185-1204. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702621996340
Budzynski, T., Stoyva, J., & Adler, C. (1970). Feedback-induced muscle relaxation: Application to tension headache. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 1(3), 205-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7916(70)90004-2
Carlson, L. E., Speca, M., Patel, K. D., & Goodey, E. (2003). Mindfulness‐based stress reduction in relation to quality of life, mood, symptoms of stress, and immune parameters in breast and prostate cancer outpatients. Psychosomatic Medicine, 65(4), 571-581. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.psy.0000074003.35911.41
Chapin, H. L., Darnall, B. D., Seppala, E. M., Doty, J. R., Hah, J. M., & Mackey, S. C. (2014). Pilot study of a compassion meditation intervention in chronic pain. J Compassionate Health Care, 1(4), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40639-014-0004-x
Cherkin, D. C., Sherman, K. J., Balderson, B. H., Cook, A. J., Anderson, M. L., Hawkes, R. J., … & Turner, J. A. (2016). Effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction vs cognitive behavioral therapy or usual care on back pain and functional limitations in adults with chronic low back pain: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 315(12), 1240-1249. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.2323
Crawford, C., Wallerstedt, D. B., Khorsan, R., Clausen, S. S., Jonas, W. B., & Walter, J. A. (2013). A systematic review of biopsychosocial training programs for the self-management of emotional stress: Potential applications for the military. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 747694: 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/747694
Davis, M., Eshelman, E.R., & McKay, M. (2019). The Relaxation and Stress Reduction Workbook. Oakland, CA: New Harbinger Publications. https://www.amazon.com/Relaxation-Reduction-Workbook-Harbinger-Self-Help/dp/1684033349
Demarzo, M. M., Montero-Marin, J., Cuijpers, P., Zabaleta-del-Olmo, E., Mahtani, K. R., Vellinga, A., Vincens, C., Lopez del Hoyo, Y., & García-Campayo, J. (2015). The efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions in primary care: A meta-analytic review. The Annals of Family Medicine, 13(6), 573-582. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.1863
Fjorback, L. O., Arendt, M., Ørnbøl, E., Fink, P., & Walach, H. (2011). Mindfulness‐Based Stress Reduction and Mindfulness‐Based Cognitive Therapy–A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 124(2), 102-119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01704.x
Goto, F., Nakai, K., & Ogawa, K. (2011). Application of autogenic training in patients with Meniere disease. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 268(10), 1431-1435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1530-1
Greeson, J., & Eisenlohr-Moul, T. (2014). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for chronic pain. In R. A. Baer (Ed.), Mindfulness-Based Treatment Approaches: Clinician’s Guide to Evidence Base and Applications, 269-292. San Diego, CA: Academic Press. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2014-40932-000
Green, E. and Green, A. (1989). Beyond Biofeedback. New York: Knoll. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Biofeedback-Elmer-Green/dp/0940267144
Hawkins, M. A. (2003). Effectiveness of the Transcendental Meditation program in criminal rehabilitation and substance abuse recovery. Journal of Offender Rehabilitation, 36(1-4), 47- 65. https://doi.org/10.1300/J076v36n01_03
Hilton, L., Hempel, S., Ewing, B. A., Apaydin, E., Xenakis, L., Newberry, S., …Maglione, M. A. (2016). Mindfulness meditation for chronic pain: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 51(2), 199-213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-016-9844-2
Hoffman, C. J., Ersser, S. J., Hopkinson, J. B., Nicholls, P. G., Harrington, J. E., & Thomas, P. W. (2012). Effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in mood, breast-and endocrine-related quality of life, and well-being in stage 0 to III breast cancer: A randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 30(12), 1335-1342. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.34.0331
Jacobson, E. (1938). Progressive relaxation. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. https://www.amazon.com/Progressive-Relaxation-Physiological-Investigation-Significance/dp/0226390594
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1994). Wherever you go, there you are: Mindfulness meditation in everyday life. New York: Hyperion. https://www.amazon.com/Wherever-You-There-Are-Mindfulness/dp/0306832011
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2003). Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). Constructivism in the Human Sciences, 8, 73–107. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2004-19791-008
Khazan, I. Z. (2013). The clinical handbook of biofeedback: A step-by-step guide for training and practice with mindfulness. New York: John Wiley & Sons. https://www.amazon.com/Clinical-Handbook-Biofeedback-Step-Step/dp/1119993717
Klein, A., & Peper, E. (2013). There Is hope: Autogenic biofeedback training for the treatment of psoriasis. Biofeedback, 41 (4), 194-201. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-41.4.01
Khoury, B., Lecomte, T., Fortin, G., Masse, M., Therien, P., Bouchard, V., Chapleau, M., Paquin, K., & Hofmann, S. G. (2013). Mindfulness-based therapy: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(6), 763-771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2013.05.005
Khoury, B., Sharma, M., Rush, S. E., & Fournier, C. (2015). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for healthy individuals: A meta-analysis. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 78(6), 519-528.
Klott, O. (2013). Autogenic Training–a self-help technique for children with emotional and behavioural problems. Therapeutic Communities: The International Journal of Therapeutic Communities, 34(4), 152-158. https://doi.org/10.1108/TC-09-2013-0027
Kreplin, U., Farias, M., & Brazil, I. A. (2018). The limited prosocial effects of meditation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep, 8, 2403. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20299-z
Kuhlmann, S. M., Huss, M., Bürger, A., & Hammerle, F. (2016). Coping with stress in medical students: results of a randomized controlled trial using a mindfulness-based stress prevention training (MediMind) in Germany. BMC Medical Education, 16(1), 316. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-016-0833-8
Lindahl, J. R., Fisher, N. E., Cooper, D. J., Rosen, R. K, & Britton, W. B. (2017). The varieties of contemplative experience: A mixed-methods study of meditation-related challenges in Western Buddhists. PLoSONE, 12(5): e0176239. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176239
Luthe, W. (1970). Autogenic therapy: Research and theory. New York: Grune and Stratton. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/the-british-journal-of-psychiatry/article/abs/autogenic-therapy-edited-by-wolfgang-luthe-volume-4-research-and-theory-by-wolfgang-luthe-grune-and-stratton-new-york-1970-pp-276-price-1475/6C8521C36C37254A08AAD1F2FE08211C
Luthe, W. (1979). About the Methods of Autogenic Therapy. In: Peper, E., Ancoli, S., Quinn, M. (eds). Mind/Body Integration. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2898-8_12
Luthe, W. & Schultz, J. H. (1970a). Autogenic therapy: Medical applications. New York: Grune and Stratton. https://www.amazon.com/Autogenic-Therapy-II-Medical-Applications/dp/B001J9W7L6
Luthe, W. & Schultz, J. H. (1970b). Autogenic therapy: Applications in psychotherapy. New York: Grune and Stratton. https://www.amazon.com/Autogenic-Therapy-Applications-Psychotherapy-v/dp/0808902725
Mackereth, P.A. & Tomlinson, L. (2010). Progressive muscle relaxation. In Cawthorn, A. & Mackereth, P.A. eds. Integrative Hypnotherapy. London: Churchill Livingstone. https://www.amazon.com/Integrative-Hypnotherapy-Complementary-approaches-clinical/dp/0702030821
Marchand, W. R. (2012). Mindfulness-based stress reduction, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, and Zen meditation for depression, anxiety, pain, and psychological distress. Journal of Psychiatric Practice, 18(4), 233-252. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pra.0000416014.53215.86
NCCIH (2024). Meditation and Mindfulness: What You Need To Know. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institutes of Health. Accessed January 31, 2024. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/meditation-and-mindfulness-what-you-need-to-know?
Paul-Labrador, M., Polk, D., Dwyer, J.H. et al. (2006). Effects of a randomized controlled trial of Transcendental Meditation on components of the metabolic syndrome in subjects with coronary heart disease. Archive of Internal Medicine, 166(11), 1218-1224. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.11.1218
Peper, E., Ancoli, S. & Quinn, M. (Eds). (1979). Mind/Body Integration: Essential Readings in Biofeedback. New York: Plenum. https://www.amazon.com/Mind-Body-Integration-Essential-Biofeedback/dp/0306401029
Peper, E. & Shaffer, F. (2010). Biofeedback History: An Alternative View. Biofeedback, 38 (4): 142–147. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-38.4.03
Peper, E., & Williams, E.A. (1980). Autogenic therapy. In A. C. Hastings, J. Fadiman, & J. S. Gordon (Eds.), Health for the whole person (pp137-141).. Boulder: Westview Press. https://biofeedbackhealth.files.wordpress.com/2016/02/autogenic-therapy-peper-and-williams.pdf
Rainforth, M.V., Schneider, R.H., Nidich, S.I., Gaylord-King, C., Salerno, J.W., & Anderson, J.W. (2007). Stress reduction programs in patients with elevated blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Current Hypertension Reports, 9(6), 520–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-007-0094-3
Stroebel, C. (1982). QR: The Quieting Reflex. New York: Putnam Pub Group. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-Quieting-Charles-M-D-Stroebel/dp/0399126570
Tanner, M. A., Travis, F., Gaylord‐King, C., Haaga, D. A. F., Grosswald, S., & Schneider, R. H. (2009). The effects of the transcendental meditation program on mindfulness. Journal of Clinical Psychology 65(6), 574-589. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.20544
Teasdale, J. D., Segal, Z., & Williams, J. M. (1995). How does cognitive therapy prevent depressive relapse and why should attentional control (mindfulness) training help? Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33, 25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(94)e0011-7
Travis, F. (2001). Autonomic and EEG patterns distinguish transcending from other experiences during transcendental meditation practice. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 42, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8760(01)00143-x
Travis, F. (2014). Transcendental experiences during meditation practice. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1307, 1–8. https://doi.og10.1111/nyas.12316
Wallace, K.W. (1970). Physiological Effects of Transcendental Meditation. Science, 167 (3926), 1751-1754. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.167.3926.1751
Whatmore, G. B., & Kohli, D. R. (1968). Dysponesis: A neurophysiologic factor in functional disorders. Behavioral Science, 13(2), 102–124. https://doi.org/10.1002/bs.3830130203
Wilson, V., Somers, K. & Peper, E. (2023). Differentiating Successful from Less Successful Males and Females in a Group Relaxation/Biofeedback Stress Management Program. Biofeedback, 51(3), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.5298/608570
Witek Janusek, L., Tel,l D., & Mathews, H.L. (2019). Mindfulness based stress reduction provides psychological benefit and restores immune function of women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: A randomized trial with active control. Brain Behav Immun, 80:358-373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.04.012