Hope for dry eyes and eye strain
Posted: March 2, 2026 Filed under: attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, computer, digital devices, emotions, health, Pain/discomfort, relaxation, screen fatigue, self-healing, stress management, techstress, Uncategorized, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: behavioral optometry, blinking, digital eye strain, dry eyes, eyes, ophthalmology, optometry, prarasympathetic regulation 1 CommentAdapted from: Peper, E., Yoshino, A., & Harvey, R. Hope for Dry eyes and Eye Strain: How Breathing-Blinking Patterns Influence Dry Eye.
Many times during the day, I let my shoulders and face relax, and with each exhalation I feel the upper eyelids slightly dropping down at the same time as I am relaxing my jaw and mouth while sitting tall. I sense my tongue and throat sinking and feeling an increase in the space between my upper and lower molars. At the same time, I sense my eyes becoming soft and sinking down as my face muscle relax and are pulled down by gravity while sensing a gentle smile. My eyes are not trying to focus on anything. I continue to breathe slowly allowing a pause before inhaling and feel totally safe and at peace. While doing this, I sense moisture at the lower eyelids. After I have inhaled and as I exhale, I slowly open my eyes, and return to my work. My eyes feel slightly moist and as I blink, the eyelids glide smoothly over the corneal surface.
Background
Dry eyes and eye strain are far more common than most people realize. More than 50% of adults in the United States and Europe experience irritated or burning eyes, dryness, eye strain, headaches, tired or heavy eyes, sensitivity to bright light, and general eye discomfort (Wozniak et al., 2025). The prevalence increases with age and is higher among people who smoke, wear contact lenses, or spend excessive time looking at screens—typically more than six hours per day (Uchino et al,, 2013).
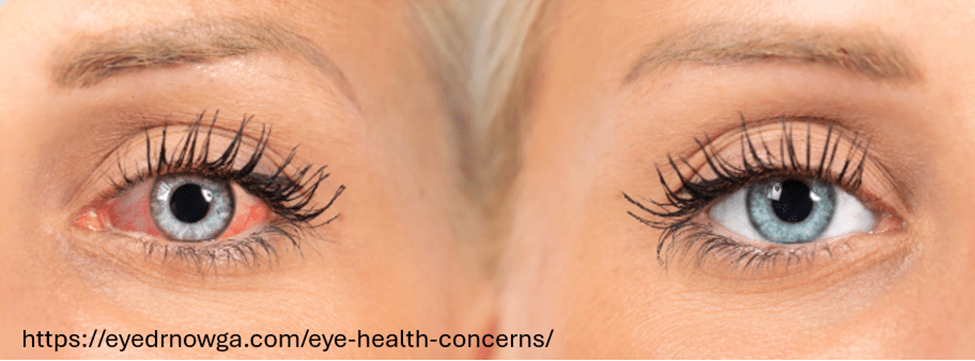
Prolonged, intense screen use—often referred to as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome—occurs when people focus and concentrate, and the muscles involved with near vision contract and do not relax (Chu et al., 2014). During near vision, the ciliary muscles tighten around the lens to allow near focus, and the medial rectus muscles contract to converge the eyes. These muscles stay contracted and only relax when looking into the distance. This ongoing tension and increased sympathetic activation combined with reduced blinking decrease tearing, and contribute to dry eye symptoms because the tears are not able to provide adequate moisture. As a result, the eyes may become irritated, red and inflamed, which increases eye discomfort (Sheppard & Wolffsohn, 2018; Portello et al., 2012; Sheedy et al., 2003).
When someone is vigilant, fearful, or anticipates a threat, sympathetic activation increases (Ranti et al., 2020) and “eye blink are inhibited at precise moments in time so as to minimize the loss of visual information that occurs during a blink. The more important the visual information is to the viewer, the more likely he or she will be to inhibit blinking” (Ranti et al., 2020).
Without being aware, many people are in a chronic state of vigilance and unknowingly are scanning the world for threats to which they must react. Clinically, I often observe this when guiding clients in relaxation. For example, when I give the instruction, “Let me lift your hand,” some clients immediately lift their hand towards me. This nonverbal response suggests that they are constantly vigilant and are monitoring the world around them—always ready to act instead of trusting that they do not have to act and that the world is safe. In most cases, their breathing pattern tends to be shallow and thoracic.
Would it be possible that this ongoing vigilance,which increases sympathetic arousal contributes to the experience of dry eye syndrome? It could be one factor explaining why women have a higher incidence of dry eye disease as well as anxiety than men since the world is often less safe for women, and they breathe more thoracically and less diaphragmatically (abdominally) than men. Shallow chest breathing is also associated with increased in anxiety (Fugl-Meyer, 1974; Mendes et al., 2020; Wilhelm et al., 2001; Banushi eat al., 2023; McLean et al., 2011; Jalnapurkar, et al., 2018).
Note: The risk of dry eye can also be further increased by a wide range of medical conditions and medications, such as diabetes; glaucoma and glaucoma medications; allergies; autoimmune diseases; arthritis; thyroid disease; high cholesterol; acne treatments; antihistamines; antidepressants; and a history of refractive surgery, conjunctival infections, or corneal abrasions. Dry eye also occurs more frequently in women (Mohamed et al., 2024).
What is usually recommended to resolve dry eyes
The primary and effective first-line treatment to reduce the symptoms of dry eye disease is the use of artificial tears (lubricating eye drops) to provide relief (Maity et al., 2025). Another recommendation to reduce eye strain associated with computer use is to implement the 20/20/20 rule developed by the American Optometric Association–take a 20-second break every 20 minutes and look at something 20 feet away (AOA, 2026). Although the 20/20/20 practice can reduce eye strain and momentarily reduce some of the symptoms associated with dry eye disease especially if the eyes are closed, how we orient, breathe and look may contribute to the experience of dry eye discomfort.
Experience how to evoke dry eyes
Sit comfortably, look around, and observe how your eyes feel. Close your eyes. Now imagine there is a threat. Take a very quick gasp through an open mouth by inhaling into your upper chest and keep breathing very shallowly and irregularly. At the same time, open your eyes wide while being vigilant and looking for danger. Simultaneously, tense your body, inclining it slightly backward as if trying to avoid something. Do not blink, as you may miss the potential threat approaching you (adapted from Lemeignan et al., 1990; Bloch, 2017). A sample physiological recording of this pattern is shown in Figure 1.
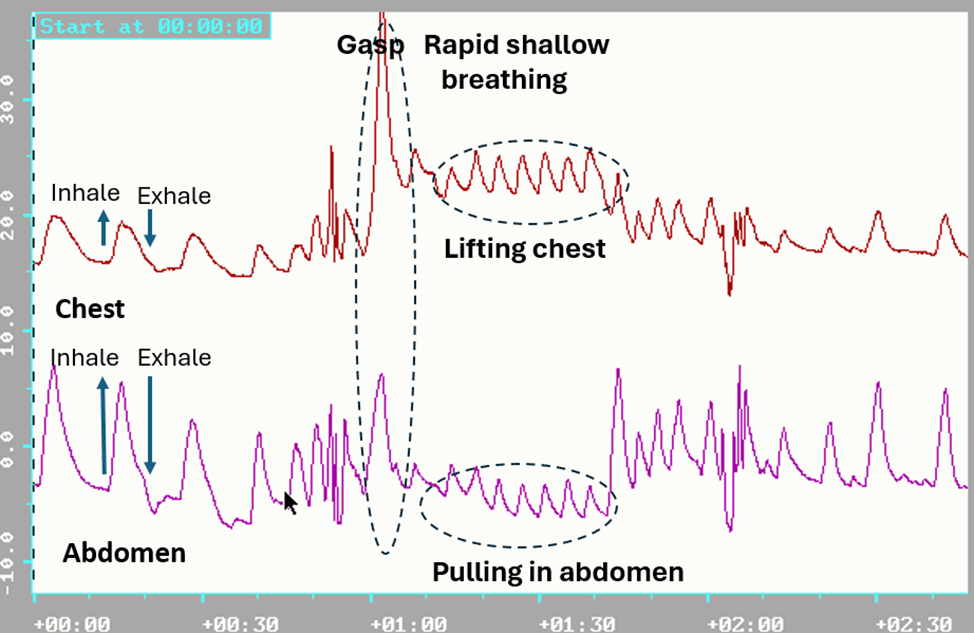
Figure 1. Breathing pattern in response to a threat; a rapid gasp into the chest and pulling the abdomen in to protect while breathing shallowly and rapidly.
Most participants report that almost immediately they feel their eyes getting cooler and after 15 seconds, drier. This facial, breathing, and posture pattern is an exaggeration of the somatic expression of fear that is evoked when we are vigilant and feel unsafe, and it increases sympathetic arousal (Kalawski, 2020).
In most cases, this pattern is automatic, and occurs without awareness, and increases sympathetic activity (Narkiewicz et al., 2006). On the other hand, slow diaphragmatic breathing tends to reduce sympathetic activity (Harada et al., 2014; Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014). Clinically, the vigilance pattern can often be observed as a person slightly lifts and expands their chest during inhalation and drops and constricts it during exhalation, while breathing shallowly and rapidly without any abdomen expansion or constriction. It is often punctuated with brief breath holding and a reduced blinking rate during concentration.
To investigate these observations more systematically, we compared the practice of gasping while opening the eyes with gentle exhalation while opening the eyes—a pattern that may reduce sympathetic activation and alter the subjective sensation of eye dryness.
Participants: 13 males and 13 females; average age, 39 years
Procedure: While sitting comfortably with their eyes closed, participants were guided through the following two practices:
1.Gasp while opening the eyes
Sit comfortably and look around and observe how your eyes feel. Now close your eyes. Now imagine there is a threat. Take a very quick gasp through an open mouth by inhaling into your upper chest and keep breathing very shallowly and irregularly. At the same time, open your eyes wide while being vigilant and looking for danger. Simultaneously, tense your body, inclining it slightly backward as if trying to avoid something. Do not blink, as you may miss the potential threat approaching you. Repeat three times.
2. Gentle exhalation while opening the eyes
Sit comfortably and look around and observe how your eyes feel. Now close your eyes. Breathe comfortably and inhale by allowing your abdomen to extend and widen while feeling your eyes sinking in their sockets and becoming softer as you gently start exhaling. While gently exhaling, begin to open your eyes very slowly, looking down through your eyelashes without caring what you see, allowing your jaw and face muscles to relax and feeling a slight smile. When you feel the urge to inhale, allow your eyes to close and let your abdomen expand as you inhale slowly. Repeat three times.
After these two practices, the participants filled out a short assessment questionnaire in which they rated how their eyes felt on a scale from -5 (dry), 0 (normal), to 5 (moist/tearing), and rated which eye-opening procedure allowed their eyes to be more relaxed and moist.
Results
92.3% of the participants reported that opening their eyes during exhalation significantly increased eye relaxation and moisture, as shown in Figure 2. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed a significant difference between the inhale condition (M = −0.19, n = 26) and the exhale condition (M = 1.00, n = 25), F(1, 49) = 9.65, p = .003. The experience of eye irritation was correlated (r = 0.64) with the self-rating of experiencing anxiety and fear during the last three months.
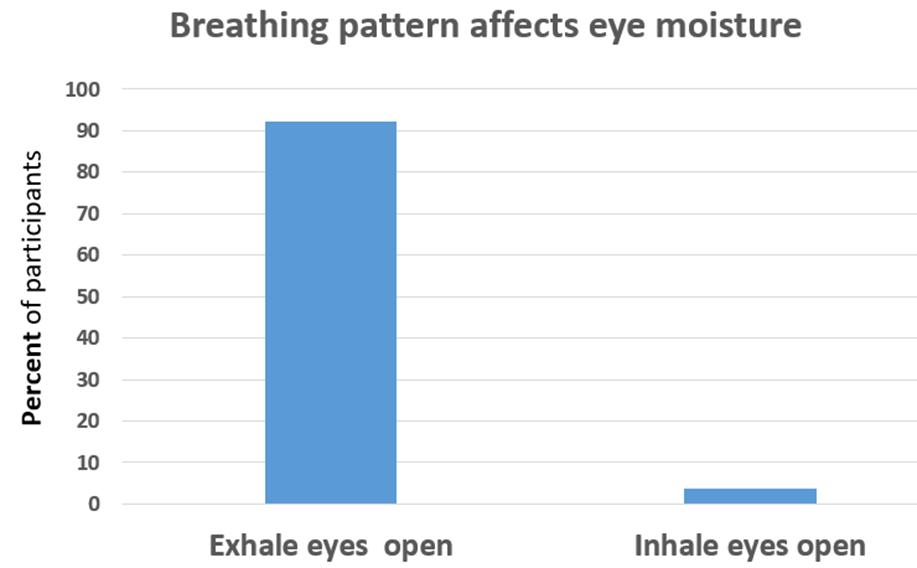
Figure 2. Gently opening the eyes during exhalation increases the experience of moisture and relaxation in the eyes.
Discussion
The results suggest that increased moisture and eye relaxation could be evoked by changing breathing-blinking patterns. Nearly all participants experienced an increase in tearing and eye relaxation; however, long-term benefits most likely occur if the person implements this practice many times during the day. By changing the breathingg-blink pattern and peacefully looking at the world with a smile, one would decrease sympathetic arousal and increase parasympathetic activity. This approach should be taught as the first self-care intervention to reduce eye irritation.
Recommendations to decrease dry eye and improve eye health
- Experience how the two different breathing and eye-opening practices described above affect your eye dryness or moistness.
- When you sense the first onset of minimal eye discomfort or when looking at screens on your computer or cellphone, implement the following practice for about 10 to 15 seconds. Allow your eyelids to close. Be aware of the sensations in your eyes, let your face and jaw relax as if they are being pulled down by gravity while sensing the eyes becoming soft and sinking into their sockets. Breathe diaphragmatically by allowing the abdomen to expand when you inhale. While gently exhaling, slowly open your eyes slightly while looking down with a gentle smile and sensing the moisture beginning to occur in the eyes. Repeat twice.
- During the day, implement the 20/20/20 vision-regeneration practice (every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and look at something 20 feet away without caring what you see), as shown in Figure 3.
- Read and incorporated the many practices described in the superb book, Vision for Life; Ten Steps to Natural Eye Improvement, by Meir Schneider (2012).

Figure 3. The 20/20/20 rule poster to prevent eye strain (AOA, 2026).
Do these practices many times and be aware of the sensations in your eyes and face. This passive awareness, in conjunction with slower breathing, tends to reduce sympathetic arousal and increase parasympathetic activity, which facilitates increased tearing. As one participant reported when she practiced this:
What a surprise it was when I closed my eyes and breathed slowly and diaphragmatically, and then, as I began to exhale, I very slowly began to open my eyes while looking down and through my eyelashes, while feeling my eyes sink into their sockets. Tearing occurred spontaneously, and my eyes felt lubricated. What a relief. It provided hope that I could help myself instead of only depending on lubricating eye drops whenever my eyes felt dry and irritated.
Two books to maintain and improve vision and reduce techstress
Vision for Life: Ten Steps to Natural Eye Improvement by Meir Schneider (2012) offers many strategies you can immediately incorporate into your daily life to improve and restore your vision. It provides guidelines on how to reverse developing vision issues before they cause damage and how to remedy existing problems, including near- and far-sightedness, lazy eye, as well as more serious conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, optic neuritis, detached retinas and retinal tears, macular degeneration, and retinitis pigmentosa.

TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey, and Nancy Fsass (2020) offers practical tools to avoid the evolutionary traps that trip us up and address the problems associated with technological overuse. It includse effective strategies and practices that individuals can use to optimize their workspace, reduce physical strain, correct posture, and improve vision. It provides fresh insights on reducing stress and enhancing health.

Additional blogs that offer strategies to improve vision
References
AOA. (2026). 20/20/20/ to prevent digital eyes strain. American Optometric Association. https://www.aoa.org/AOA/Images/Patients/Eye%20Conditions/20-20-20-rule.pdf
Banushi, B., Brendle, M., Ragnhildstveit, A., Murphy, T., Moore, C., Egberts, J., & Robison, R. (2023). Breathwork interventions for adults with clinically diagnosed anxiety disorders: A scoping review. Brain Sciences, 13(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020256
Bloch, S. (2017). Alba Emoting: A scientific method for emotional induction. Scotts Valley, CA: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. https://www.amazon.com/Alba-Emoting-Scientific-Emotional-Induction/dp/154254884
Chu, C.A., Rosenfield, M., Portello, J.K. (2014). Blink patterns: reading from a computer screen versus hard copy. Optom Vis Sci., 91(3),297-302. https://doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000000157
Craig, J. P., Nichols, K. K., Akpek, E. K., et al. (2017). TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report. The Ocular Surface, 15(3), 276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2017.05.008
Dartt, D. A. (2009). Neural regulation of lacrimal gland secretory processes: Relevance in dry eye diseases. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 28(3), 155–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2009.04.003
Fugi-Meyer, A.R. (1974). Relative respiratory contribution of the rib cage and the abdomen in males and females with special regard to posture. Respiration, 31(3), 240–251. https://doi.org/10.1159/000193113
Harada, D., Asanoi, H., Takagawa, J., Ishise, H., Ueno, H., Oda, Y., Goso, Y., Joho, S., & Inoue, H. (2014). Slow and deep respiration suppresses steady-state sympathetic nerve activity in patients with chronic heart failure: from modeling to clinical application. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 307(8), H1159–H1168. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00109.2014
Jalnapurkar, I., Allen, M., & Pigott, T. (2018). Sex differences in anxiety disorders: A review. Journal of Psychiatry, Depression & Anxiety, 4, 011. https://doi.org/10.24966/PDA-0150/100011
Kalawski, J.P. (2020) The Alba Method and the Science of Emotions. Integr. Psych. Behav. 54, 903–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-020-09525-4
Lehrer, P. M., & Gevirtz, R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Frontiers in Psychology, 5, Article 756. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4104929/
Lemeignan, M., Guitart, L., & Bloch, S. (1990). Autonomic differentiation of emotional effector pattern of 6 basic emotions. Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Psychophysiology, Budapest, July 9–14, 199
Maity, M., Allay, M. B., Ali, M. H., Basu, S., & Singh, S. (2025). Effect of different artificial tears on tear film parameters in dry eye disease. Optometry and Vision Science, 102(1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000002206
McLean, C. P., Asnaani, A., Litz, B. T., & Hofmann, S. G. (2011). Gender differences in anxiety disorders: Prevalence, course of illness, comorbidity and burden of illness. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45(8), 1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.03.006
Mendes, L. P. S., Vieira, D. S. R., Gabriel, L. S., Ribeiro-Samora, G. A., Dornelas de Andrade, A., Brandão, D. C., Goes, M. C., Fregonezi, G. A. F., Britto, R. R., & Parreira, V. F. (2020). Influence of posture, sex, and age on breathing pattern and chest wall motion in healthy subjects. Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy, 24(3), 240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjpt.2019.02.007
Mohamed, Z., Alrasheed, S., Abdu, M., & Allinjawi, K. (2024). Dry eye disease prevalence and associated risk factors among the Middle East population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus, 16(9), e70522. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.70522
Narkiewicz, K., van de Borne, P., Montano, N., Hering, D., Kara, T., & Somers, V. K. (2006). Sympathetic neural outflow and chemoreflex sensitivity are related to spontaneous breathing rate in normal men. Hypertension, 47(1), 51–55. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000197613.47649.0
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics, North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X
Portello, J.K., Rosenfield, M., Bababekova, Y., et al. (2012). Computer-related visual symptoms in office workers. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 32, 375–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1313.2012.00925.x
Ranti, C., Jones, W., Klin, A. et al. Blink Rate Patterns Provide a Reliable Measure of Individual Engagement with Scene Content. Sci Rep 10, 8267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64999-x
Schneider, M. (2012). Vision for Life: Ten Steps to Natural Eye Improvement. North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Vision-Life-Natural-Eyesight-Improvement/dp/158394494X/
Sheedy, J.E., Hayes, J.N., & Engle, J.(2003). Is all asthenopia the same? Optom Vis Sci, 80, 732–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006324-200311000-00008
Sheppard, A. L., & Wolffsohn, J. S. (2018). Digital eye strain: prevalence, measurement and amelioration. BMJ open Ophthalmology, 3(1), e000146. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjophth-2018-000146
Stern, M. E., Gao, J., Siemasko, K. F., Beuerman, R. W., & Pflugfelder, S. C. (2004). The role of the lacrimal functional unit in the pathophysiology of dry eye. Experimental Eye Research, 78(3), 409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2003.09.003
Swamynathan, S. K., & Wells, A. (2020). Conjunctival goblet cells: Ocular surface functions, disorders that affect them, and the potential for their regeneration. The Ocular Surface, 18(1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2019.11.005
Uchino, M., Yokoi, N., Uchino, Y., Dogru, M., Kawashima, M., Komuro, A., Sonomura, Y., Kato, H., Kinoshita, S., Schaumberg, D.A., & Tsubota, K. (2013). Prevalence of Dry Eye Disease and its Risk Factors in Visual Display Terminal Users: The Osaka Study. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 156(4), 759-766.e1, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2013.05.040
The epidemiology of dry eye disease: report of the Epidemiology Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf. , 5(2), 93-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1542-0124(12)70082-4
Wilhelm, F. H., Gevirtz, R., & Roth, W. T. (2001). Respiratory dysregulation in anxiety, functional cardiac, and pain disorders: Assessment, phenomenology, and treatment. Behavior Modification, 25(4), 513–545. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445501254003
Wozniak, P., et al. (2025, September 12–16). Dry eye symptoms, severity, treatment and unmet needs: An analysis of the United States of America and a multinational snapshot (NESTS Study) [Poster presentation]. 43rd Congress of the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons (ESCRS), Copenhagen, Denmark. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/09/250914205829.htm
Ziemssen, F., & Ruprecht, K. W. (2005).Autonomic dysfunction in dry eye syndrome. Ophthalmologe, 102(8), 744–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00347-005-1169-1
Ensorcelled: Breaking the Digital Enchantment
Posted: October 7, 2025 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, cellphone, computer, digital devices, education, emotions, healing, health, laptops, techstress, Uncategorized | Tags: anxiety, depression, health, human connection, life, loneliness, media addictdion, mental-health, storytelling 1 Comment
My mom called, “Stop playing on your computer and come for dinner!” I heard her, but I was way too into my game. It felt like I was actually inside it. I think I yelled “Yeah!” back, but I didn’t move.
A few seconds later, I was totally sucked into this awesome world where I was conquering other galaxies. My avatar was super powerful, and I was winning this crazy battle.
Then, all of a sudden, my mom came into my room and just turned off the computer. I was so mad. I was about to win! The real world around me felt boring and empty. I didn’t even feel hungry anymore. I didn’t say anything, I just wanted to go back to my game.
For some, the virtual world feels more real and exciting than the actual one. It can seem more vivid precisely because they have not yet tasted the full, multi-dimensional richness of real human connection, those moments when you feel seen, touched, and understood.
This theme comes vividly alive in my son Eliot Peper’s new novella, Ensorcelled. I am so proud of him. He has crafted a story in which a young boy, captured by the spell of the immersive digital world, discovers that real-life experiences carry far deeper meaning. I won’t give away the plot, but the story creates the experience, it doesn’t just tell it. It reminds us that meaning and belonging arise through genuine connection, not through screens. As Eliot writes, “Sometimes a story is the only thing that can save your life.” It’s a story everyone should read.
The effects of our immersive digital world
Our new world of digital media can take over the reality of actual experiences. It is no wonder that more young people feel stressed and have social anxiety when they have to make an actual telephone call instead of texting (Jin, 2025). They also experience a significant increase in anxiety and depression and feel more awkward initiating in-person social communication with others. The increase in mental health problems and social isolation affects predominantly those who are cellphone and social media natives; namely, those who started to use social media after Facebook was released in 2004 and the iPhone in 2007 (Braghieri et al., 2022).
Students who are most often on their phone whether streaming videos, scrolling, texting, watching YouTube, Instagram or TikTok, and more importantly responding to notifications from phones when they are socializing, report higher levels of loneliness, depression and anxiety as shown inf Figure 1 (Peper & Harvey 2018). They also report less positive feelings and energy when they communicate with each other online as compared to in person (Peper & Harvey, 2024).

Figure 1. The those with the highest phone use were the most lonely, depressed and anxious (Peper and Harvey, 2018).
Even students’ sexual activity has decreased in U.S. high-school from 2013 to 2023 and young adults (ages 18-44) from 2000-2018 (CDC, 2023; Ueda et al., 2020). Much of this may be due to the reality that adolescents have reduced face-to-face socializing (dating, parties, going out) while increasing their time on digital media (Twenge et al., 2019).
What to do
As a parent it often feels like a losing battle to pull your child, or even yourself, away from the intoxicating digital media, since the digital world is supercharged with AI-generated media. It is all aimed at capturing eyeballs (your attention and time), resulting reducing genuine human social connection. (Peper at al., 2020; Haidt, 2024). To change behavior is challenging and yet rewarding. If possible, implement the following (Peper at al., 2020; Twenge, 2025; Haidt, 2024):
- Create tech-free zones. Keep phones and devices out of bedrooms, the dinner table, and family gatherings. Make these spaces sacred for real connection.
- Avoid screens before bedtime. Turn off screens at least an hour before bed. Replace scrolling with quiet reflection, reading, or gentle stretching. Read or tell actual stories before bedtime.
- Explore why we turn to digital media. Before you open an app, ask: Why am I doing this? Am I bored, anxious, or avoiding something? Awareness shifts behavior.
- Provide unstructured time. Let yourself and your children be bored sometimes. Boredom sparks creativity, imagination, and self-discovery.
- Create shared experiences. Plan family activities that don’t involve screens—cooking, hiking, playing music, or simply talking. Real connection satisfies what digital media only mimics.
- Implement social support. Coordinate with other parents, friends, or colleagues to agree on digital limits. Shared norms make it easier to follow through.
- Model what you want your children to do. Children imitate what they see. When adults practice digital restraint, kids learn that real life matters more than screen life.
We have a choice.
We can set limits now and experience real emotional connection and growth or become captured, enslaved, and manipulated by the corporate creators, producers and sellers of media.
Read Ensorcelled. which uses storytelling, the traditional way to communicate concepts and knowledge. Read it, share it. It may change your child’s life and your own.

Available from
Signed copy by author: https://store.eliotpeper.com/products/ensorcelled
Paperback: https://www.amazon.com/Ensorcelled-Eliot-Peper/dp/1735016535/
Kindle: https://www.amazon.com/Ensorcelled-Eliot-Peper-ebook/dp/B0FLGQC3BS/
References
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022) http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
CDC. (2023). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). Youth Risk Behavior Survey: Data summary & trends report 2011–2021. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/data/yrbs/index.htm
Haidt, J. (2024). The Anxious Generation: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental Illness. New York: Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Anxious-Generation-Rewiring-Childhood-Epidemic/dp/0593655036
Jin, B. (2025). Avoidance and Anxiety About Phone Calls in Young Adults: The Role of Social Anxiety and Texting Controllability. Communication Reports, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/08934215.2025.2542562
Peper, E. & Harvey, R. (2018). Digital addiction: increased loneliness, depression, and anxiety. NeuroRegulation. 5(1),3–8. doi:10.15540/nr.5.1.3 5(1),3–8. http://www.neuroregulation.org/article/view/18189/11842
Peper, E. & Harvey, R. (2024). Smart phones affects social communication, vision, breathing, and mental and physical health: What to do! Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives, September 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/smartphone-affects-social-communication-vision-breathing-and-mental-and-physical-health-what-to-do/
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books.
Ueda, P., Mercer, C. H., Ghaznavi, C., & Herbenick, D. (2020). Trends in frequency of sexual activity and number of sexual partners among adults aged 18 to 44 years in the US, 2000–2018. JAMA Network Open, 3(6), e203833. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.3833
Twenge, J.M. (2025). 10 Rules for Raising Kids in a High-Tech World: How Parents Can Stop Smartphones, Social Media, and Gaming from Taking Over Their Children’s Lives. New York: Atria Books. https://www.amazon.com/Rules-Raising-Kids-High-Tech-World/dp/1668099993
Twenge, J. M., Spitzberg, B. H., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Less in-person social interaction with peers among U.S. adolescents in the 21st century and links to loneliness. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 36(6), 1892-1913. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407519836170
Cellphones affects social communication, vision, breathing, and health: What to do!
Posted: September 4, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, cellphone, computer, digital devices, educationj, ergonomics, health, laptops, Neck and shoulder discomfort, posture, screen fatigue, self-healing, stress management, techstress, Uncategorized, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: communication, myopia, pedestrian deaths, peripheral vision, text neck 7 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. & Harvey, R. (2024). Cell phones affects social communication, vision, breathing, and mental and physical health: What to do! TownsendLetter-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine,September 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/smartphone-affects-social-communication-vision-breathing-and-mental-and-physical-health-what-to-do/

Abstract
Smartphones are an indispensable part of our lives. Unfortunately too much of a ‘good thing’ regarding technology can work against us, leading to overuse, which in turn influences physical, mental and emotional development among current ‘Generation Z’ and ‘Millennial’ users (e.g., born 1997-2012, and 1981-1996, respectively). Compared to older technology users, Generation Z report more mental and physical health problems. Categories of mental health include attentional deficits, feelings of depression, anxiety social isolation and even suicidal thoughts, as along with physical health complaints such as sore neck and shoulders, eyestrain and increase in myopia. Long duration of looking downward at a smartphone affects not only eyestrain and posture but it also affects breathing which burden overall health. The article provides evidence and practices so show how technology over use and slouching posture may cause a decrease in social interactions and increases in emotional/mental and physical health symptoms such as eyestrain, myopia, and body aches and pains. Suggestions and strategies are provided for reversing the deleterious effects of slouched posture and shallow breathing to promote health.
We are part of an uncontrolled social experiment
We, as technology users, are all part of a social experiment in which companies examine which technologies and content increase profits for their investors (Mason, Zamparo, Marini, & Ameen, 2022). Unlike University research investigations which have a duty to warn of risks associated with their projects, we as participants in ‘profit-focused’ experiments are seldom fully and transparently informed of the physical, behavioral and psychological risks (Abbasi, Jagaveeran, Goh, & Tariq, 2021; Bhargava, & Velasquez, 2021). During university research participants must be told in plain language about the risks associated with the project (Huh-Yoo & Rader, 2020; Resnik, 2021). In contrast for-profit technology companies make it possible to hurriedly ‘click through’ terms-of-service and end-user-license-agreements, ‘giving away’ our rights to privacy, then selling our information to the highest bidder (Crain, 2021; Fainmesser, Galeotti, & Momot, 2023; Quach et al., 2022; Yang, 2022).
Although some people remain ignorant and or indifferent (e.g., “I don’t know and I don’t care”) about the use of our ‘data,’ an unintended consequence of becoming ‘dependent’ on technology overuse includes the strain on our mental and physical health (Abusamak, Jaber & Alrawashdeh, 2022; Padney et al., 2020). We have adapted new technologies and patterns of information input without asking the extent to which there were negative side effects (Akulwar-Tajane, Parmar, Naik & Shah, 2020; Elsayed, 2021). As modern employment shifted from predominantly blue-collar physical labor to white collar information processing jobs, people began sitting more throughout the day. Workers tended to look down to read and type. ‘Immobilized’ sitting for hours of time has increased as people spend time working on a computer/laptop and looking down at smartphones (Park, Kim & Lee, 2020). The average person now sits in a mostly immobilized posture 10.4 hours/day and modern adolescents spent more than two thirds of their waking time sitting and often looking down at their smartphones (Blodgett, et al., 2024; Arundell et al., 2019).
Smartphones are an indispensable part of our lives and is changing the physical and mental emotional development especially of Generation Z who were born between 1997-2012 (Haidt, 2024). They are the social media and smartphone natives (Childers & Boatwright, 2021). The smartphone is their personal computer and the gateway to communication including texting, searching, video chats, social media (Hernandez-de-Menendez, Escobar Díaz, & Morales-Menendez, 2020; Nichols, 2020; Schenarts, 2020; Szymkowiak et al., 2021). It has 100,000 times the processing power of the computer used to land the first astronauts on the moon on July 20, 1969 according to University of Nottingham’s computer scientist Graham Kendal (Dockrill, 2020). More than one half of US teens spend on the average more than 7 hours on daily screen time that includes watching streaming videos, gaming, social media and texting and their attention span has decreased from 150 seconds in 2004 to an average of 44 seconds in 2021 (Duarte, F., 2023; Mark, 2022, p. 96).
For Generation Z, social media use is done predominantly with smartphones while looking down. It has increased mental health problems such as attentional deficits, depression, anxiety suicidal thoughts, social isolation as well as decreased physical health (Haidt, 2024; Braghieri et al., 2023; Orsolini, Longo & Volpe, 2023; Satılmış, Cengız, & Güngörmüş, 2023; Muchacka-Cymerman, 2022; Fiebert, Kistner, Gissendanner & DaSilva, 2021; Mohan et al., 2021; Goodwin et al., 2020).
The shift in communication from synchronous (face-to-face) to asynchronous (texting) has transformed communications and mental health as it allows communication while being insulated from the other’s reactions (Lewis, 2024). The digital connection instead of face-to-face connection by looking down at the smart phone also has decreased the opportunity connect with other people and create new social connections, with three typical hypotheses examining the extent to which digital technologies (a) displace/ replace; (b) compete/ interfere with; and/or, (c) complement/ enhance in-person activities and relationships (Kushlev & Leitao, 2020).
As described in detail by Jonathan Haidt (2024), in his book, The Anxious Generation, the smartphone and the addictive nature of social media combined with the reduction in exercise, unsupervised play and childhood independence was been identified as the major factors in the decrease in mental health in your people (Gupta, 2023). This article focuses less on distraction such as attentional deficits, or dependency leading to tolerance, withdrawal and cravings (e.g., addiction-like symptoms) and focuses more on ‘dysregulation’ of body awareness (posture and breathing changes) and social communication while people are engaged with technology (Nawaz,Bhowmik, Linden & Mitchell, 2024).
The excessive use of the smartphones is associated with a significant reduction of physical activity and movement leading to a so-called sedentarism or increases of sitting disease (Chandrasekaran & Ganesan, 2021; Nakshine, Thute, Khatib, & Sarkar, 2022). Unbeknown to the smartphone users their posture changes, as they looks down at their screen, may also affect their mental and physical health (Aliberti, Invernizzi, Scurati & D’lsanto, 2020).
(1) Explore how looking at your smartphone affects you (adapted from: Peper, Harvey, & Rosegard, 2024)
For a minute, sit in your normal slouched position and look at your smartphone while intensely reading the text or searching social media. For the next minute sit tall and bring the cell phone in front of you so you can look straight ahead at it. Again, look at your smartphone while intensely reading the text or searching social media.
Compare how the posture affects you. Most likely, your experience is similar to the findings from students in a classroom observational study. Almost all experienced a reduction in peripheral awareness and breathed more shallowly when they slouched while looking at their cellphone.
Decreased peripheral awareness and increased shallow breathing that affects physical and mental health and performance. The students reported looking down position reduces the opportunity of creating new social connections. Looking down my also increases the risk for depression along with reduced cognitive performance during class (Peper et al., 2017; Peper et al., 2018).
(2) Explore how posture affects eye contact (adapted from the exercise shared by Ronald Swatzyna, 2023)[2]
Walk around your neighborhood or through campus either looking downwards or straight ahead for 30 minutes while counting the number of eye contacts you make.
Most likely, when looking straight ahead and around versus slouched and looking down you had the same experience as Ronald Swatzyna (2023), Licensed Clinical Social Worker. He observed that when he walked a three-mile loop around the park in a poor posture with shoulders forward in a head down position, and then reversed direction and walked in good posture with the shoulders back and the head level, he would make about five times as many eye contacts with a good posture compared to the poor posture.
Anecdotal observations, often repeated by many educators, suggest before the omnipresent smartphone, students would look around and talk to each other before a university class began. Now, when Generation Z students enter an in-person class, they sit down, look down at their phone and tend not to interact with other students.
(3) Experience the effect of face-to-face in-person communication
During the first class meeting, ask students to put their cellphones away, meet with three or four other students for a few minutes, and share a positive experience that happened to them last week as well as what they would like to learn in the class. After a few minutes, ask them to report how their energy and mood changed.
In our observational class study with 24 junior and senior college students in the in-person class and 54 students in the online zoom class, almost all report that that their energy and positive mood increased after they interacted with each other. The effects were more beneficial for the in-person small group sharing than the online breakout groups sharing on Zoom as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Change in subjective energy and mood after sharing experiences synchronously in small groups either in-person or online.
Without direction of a guided exercise to increase social connections, students tend to stay within their ‘smartphone bubble’ while looking down (Bochicchio et al., 2022). As a result, they appear to be more challenged to meet and interact with other people face-to-face or by phone as is reflected in the survey data that Generation Z is dating much less and more lonely than the previous generations (Cox et al., 2023).
What to do:
- Put the smartphone away so that you do not see it in social settings such as during meals or classes. This means that other people can be present with you and the activity of eating or learning.
- Do not permit smartphones in the classroom including universities unless it is required for a class assignment.
- In classrooms and in the corporate world, create activities that demands face-to-face synchronous communication.
- Unplug from the audio programs when walking and explore with your eyes what is going on around you.
(4) Looking down increases risk of injury and death
Looking down at a close screen reduces peripheral awareness and there by increases the risk of accidents and pedestrian deaths. Pedestrian deaths are up 69% since 2011 (Cova, 2024) and have consistently increased since the introduction of the iPhone in 2007 as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Increase in pedestrian death since the introduction of the iphone (data plotted from https://www.iihs.org/topics/fatality-statistics/detail/pedestrians)
In addition, the increase use of mobile phones is also associated with hand and wrist pain from overuse and with serious injuries such as falls and texting while driving due to lack of peripheral awareness. McLaughlin et al (2023) reports an increase in hand and wrist injuries as well serious injuries related to distracted behaviors, such as falls and texting while driving. The highest phone related injuries (lacerations) as reported from the 2011 to 2020 emergency room visits were people in the age range from 11–20 years followed by 21–30 years.
What to do:
- Do not walk while looking at your smartphone. Attend to the environment around you.
- Unplug from the audio podcasts when walking and explore with your eyes what is going on around you.
- Sit or stop walking when answering the smartphone to reduce the probability of an accident.
- For more pragmatic suggestions, see the book, TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics, by Peper, Harvey and Faass (2020).
(5) Looking at screens increases the risk of myopia
Looking at a near screen for long periods of time increases the risk of myopia (near sightedness) which means that distant vision is more blurry. Myopia has increased as children predominantly use computers or, smartphones with smaller screen at shorter distances. By predominantly focusing on nearby screens without allowing the eye to relax remodels the eyes structure. Consequently, myopia has increase in the U.S. from 25 percent in the early 1970s to nearly 42 percent three decades later (OHSU, 2022).
Looking only at nearby screens, our eyes converge and the ciliary muscles around the lens contract and remain contracted until the person looks at the far distance. The less opportunity there is to allow the eyes to look at distant vision, the more myopia occurs. in Singapore 80 per cent of young people aged 18 or below have nearsightedness and 20 % of the young people have high myopia as compared to 10 years ago (Singapore National Eye Centre, 2024). The increase in myopia is a significant concern since high myopia is associated with an increased risk of vision loss due to cataract, glaucoma, and myopic macular degeneration (MMD). MMD is rapidly increasing and one of the leading causes of blindness in East Asia that has one of the highest myopia rates in the world (Sankaridurg et al., 2021).
What to do:
- Every 20 minutes stop looking at the screen and look at the far distance to relax the eyes for 20 seconds.
- Do not allow young children access to cellphones or screens. Let them explore and play in nature where they naturally alternate looking at far and near objects.
- Implement the guided eye regenerating practices descrubed in the article, Resolve eyestrain and screen fatigue, by Peper (2021).
- Read Meir Schneider’s (2016) book, Vision for Life, for suggestions how to maintain and improve vision.
(6) Looking down increases tech neck discomfort
Looking down at the phone while standing or sitting strains the neck and shoulder muscles because of the prolonged forward head posture as illustrated in the YouTube video, Tech Stress Symptoms and Causes (DeWitt, 2018). Using a smartphone while standing or walking causes a significant increase in thoracic kyphosis and trunk (Betsch et al., 2021). When the head is erect, the muscle of the neck balance a weight of about 10 to 12 pounds or, approximately 5 kilograms; however, when the head is forward at 60 degrees looking at your cell phone the forces on the muscles are about 60 pound or more than 25 kilograms, as illustrated in Figure 4 (Hansraj, 2014).

Figure 4. The head forward position puts as much as sixty pounds of pressure on the neck muscles and spine (by permission from Dr. Kenneth Hansraj, 2014).
This process is graphically illustrated in the YouTube video, Text Neck Symptoms and Causes Video, produced by Veritas Health (2020).
What to do:
- Keep the phone in front of you so that you do not slouch down by having your elbow support on the table.
- Every ten minutes stretch, look up and roll your shoulders backwards.
- Wear a posture feedback device such as the UpRight Go 2 to remind you when you slouch to change posture and activity (Peper et al., 2019; Stuart, Godfrey & Mancini, 2022).
- Take Alexander Technique lessons to improve your posture (Cacciatore, Johnson, & Cohen, 2020; AmAT, 2024; STAT, 2024).
(7) Looking down increases negative memory recall and depression
In our previous research, Peper et al. (2017) have found that recalling hopeless, helpless, powerless, and defeated memories is easier when sitting in a slouched position than in an upright position. Recalling positive memories is much easier when sitting upright and looking slightly upward than sitting slouched position. If attempting to recall positive memories the brain has to work hard as indicated by an significantly higher amplitudes of beta2, beta3, and beta4 EEG (i.e., electroencephalograph) when sitting slouched then when sitting upright (Tsai et al., 2016).
Not only does the postural position affect memory recall, it also affects mental math under time-pressure performance. When students sit in a slouched position, they report that is much more difficult to do mental math (serial 7ths) than when in the upright position (Peper et al., 2018). The effect of posture is most powerful for the 70% of students who reported that they blanked out on exams, were anxious, or worried about class performance or math. For the 30% who reported no performance anxiety, posture had no significant effect. When students become aware of slouching thought posture feedback and then interrupt their slouching by sitting up, they report an increase in concentration, attention and school performance (Peper et al., 2024).
How we move and walk also affects our subjective energy. In most cases, when people sit for a long time, they report feeling more fatigue; however, if participants interrupt sitting with short movement practices they report becoming less fatigue and improved cognition (Wennberg et al., 2016). The change in subjective energy and mood depends upon the type of movement practice. Peper & Lin (2012) reported that when students were asked to walk in a slow slouching pattern looking down versus to walk quickly while skipping and looking up, they reported that skipping significantly increased their subjective energy and mood while the slouch walking decreased their energy. More importantly, student who had reported that they felt depressed during the last two years had their energy decrease significantly more when walking very slowly while slouched than those who did not report experiencing depression. Regardless of their self-reported history of depression, when students skipped, they all reported an increase in energy (Peper & Lin, 2012; Miragall et al., 2020).
What to do:
- Walk with a quick step while looking up and around.
- Wear a posture feedback device such as the UpRight Go 2 to remind you when you slouch to change posture and activity (Peper et al., 2019; Roggio et al., 2021).
- When sitting put a small pillow in the mid back so that you can sit more erect (for more suggestions, see the article by Peper et al., 2017a, Posture and mood: Implications and applications to therapy).
- Place photo and other objects that you like to look a slightly higher on your wall so that you automatically look up.
(8) Shallow breathing increases the risk for anxiety
When slouching we automatically tend to breathe slightly faster and more shallowly. This breathing pattern increases the risk for anxiety since it tends to decrease pCO2 (Feinstein et al., 2022; Meuret, Rosenfield, Millard & Ritz, 2023; Paulus, 2013; Smits et al., 2022; Van den Bergh et al., 2013). Sitting slouched also tends to inhibit abdominal expansion during the inhalation because the waist is constricted by clothing or a belt –sometimes labeled as ‘designer jean syndrome’ and may increase abdominal symptoms such as acid reflux and irritable bowel symptoms (Engeln & Zola, 2021; Peper et al., 2016; Peper et al., 2020). When students learn diaphragmatic breathing and practice diaphragmatic breathing whenever they shallow breathe or hold their breath, they report a significant decrease in anxiety, abdominal symptoms and even menstrual cramps (Haghighat et al., 2020; Peper et al., 2022; Peper et al., 2023).
What to do:
- Loosen your belt and waist constriction when sitting so that the abdomen can expand.
- Learn and practice effortless diaphragmatic breathing to reduce anxiety.
Conclusion
There are many topics related to postural health and technology overuse that were addressed in this article. Some topics are beyond the scope of the article, and therefore seen as limitations. These relate to diagnosis and treatment of attentional deficits, or dependency leading to tolerance, withdrawal and cravings (e.g., addiction-like symptoms), or of modeling relationships between factors that contribute to the increasing epidemic of mental and physical illness associated with smartphone use and social media, such as hypotheses examining the extent to which digital technologies (a) displace/ replace; (b) compete/ interfere with; and/or, (c) complement/ enhance in-person activities and relationships. Typical pharmaceutical ‘treat-the-symptom’ approaches for addressing ‘tech stress’ related to technology overuse includes prescribing ‘anxiolytics, pain-killers and muscle relaxants’ (Kazeminasab et al., 2022; Kim, Seo, Abdi, & Huh, 2020). Although not usually included in diagnosis and treatment strategies, suggesting improving posture and breathing practices can significantly affect mental and physical health. By changing posture and breathing patterns, individuals may have the option to optimize their health and well-being.
See the book, TechStress-How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey and Nancy Faass. Available from: https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X/

Explore the following blogs for more background and useful suggestions
References
Abbasi, G. A., Jagaveeran, M., Goh, Y. N., & Tariq, B. (2021). The impact of type of content use on smartphone addiction and academic performance: Physical activity as moderator. Technology in Society, 64, 101521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101521
Abusamak, M., Jaber, H. M., & Alrawashdeh, H. M. (2022). The effect of lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic on digital eye strain symptoms among the general population: a cross-sectional survey. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, 895517. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.895517
Akulwar-Tajane, I., Parmar, K. K., Naik, P. H., & Shah, A. V. (2020). Rethinking screen time during COVID-19: impact on psychological well-being in physiotherapy students. Int J Clin Exp Med Res, 4(4), 201-216. https://doi.org/10.26855/ijcemr.2020.10.014
Aliberti, S., Invernizzi, P. L., Scurati, R., & D’Isanto, T. (2020). Posture and skeletal muscle disorders of the neck due to the use of smartphones. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise , 15 (3proc), S586-S598. https://www.jhse.ua.es/article/view/2020-v15-n3-proc-posture-skeletal-muscle-disorders-neck-smartpho; https://air.unimi.it/retrieve/handle/2434/774436/1588570/HSE%20-%20Posture%20and%20skeletal%20muscle%20disorders.pdf
AmSAT. (2024). American Society for the Alexander Technique. Accessed July 27, 2024. https://alexandertechniqueusa.org/
Arundell, L., Salmon, J., Koorts, H. et al. (2019). Exploring when and how adolescents sit: cross-sectional analysis of activPAL-measured patterns of daily sitting time, bouts and breaks. BMC Public Health 19, 653. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-6960-5
Bhargava, V. R., & Velasquez, M. (2021). Ethics of the attention economy: The problem of social media addiction. Business Ethics Quarterly, 31(3), 321-359. https://doi.org/10.1017/beq.2020.32
Betsch, M., Kalbhen, K., Michalik, R., Schenker, H., Gatz, M., Quack, V., Siebers, H., Wild, M., & Migliorini, F. (2021). The influence of smartphone use on spinal posture – A laboratory study. Gait Posture, 85, 298-303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.02.018
Blodgett, J.M., Ahmadi, M.N., Atkin, A.J., Chastin, S., Chan, H-W., Suorsa, K., Bakker, E.A., Hettiarcachchi, P., Johansson, P.J., Sherar,L. B., Rangul, V., Pulsford, R.M…. (2024). ProPASS Collaboration , Device-measured physical activity and cardiometabolic health: the Prospective Physical Activity, Sitting, and Sleep (ProPASS) consortium, European Heart Journal, 45(6) 458–471, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad717
Bochicchio, V., Keith, K., Montero, I., Scandurra, C., & Winsler, A. (2022). Digital media inhibit self-regulatory private speech use in preschool children: The “digital bubble effect”. Cognitive Development, 62, 101180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogdev.2022.101180
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Cacciatore, T. W., Johnson, P. M., & Cohen, R. G. (2020). Potential mechanisms of the Alexander technique: Toward a comprehensive neurophysiological model. Kinesiology Review, 9(3), 199-213. https://doi.org/10.1123/kr.2020-0026
Chandrasekaran, B., & Ganesan, T. B. (2021). Sedentarism and chronic disease risk in COVID 19 lockdown–a scoping review. Scottish Medical Journal, 66(1), 3-10. https://doi.org/10.1177/0036933020946336
Childers, C., & Boatwright, B. (2021). Do digital natives recognize digital influence? Generational differences and understanding of social media influencers. Journal of Current Issues & Research in Advertising, 42(4), 425-442. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641734.2020.1830893
Cox, D.A., Hammond, K.E., & Gray, K. (2023). Generation Z and the Transformation of American Adolescence: How Gen Z’s Formative Experiences Shape Its Politics, Priorities, and Future. Survey Center of American Life, November 23, 2023. Accessed July 4, 2024. https://www.americansurveycenter.org/research/generation-z-and-the-transformation-of-american-adolescence-how-gen-zs-formative-experiences-shape-its-politics-priorities-and-future/
Crain, M. (2021). Profit over privacy: How surveillance advertising conquered the internet. U of Minnesota Press. https://www.amazon.com/Profit-over-Privacy-Surveillance-Advertising/dp/1517905044
Cova, E. (2024). Pedestrian fatalities at historic high. Smart Growth America (data from U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT). Accessed July 2, 2024. https://smartgrowthamerica.org/pedestrian-fatalities-at-historic-high/
Duarte, F. (2023). Average Screen Time for Teens (2024). Exploding Topics. Accessed July 5, 2024. https://explodingtopics.com/blog/screen-time-for-teens#average
DeWitt, D. (2018). How Does Text Neck Cause Pain? Spine-Health October 26, 2018. Accessed July 5, 2024. https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/neck-pain/how-does-text-neck-cause-pain
Dockrill, P. (2020). Your laptop charger is more powerful than Apollo11’s computer, says apple developer. Science Alert, Janural 12, 2020. Accessed July 4, 2024. https://www.sciencealert.com/apollo-11-s-computer-was-less-powerful-than-a-usb-c-charger-programmer-discovers
Elsayed, W. (2021). Covid-19 pandemic and its impact on increasing the risks of children’s addiction to electronic games from a social work perspective. Heliyon, 7(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08503
Engeln, R., & Zola, A. (2021). These boots weren’t made for walking: gendered discrepancies in wearing painful, restricting, or distracting clothing. Sex roles, 85(7), 463-480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-021-01230-9
Fainmesser, I. P., Galeotti, A., & Momot, R. (2023). Digital privacy. Management Science, 69(6), 3157-3173. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2022.4513
Feinstein, J. S., Gould, D., & Khalsa, S. S. (2022). Amygdala-driven apnea and the chemoreceptive origin of anxiety. Biological psychology, 170, 108305. https://10.1016/j.biopsycho.2022.108305
Fiebert, I., Kistner, F., Gissendanner, C., & DaSilva, C. (2021). Text neck: An adverse postural phenomenon. Work, 69(4), 1261-1270. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-213547
Goodwin, R. D., Weinberger, A. H., Kim, J. H., Wu. M., & Galea, S. (2020). Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008–2018: Rapid increases among young adults. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 130, 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.08.014
Gupta, N. (2023). Impact of smartphone overuse on health and well-being: review and recommendations for life-technology balance. Journal of Applied Sciences and Clinical Practice, 4(1), 4-12. https://doi.org/10.4103/jascp.jascp_40_22
Haghighat, F., Moradi, R., Rezaie, M., Yarahmadi, N., & Ghaffarnejad, F. (2020). Added Value of Diaphragm Myofascial Release on Forward Head Posture and Chest Expansion in Patients with Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-53279/v1
Haidt, J. (2024). The Anxious generation: How the great rewiring of childhood is causing an epidemic of mental illness. New York: Penguin Press. https://www.anxiousgeneration.com/book
Hansraj, K.K. (2014). Assessment of stresses in the cervical spine caused by posture and position of the head. Surg Technol Int. 25, 277-279. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25393825/
Hernandez-de-Menendez, M., Escobar Díaz, C. A., & Morales-Menendez, R. (2020). Educational experiences with Generation Z. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM), 14(3), 847-859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-020-00674-9
Huh-Yoo, J., & Rader, E. (2020). It’s the Wild, Wild West: Lessons learned from IRB members’ risk perceptions toward digital research data. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 4(CSCW1), 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1145/3392868
IIHS (2024). Fatality Facts 2022Pedestrians. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). Accessed July 2, 2024. https://www.iihs.org/topics/fatality-statistics/detail/pedestrians
Kazeminasab, S., Nejadghaderi, S. A., Amiri, P., Pourfathi, H., Araj-Khodaei, M., Sullman, M. J., … & Safiri, S. (2022). Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC musculoskeletal disorders, 23, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04957-4
Kim, K. H., Seo, H. J., Abdi, S., & Huh, B. (2020). All about pain pharmacology: what pain physicians should know. The Korean journal of pain, 33(2), 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2020.33.2.108
Kushlev, K., & Leitao, M. R. (2020). The effects of smartphones on well-being: Theoretical integration and research agenda. Current opinion in psychology, 36, 77-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.05.001
Lewis, H.R. (2024). Mechanical intelligence and counterfeit humanity. Harvard Magazine, 126(6), 38-40. https://www.harvardmagazine.com/2024/07/harry-lewis-computers-humanity#google_vignette
Mark, G. (2023). Attention Span: A Groundbreaking Way to Restore Balance, Happiness and Productivity. Toronto, Canada: Hanover Square Press. https://www.amazon.com/Attention-Span-Finding-Fighting-Distraction-ebook/dp/B09XBJ29W9
Mason, M. C., Zamparo, G., Marini, A., & Ameen, N. (2022). Glued to your phone? Generation Z’s smartphone addiction and online compulsive buying. Computers in Human Behavior, 136, 107404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107404
McLaughlin, W.M., Cravez, E., Caruana, D.L., Wilhelm, C., Modrak, M., & Gardner, E.C. (2023). An Epidemiological Study of Cell Phone-Related Injuries of the Hand and Wrist Reported in United States Emergency Departments From 2011 to 2020. J Hand Surg Glob, 5(2),184-188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2022.11.009
Meuret, A. E., Rosenfield, D., Millard, M. M., & Ritz, T. (2023). Biofeedback Training to Increase Pco2 in Asthma With Elevated Anxiety: A One-Stop Treatment of Both Conditions?. Psychosomatic medicine, 85(5), 440-448. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0000000000001188
Miragall, M., Borrego, A., Cebolla, A., Etchemendy, E., Navarro-Siurana, J., Llorens, R., … & Baños, R. M. (2020). Effect of an upright (vs. stooped) posture on interpretation bias, imagery, and emotions. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 68, 101560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101560
Mohan, A., Sen, P., Shah, C., Jain, E., & Jain, S. (2021). Prevalence and risk factor assessment of digital eye strain among children using online e-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: Digital eye strain among kids (DESK study-1). Indian journal of ophthalmology, 69(1), 140-144. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_2535_20
Muchacka-Cymerman, A. (2022). ‘I wonder why sometimes I feel so angry’ The associations between academic burnout, Facebook intrusion, phubbing, and aggressive behaviours during pandemic Covid 19. Polish Psychological Bulletin, 53(4). https://doi.org/10.24425/ppb.2022.143376
Nakshine, V. S., Thute, P., Khatib, M. N., & Sarkar, B. (2022). Increased screen time as a cause of declining physical, psychological health, and sleep patterns: a literary review. Cureus, 14(10). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.30051
Nawaz, S., Bhowmik, J., Linden, T., & Mitchell, M. (2024). Validation of a modified problematic use of mobile phones scale to examine problematic smartphone use and dependence. Heliyon, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24832
Nicholas, A. J. (2020). Preferred learning methods of generation Z. Faculty and Staff – Articles & Papers. Digital Commons @ Salve Regina. Salve Regina University. https://digitalcommons.salve.edu/fac_staff_pub/74
OHSU. (2022). Myopia on the rise, especially among children. Casey Eye Institute. Oregan Health and Science University. Accessed July 7, 2024. https://www.ohsu.edu/casey-eye-institute/myopia-rise-especially-among-children
Orsolini, L., Longo, G., & Volpe, U. (2023). The mediatory role of the boredom and loneliness dimensions in the development of problematic internet use. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054446
Pandey, R., Gaur, S., Kumar, R., Kotwal, N., & Kumar, S. (2020). Curse of the technology-computer related musculoskeletal disorders and vision syndrome: a study. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 8(2), 661. https://doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20200253
Park, J. C., Kim, S., & Lee, H. (2020). Effect of work-related smartphone use after work on job burnout: Moderating effect of social support and organizational politics. Computers in human behavior, 105, 106194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.106194
Paulus, M.P. (2013). The breathing conundrum-interoceptive sensitivity and anxiety. Depress Anxiety.30(4), 315-20. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22076
Peper, E. (2021). Resolve eyestrain and screen fatigue. Well Being Journal, 30(1), 24-28. https://wellbeingjournal.com/resolve-eyestrain-and-screen-fatigue/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N. & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Cuellar, Y., & Membrila, C. (2022). Reduce anxiety. NeuroRegulation, 9(2), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.9.2.91
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Mason, L. (2019). “Don’t slouch!” Improve health with posture feedback. Townsend Letter-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine, 436, 58-61. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337424599_Don%27t_slouch_Improve_health_with_posture_feedback
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Mason, L., & Lin, I.-M. (2018). Do better in math: How your body posture may change stereotype threat response. NeuroRegulation, 5(2), 67–74. http://dx.doi.org/10.15540/nr.5.2.67
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Rosegard, E. (2024). Increase attention, concentration and school performance with posture feedback. Biofeedback, 52(2). https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-52.02.07
Peper, E. & Lin, I-M. (2012). Increase or decrease depression-How body postures influence your energy level. Biofeedback, 40 (3), 126-130. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-40.3.01
Peper, E., Lin, I-M, & Harvey, R. (2017a). Posture and mood: Implications and applications to therapy. Biofeedback, 35(2), 42-48. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.03
Peper, E., Lin, I-M., Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback.45 (2), 36-41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E., Mason, L., Harvey, R., Wolski, L, & Torres, J. (2020). Can acid reflux be reduced by breathing? Townsend Letters-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine, 445/446, 44-47. https://www.townsendletter.com/article/445-6-acid-reflux-reduced-by-breathing/
Quach, S., Thaichon, P., Martin, K. D., Weaven, S., & Palmatier, R. W. (2022). Digital technologies: tensions in privacy and data. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 50(6), 1299-1323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-022-00845-y
Resnik, D. B. (2021). Standards of evidence for institutional review board decision-making. Accountability in research, 28(7), 428-455. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989621.2020.1855149
Roggio, F., Ravalli, S., Maugeri, G., Bianco, A., Palma, A., Di Rosa, M., & Musumeci, G. (2021). Technological advancements in the analysis of human motion and posture management through digital devices. World journal of orthopedics, 12(7), 467. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v12.i7.467
Sankaridurg, P., Tahhan, N., Kandel, H., Naduvilath, T., Zou, H., Frick,K.D., Marmamula, S., Friedman, D.S., Lamoureux, e. Keeffe, J. Walline, J.J., Fricke, T.R., Kovai, V., & Resnikoff, S. (2021) IMI Impact of Myopia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci, 62(5), 2. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.62.5.2
Satılmış, S. E., Cengız, R., & Güngörmüş, H. A. (2023). The relationship between university students’ perception of boredom in leisure time and internet addiction during social isolation process. Bağımlılık Dergisi, 24(2), 164-173. https://doi.org/10.51982/bagimli.1137559
Schenarts, P. J. (2020). Now arriving: surgical trainees from generation Z. Journal of surgical education, 77(2), 246-253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2019.09.004
Schneider, M. (2016). Vision for life. Ten Steps to Natural Eyesight Improvement. Berkeley: North Atlantic books. https://www.amazon.com/Vision-Life-Revised-Eyesight-Improvement/dp/1623170087
Singapore National Eye Centre. (2024). Severe myopia cases among children in Singapore almost doubled in past decade. CAN. Accessed July 4, 2024. https://www.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/myopia-children-cases-almost-double-glasses-eye-checks-4250266
Smits, J. A., Monfils, M. H., Otto, M. W., Telch, M. J., Shumake, J., Feinstein, J. S., … & Exposure Therapy Consortium. (2022). CO2 reactivity as a biomarker of exposure-based therapy non-response: study protocol. BMC psychiatry, 22(1), 831. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-022-04478-x
STAT (2024). The society of teachers of the Alexander Technique. Assessed July 27, 2024. https://alexandertechnique.co.uk/
Stuart, S., Godfrey, A., & Mancini, M. (2022). Staying UpRight in Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study of a novel wearable postural intervention. Gait & Posture, 91, 86-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.09.202
Swatzyna, R. (2023). Personal communications.
Szymkowiak, A., Melović, B., Dabić, M., Jeganathan, K., & Kundi, G. S. (2021). Information technology and Gen Z: The role of teachers, the internet, and technology in the education of young people. Technology in Society, 65, 101565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101565
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I. M.*(2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23-27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
Van den Bergh, O., Zaman, J., Bresseleers, J., Verhamme, P., Van Diest, I. (2013). Anxiety, pCO2 and cerebral blood flow, International Journal of Psychophysiology, 89 (1), 72-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.05.011
Veritas Health. (2020). Text Neck Symptoms and Causes Video. YouTube video, accessed August 29, 2024. https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/neck-pain/how-does-text-neck-cause-pain?source=YT
Wennberg, P., Boraxbekk, C., Wheeler, M., et al. (2016). Acute effects of breaking up prolonged sitting on fatigue and cognition: a pilot study. BMJ Open, 6, e009630. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009630
Yang, K. H. (2022). Selling consumer data for profit: Optimal market-segmentation design and its consequences. American Economic Review, 112(4), 1364-1393. https://www.aeaweb.org/articles/pdf/doi/10.1257/aer.20210616
[1] Correspondence should be addressed to: Erik Peper, Ph.D., Institute for Holistic Health Studies, Department of Recreation, Parks, Tourism and Holistic Health, San Francisco State University, 1600 Holloway Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94132 Email: epeper@sfsu.edu; web: www.biofeedbackhealth.org; blog: www.peperperspective.com
[2] I thank Ronald Swatzyna (2023), Licensed Clinical Social Worker for sharing this exercise with me. He discovered that a difference in the number of eye contacts depending how he walked. When he walked a 3.1 mile loop around the park in a poor posture- shoulders forward, head down position- and then reversed direction and walked in good posture with the shoulders back and the head level, that that he make about 5 times as many eye contacts with good posture compared to the poor posture. He observed that he make about five times as many eye contacts with good posture as compared to the poor posture.
Increase attention, concentration and school performance
Posted: August 15, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, digital devices, education, ergonomics, posture, screen fatigue, stress management, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: cellphone, concentration 5 CommentsReproduced from: Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Rosegard, E. (2024). Increase attention, concentration and school performance with posture feedback. Biofeedback, 52(2), 48-52. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-52.02.07

When I sit with good posture on my computer, I am significantly more engaged in what I’m doing. When I slouch on my computer I tend to procrastinate, go on my phone, and get distracted so it ends up taking much longer to do my work when my posture is bad.…I have ADHD and I struggle a lot with my mind wandering when I should be paying attention. Having good posture really helps me to lock in and focus.—22 year old male student.
Over the past two decades, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, and depression. ADHD rates have increased from 6% in 1997 to approximately 10% in 2018 (CDC, 2022). The rates of anxiety among 18–25 year-olds have also increased from 7.97% in 2008 to 14.66% in 2018 (Goodwin et al., 2020). Students are more distracted, stressed and exhausted (Hanscom, 2022; Hoyt et al., 2021). The more students are distracted, the lower their academic achievement (Feng et al., 2019). In our recent class survey of more than 100 junior and senior college students on the first day of class, 54% reported that they were tired and dreading the day when they woke up. When you are tired and stressed it is difficult to focus attention and have clarity of thought. Their self-report is similar to the mental health trends in the United States by age group in 2008–2019. Mental health of young people has significantly deteriorated over the last 15 years (Braghieri et al., 2021/2023).
The increase in psychological distress is most prevalent in people ages 18–29 and who were brought up with the cellphone (the iPhone was introduced in 2007) and social media. Now when students enter a class, they tend to sit down, look down at their cellphone while slouching, and they do not make contact with most other students unless instructed or reminded by the instructor. When instructed to talk to another student for less than 5 minutes (e.g., share something positive that happened to you this week), 93% of the students reported an increase in subjective energy and alertness (Peper, 2024).
As a group, students are social media and cell phone natives and thus have many distractions and stimuli to which they continuously respond. It is not surprising that the average attention span has decreased from 150 seconds in 2004 to 44 seconds in 2021 (Mark, 2023). More importantly, they now tend to sit in a slouched collapsed position, which facilitates access to hopeless, helpless, powerless and defeated thoughts and memories (Tsai et al., 2016; Peper et al., 2017) and reduces cognitive performance when performing mental math (Peper et al., 2018). Sitting slouched and looking down also reduces peripheral awareness and increases shallow thoracic breathing—a breathing pattern that increases the risk of anxiety. Experience this yourself.
For a minute, look at your cellphone while intensely reading the text or searching social media in the following two positions: sitting straight up and looking straight ahead at your cell phone or slouching and looking down at your cell phone, as shown in Figure 1. Most likely, your experience is similar to the findings from the classroom observational study in which half the students looked down and the other half looked straight ahead and then reversed their positions (Peper, unpublished). They then compared the subjective experience associated with the position. In the slouched position, most experienced a reduction in peripheral awareness and breathed more shallowly (see Figure 1).

Figure 1. Effect of slouching or looking straight ahead on vision and breathing.
The slouched position reduces social awareness and decreases awareness of external stimuli as illustrated in Steve Cutts’ superb animation, Mobile world (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wUW1wjlKvmY).
Given the constant stimulation, distractions and shortened attention span, it is more challenging to be calm and have clarity of mind when having to study or take an exam at school. As educators, we constantly explore ways to engage students and support their learning and especially share quick skills they can use to optimize performance (Peper& Wilson, 2021). In previous research, Harvey et al., 2020 showed that students who used posture feedback improved their health scores compared to the control group. The purpose of this paper is to share a 4-week class assignment by which numerous students reported an increase in attention, concentration, confidence, school performance and a decrease in stress.
Participants: 18 undergraduate students (7 males and 11 females, average age 22 [STDEV 2.2]) enrolled in an upper division class. As a report about an effort to improve the quality of a classroom activity, this report of findings was exempted from Institutional Review Board oversight.
Equipment: Wearable posture feedback device, UpRight Go 2, which the person wears on their neck and which provides vibratory feedback whenever they slouch, as shown in Figure 2. It is used in conjunction with the cellphone app that allows them to calibrate the feedback device.

Figure 2. Attachment of posture feedback device on neck or spine and the app to calibrate the device.
Procedure: Students attended the 3-hour weekly class that explored autogenic training, somatic awareness, psychobiology of stress, the role of posture, and the psychophysiology of respiration. The lectures included short experiential practices demonstrating the body-mind connections such as imagining a lemon to increase salivation, the effect of slouched versus erect posture on evoking positive/empowering or hopeless/helpless/powerless/defeated thoughts, and the effect of sequential 70% exhalation for 30 seconds on increasing anxiety (Tsai et al., 2016; Peper et al., 2017).
Each week for 4 weeks the students were assigned a self-practice that they would implement daily at home and record their experiences. At the end of the week, they reviewed their own log and summarized their own observations (benefits, difficulties). During the next class session, they met in small groups of 5 to 6 students to discuss their experiences and extract common themes.
The 4-week curriculum was sequenced as follows:
Week 1
- Lecture on the benefits/harms of posture with experiential practices (effect of slouching vs erect on access to hopeless/helpless/powerless thoughts versus optimistic and empowering thoughts; posture and arm strength (Peper, 2022).
- Homework assignments:
- Watch the great Ted Talk and one of the most viewed by Amy Cuddy (2013), “Your body language shapes who you are.”
- Keep a detailed log to monitor situations where they slouched and identify situations that were associated with slouching.
Week 2
- Lecture on psychophysiology and class discussion in which students shared their experiences of slouching; namely, what were the triggers, how it affected them and what they could do to change.
- Demonstration, explanation, and how to use the posture feedback device, UpRight Go 2.
- Homework assignment: Wear UpRight Go 2 during the day, use it in different settings (studying, walking, work), and keep a log. When it vibrates (slouching) observe what was going on and change your behavior such as when tired>get rest or do exercise; when depressed>change internal language; ergonomic issues>change the environment, posture>give yourself lower back support.
Week 3
- Class discussion on what to do when slouching is triggered by tiredness, negative and hopeless thoughts, ergonomics such as laptop placement and chair. Students meet in groups to share their experiences and what they did in response to the vibratory feedback.
- Homework assignment: Continue to wear the UpRight Go 2 during the day and keep a log.
Week 4
- Class discussion in groups of five students about their experiences of slouching, what to do and how it affects them.
- Homework assignment: Wear UpRight Go 2 during the day and keep a log. Submit a paper that describes their experience with the posture feedback from the UpRight Go 2 and fill out a short anonymous survey in which they rated their change in experience since using the posture feedback device on a scale from 3 (worse) to 0 (no change) to 3 (better) .
Results
All students reported that wearing the feedback device increased attention and concentration as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Amount of time using the UpRight Go 2:On the average the students used the device 4.8 days a week (STDEV 2.0) and 2.2 hours per day (STDEV 1.3).
Location of use:Although most students practiced sitting in front of their computer, they also reported using it while at work, playing pool or doing yoga and even while seeing a therapist.
Discussion
All the students reported that the posture feedback helped them to become more aware of slouching and when they then interrupted their slouching, they experienced an increase in energy and a decrease in stress. As a 21-year-old male student said: “I felt more engaged with whatever I was doing. I tend to … daydream and get distracted, but I experience much less of that when I sit with good posture.”
Many reported that it helped identify their emotions when they were feeling overwhelmed. Then they could sit up, shift their perspective, and many reported a decrease in back and neck pain as well as a decrease in tiredness. When participants wear non-invasive wearables that provide accurate feedback, they are often surprised what triggers are associated with feedback or how their performance improves when they respond to the feedback signal by changing their thoughts and behavior. This posture self-awareness project should be embedded in strategies that optimize the learning state as described by Peper & Wilson (2021).
To the students’ surprise, they were often unaware that they started to slouch, nor were they aware of how much this slouching was connected to their emotions, mental state or external factors. For example, one student reported that he wore the device while being in a therapy session. All of a sudden, it vibrated. At that moment, he realized that he was becoming anxious, although he and therapist were unaware. He then shared what happened with the therapist, and that helped the therapeutic process.
The benefits may not only be due to posture change but that the students became aware and interrupted their habitual pattern. This process is similar to that described by Charles Stroebel (1985) when he taught patients the Quieting Reflect that reduced numerous somatic symptoms ranging from headaches to hypertension.
The posture feedback intervention is both simple and challenging since it requires the participants to wear the device, identify factors that trigger the slouching, and interrupt their automatic patterns by changing posture and behavior whenever they felt the vibratory feedback. The awareness gave them the opportunity to change posture and thoughts. By shifting to an upright posture, they experienced that they could concentrate more and have increased energy. As a 19-year-old female student wrote: “My breathing was better and sitting in an upright position gave me more energy when doing tasks.”
Conclusion
We recommend that a 4-week home practice module that incorporates wearable posture feedback is offered to all students to enhance their well-being. With the posture feedback, participants can increase their awareness of slouching, identify situations that trigger slouch, and learn strategies to shift their posture, thoughts, emotions and external environment to optimize maintaining an empowered position. As a 20-year old male student reported, “The app helped me when I was feeling overwhelmed and then I would sit up. When I had it on, I did a lot of work. I was more concentrated.”
Explore the following blogs for more background and useful suggestions
References
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2023). Media and mental health (July 28, 2022). SSRN. (Original work published 2021). https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). ADHD through the years. Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Retrieved March 27, 2023, from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/timeline.html
Cuddy, A. (2012) Your body language may shape who you are. TED Talk. Retrieved March 16, 2024 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ks-_Mh1QhMc
Feng, S., Wong, Y. K., Wong, L. Y., & Hossain, L. (2019). The internet and Facebook usage on academic distraction of college students, Computers & Education, 134, 41-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j
Goodwin, R. D., Weinberger, A. H., Kim, J. H., Wu. M., & Galea, S. (2020). Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008–2018: Rapid increases among young adults. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 130, 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.08.014
Hanscom, N. (2022). Students, staff notice higher levels of student distraction this school year, reflect on potential causes. Retrieved September 28, 2023, from https://dgnomega.org/13162/feature/students-staff-notice-higher-levels-of-student-distraction-this-school-year-reflect-on-potential-causes/
Harvey, R., Peper, E., Mason, L., & Joy, M. (2020). Effect of posture feedback training on health. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 45(1), 59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-020-09457-0
Hoyt, L. T., Cohen, A. K., Dull, B., Castro, E. M., & Yazdani, N. (2021). “Constant stress has become the new normal”: Stress and anxiety inequalities among U.S. college students in the time of COVID-19. Journal of Adolescent Health. 68(2), 270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.10.030
Mark, G. (2023). Attention span: A groundbreaking way to restore balance, happiness and productivity. Hanover Square Press.
Peper, E. (2022, March 4). A breath of fresh air: Breathing and posture to optimize health. [Conference presentation at the 2nd Virtual Ergonomics Summit], Krista Burns, PhD. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PhV7Ulhs38s
Peper, E. (2024a). Change in energy and alertness after talking with each other versus looking at cellphone. Data collected from HH380 class fall 2023. Unpublished.
Peper, E. (2024b). Changes in vision and breathing when looking down or straight ahead at the cellphone. Data collected from HH380 class, Spring, 2024, San Francisco State University. Unpublished.
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Mason, L., & Lin, I.-M. (2018). Do better in math: How your body posture may change stereotype threat response. NeuroRegulation, 5(2), 67–74. http://dx.doi.org/10.15540/nr.5.2.67
Peper, E., Lin, I.-M., Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback.45(2), 36–41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E. & Wilson, V. (2021). Optimize the learning state: Techniques and habits. Biofeedback, 49(2), 46-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-49-2-04
Stroebel, C. F. (1985). QR: The Quieting Reflex. Berkley. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-Quieting-Charles-M-D-Stroebel/dp/0399126570
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I.-M.(2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23–27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 2- Exposure to neurotoxins and ultra-processed foods
Posted: June 30, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, CBT, digital devices, education, emotions, Evolutionary perspective, health, mindfulness, neurofeedback, Nutrition/diet, Uncategorized | Tags: ADHD, anxiety, depression, diet, glyphosate, herbicide, herbicites, mental-health, neurofeedback, pesticides, supplements', ultraprocessed foods, vitamins 4 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. & Shuford, J. (2024). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 2- Exposure to neurotoxins and ultra-processed foods. NeuroRegulation, 11(2), 219–228. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.11.2.219
Look at your hand and remember that every cell in your body including your brain is constructed out the foods you ingested. If you ingested inferior foods (raw materials to be built your physical structure), then the structure can only be inferior. If you use superior foods, you have the opportunity to create a superior structure which provides the opportunity for superior functioning. -Erik Peper
Summary
Mental health symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Autism, anxiety and depression have increased over the last 15 years. An additional risk factor that may affect mental and physical health is the foods we eat. Even though, our food may look and even taste the same as compared to 50 years ago, it contains herbicide and pesticide residues and often consist of ultra-processed foods. These foods (low in fiber, and high in sugar, animal fats and additives) are a significant part of the American diet and correlate with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in children with ADHD. Due to affluent malnutrition, many children are deficient in essential vitamins and minerals. We recommend that before beginning neurofeedback and behavioral treatments, diet and lifestyle are assessed (we call this Grandmother therapy assessment). If the diet appears low in organic foods and vegetable, high in ultra-processed foods and drinks, then nutritional deficiencies should be assessed. Then the next intervention step is to reduce the nutritional deficiencies and implement diet changes from ultra-processed foods to organic whole foods. Meta-analysis demonstrates that providing supplements such as Vitamin D, etc. and reducing simple carbohydrates and sugars and eating more vegetables, fruits and healthy fats during regular meals can ameliorate the symptoms and promote health.
The previous article and blog, Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms, pointed out how the changes in bonding, screen time and circadian rhythms affected physical and mental health (Peper, 2023a; Peper, 2023b). However, there are many additional factors including genetics that may contribute to the increase is ADHD, autism, anxiety, depression, allergies and autoimmune illnesses (Swatzyna et al., 2018). Genetics contribute to the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD); since, family, twin, and adoption studies have reported that ADHD runs in families (Durukan et al., 2018; Faraone & Larsson, 2019). Genetics is in most cases a risk factor that may or may not be expressed. The concept underlying this blog is that genetics loads the gun and environment and behavior pulls the trigger as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Interaction between Genetics and Environment
The pandemic only escalated trends that already was occurring. For example, Bommersbach et al (2023) analyzed the national trends in mental health-related emergency department visits among USA youth, 2011-2021. They observed that in the USA, Over the last 10 years, the proportion of pediatric ED visits for mental health reasons has approximately doubled, including a 5-fold increase in suicide-related visits. The mental health-related emergency department visits increased an average of 8% per year while suicide related visits increased 23.1% per year. Similar trends have reported by Braghieri et al (2022) from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Mental health trends in the United States by age group in 2008–2019. The data come from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Reproduced with permission from Braghieri, Luca and Levy, Ro’ee and Makarin, Alexey, Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022) https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
The trends reported from this data shows an increase in mental health illnesses for young people ages 18-23 and 24-29 and no changes for the older groups which could be correlated with the release of the first iPhone 2G on June 29, 2007. Thus, the Covid 19 pandemic and social isolation were not THE CAUSE but an escalation of an ongoing trend. For the younger population, the cellphone has become the vehicle for personal communication and social connections, many young people communicate more with texting than in-person and spent hours on screens which impact sleep (Peper, 2023a). At the same time, there are many other concurrent factors that may contributed to increase of ADHD, autism, anxiety, depression, allergies and autoimmune illnesses.
Without ever signing an informed consent form, we all have participated in lifestyle and environmental changes that differ from that evolved through the process of evolutionary natural selection and promoted survival of the human species. Many of those changes in lifestyle are driven by demand for short-term corporate profits over long-term health of the population. As exemplified by the significant increase in vaping in young people as a covert strategy to increase smoking (CDC, 2023) or the marketing of ultra-processed foods (van Tulleken, 2023).
This post focusses how pesticides and herbicides (exposure to neurotoxins) and changes in our food negatively affects our health and well-being and is may be another contributor to the increase risk for developing ADHD, autism, anxiety and depression. Although our food may look and even taste the same compared to 50 years ago, it is now different–more herbicide and pesticide residues and is often ultra-processed. lt contains lower levels of nutrients and vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin B2, Protein, Iron, Calcium and Phosphorus than 50 years ago (Davis et al, 2004; Fernandez-Cornejo et al., 2014). Non-organic foods as compared to organic foods may reduce longevity, fertility and survival after fasting (Chhabra et al., 2013).
Being poisoned by pesticide and herbicide residues in food
Almost all foods, except those labeled organic, are contaminated with pesticides and herbicides. The United States Department of Agriculture reported that “Pesticide use more than tripled between 1960 and 1981. Herbicide use increased more than tenfold (from 35 to 478 million pounds) as more U.S. farmers began to treat their fields with these chemicals” (Fernandez-Cornejo, et al., 2013, p 11). The increase in herbicides and pesticides is correlated with a significant deterioration of health in the United States (Swanson, et al., 2014 as illustrated in the following Figure 3.


Figure 3. Correlation between Disease Prevalence and Glyphosate Applications (reproduced with permission from Swanson et al., 2014.
Although correlation is not causation and similar relationships could be plotted by correlating consumption of ultra-refined foods, antibiotic use, decrease in physical activity, increase in computer, cellphone and social media use, etc.; nevertheless, it may suggest a causal relationship. Most pesticides and herbicides are neurotoxins and can accumulate in the person over time this could affect physical and mental health (Bjørling-Poulsen et al., 2008; Arab & Mostaflou, 2022). Even though the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has determined that the residual concentrations in foods are safe, their long-term safety has not been well established (Leoci & Ruberti, 2021). Other countries, especially those in which agribusiness has less power to affect legislation thorough lobbying, and utilize the research findings from studies not funded by agribusiness, have come to different conclusions…
For example, the USA allows much higher residues of pesticides such as, Round-Up, with a toxic ingredient glyphosate (0.7 parts per million) in foods than European countries (0.01 parts per million) (Wahab et al., 2022; EPA, 2023; European Commission, 2023) as is graphically illustrated in figure 4.

Figure 4: Percent of Crops Sprayed with Glyphosate and Allowable Glyphosate Levels in the USA versus the EU
The USA allows this higher exposure than the European Union even though about half of the human gut microbiota are vulnerable to glyphosate exposure (Puigbo et al., 2022). The negative effects most likely would be more harmful in a rapidly growing infant than for an adult. Most likely, some individuals are more vulnerable than others and are the “canary in mine.” They are the early indicators for possible low-level long-term harm. Research has shown that fetal exposure from the mother (gestational exposure) is associated with an increase in behaviors related to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders and executive function in the child when they are 7 to 12 years old (Sagiv et al., 2021). Also, organophosphate exposure is correlated with ADHD prevalence in children (Bouchard et al., 2010). We hypothesize this exposure is one of the co-factors that have contributed to the decrease in mental health of adults 18 to 29 years.
At the same time as herbicides and pesticides acreage usage has increased, ultra-processed food have become a major part of the American diet (van Tulleken, 2023). Eating a diet high in ultra-processed foods, low in fiber, high sugar, animal fats and additives has been associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in children with ADHD; namely, high consumption of sugar, candy, cola beverages, and non-cola soft drinks and low consumption of fatty fish were also associated with a higher prevalence of ADHD diagnosis (Ríos-Hernández et al., 2017).
In international studies, less nutritional eating behaviors were observed in ADHD risk group as compared to the normal group (Ryu et al., 2022). Artificial food colors and additives are also a public health issue and appear to increase the risk of hyperactive behavior (Arnold et al., 2012). In a randomized double-blinded, placebo controlled trial 3 and 8/9 year old children had an increase in hyperactive behavior for those whose diet included extra additives (McCann et al., 2007). The risk may occur during fetal development since poor prenatal maternal is a critical factor in the infants neurodevelopment and is associated with an increased probability of developing ADHD and autism (Zhong et al., 2020; Mengying et al., 2016).
Poor nutrition even affects your unborn grandchild
Poor nutrition not only affects the mother and the developing fetus through epigenetic changes, it also impacts the developing eggs in the ovary of the fetus that can become the future granddaughter (Wilson, 2015). At birth, the baby has all of her eggs. Thus, there is a scientific basis for the old wives tale that curses may skip a generation. Providing maternal support is even more important since it affects the new born and the future grandchild. The risk may even begin a generation earlier since the grandmother’s poor nutrition as well as stress causes epigenetic changes in the fetus eggs. Thus 50% of the chromosomes of the grandchild were impacted epigenetically by the mother’s and grandmother’s dietary and health status .
Highly processed foods
Highly refined foods have been processed to remove many of their nutrients. These foods includes white bread, white rice, pasta, and sugary drinks and almost all the fast foods and snacks. These foods are low in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they are high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and calories. In addition, additives may have been added to maximize taste and mouth feel and implicitly encourage addiction to these foods. A diet high in refined sugars and carbohydrates increases the risk of diabetes and can worsen the symptoms of ADHD, autism, depression, anxiety and increase metabolic disease and diabetes (Woo et al., 2014; Lustig, 2021; van Tulleken, 2023). Del-Ponte et al. (2019) noted that a diet high in refined sugar and saturated fat increased the risk of symptoms of ADHD, whereas a healthy diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits and vegetables, would protect against the symptoms.
Most likely, a diet of highly refined foods may cause blood sugar to spike and crash, which can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression and cognitive decline and often labeled as “hangryness” (the combination of anger and hunger) (Gomes et al., 2023; Barr et al., 2019). At the same time a Mediterranean diet improves depression significantly more than the befriending control group (Bayles et al., 2022). In addition, refined foods are low in essential vitamins and minerals as well as fiber. Not enough fiber can slow down digestion, affect the human biome, and makes it harder for the body to absorb nutrients. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can contribute to the symptoms of ADHD, autism, depression, and anxiety. Foods do impact our mental and physical health as illustrated by foods that tend to reduce depression (LaChance & Ramsey, 2018; MacInerney et al., 2017). By providing appropriate micronutrients such as minerals (Iron, Magnesium Zinc), vitamins (B6, B12, B9 and D), Omega 3s (Phosphatidylserine) and changing our diet, ADHD symptoms can be ameliorated.
Many children with ADHD, anxiety, depression are low on essential vitamins and minerals. For example, low levels of Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D may be caused by eating ultra-refined foods, fast foods, and drinking soft drink. At the same time, the children are sitting more in indoors in front of the screen and thereby have lower sun exposure that is necessary for the vitamin D production.
“Because of lifestyle changes and sunscreen use, about 42% of Americans are deficient in vitamin D. Among children between 1 to 11 years old, an estimated 15% have vitamin D deficiency. And researchers have found that 17% of adolescents and 32% of young adults were deficient in vitamin D.” (Porto and Abu-Alreesh, 2022).
Reduced sun exposure is even more relevant for people of color (and older people); since, their darker skin (increased melanin) protects them from ultraviolet light damage but at the same time reduces the skins production of vitamin D. Northern Europeans were aware of the link between sun exposure and vitamin D production. To prevent rickets (a disease caused by vitamin D deficiency) and reduce upper respiratory tract infections the children were given a tablespoon of cod liver oil to swallow (Linday, 2010). Cod liver oil, although not always liked by children, is more nutritious than just taking a Vitamin D supplements. It is a whole food and a rich source of vitamin A and D as well as containing a variety of Omega 3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (USDA, 2019).
Research studies suggest that ADHD can be ameliorated with nutrients, and herbs supplements (Henry & CNS, 2023). Table 1 summarizes some of the nutritional deficits observed and the reduction of ADHD symptoms when nutritional supplements were given (adapted from Henry, 2023; Henry & CNS, 2023).
| Nutritional deficits observed in people with ADHD | Decrease in ADHD symptoms with nutritional supplements |
| Vitamin D: In meta-analysis with a total number of 11,324 children, all eight trials reported significantly lower serum concentrations of 25(OH)D in patients diagnosed with ADHD compared to healthy controls. (Kotsi et al, 2019) | After 8 weeks children receiving vitamin D (50,000 IU/week) plus magnesium (6 mg/kg/day) showed a significant reduction in emotional problems as observed in a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Hemamy et al., 2021). |
| Iron: In meta-analysis lower serum ferritin was associated with ADHD in children (Wang et al., 2017) and the mean serum ferritin levels are lower in the children with ADHD than in the controls (Konofal et al., 2004). | After 12 weeks of supplementation with Iron (ferrous sulfate) in double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, clinical trials symptoms of in children with ADHD as compared to controls were reduced (Tohidi et al., 2021; Pongpitakdamrong et all, 2022). |
| Omega 3’s: Children with ADHD are more likely to be deficient in omega 3’s than children without ADHD (Chang et al., 2017). | Adding Omega-3 supplements to their diet resulted in an improvement in hyperactivity, impulsivity, learning, reading and short term memory as compared to controls in 16 randomized controlled trials including 1514 children and young adults with ADHD (Derbyshire, 2017) |
| Magnesium: In meta-analysis, subjects with ADHD had lower serum magnesium levels compared with to their healthy controls (Effatpahah et al., 2019) | 8 weeks of supplementation with Vitamin D and magnesium caused a significant decrease in children with conduct problems, social problems, and anxiety/shy scores (Hemamy et al., 2020). |
| Vitamin B2, B6, B9 and B12deficiency has been found in many patients with Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder (Landaas et al, 2016; Unal et al., 2019). | Vitamin therapy appears to reduce symptoms of ADHD and ASD (Poudineh et al., 2023; Unal et al., 2019). An 8 weeks supplementing with Vitamin B6 and magnesium decreased hyperactivity and hyperemotivity/aggressiveness. When supplementation was stopped, clinical symptoms of the disease reappeared in few weeks (Mousain-Bosc et al., 2006). |
Table 1. Examples of vitamin and mineral deficiencies associated with symptoms of ADHD and supplementation to reduction of ADHD symptoms.
Supplementation of vitamins and minerals in many cases consisted of more than one single vitamin or mineral. For an in-depth analysis and presentation, see the superb webinar by Henry & CNS (2023): https://divcom-events.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/divcom-events/recording/e29cefcae6c1103bb7f3aa780efee435/playback? (Henry & CNS, 2023).
Whole foods are more than the sum of individual parts (the identified individual constituents/nutrients). The process of digestion is much more complicated than ingesting simple foods with added vitamins or minerals. Digestion is the interaction of many food components (many of which we have not identified) which interact and affect the human biome. A simple added nutrient can help; however, eating whole organic foods it most likely be healthier. For example, whole-wheat flour is much more nutritious. Whole wheat is rich in vitamins B-1, B-3, B-5, riboflavin, folate well as fiber while refined white flour has been bleached and stripped of fiber and nutrients to which some added vitamins and iron are added.
Recommendation
When working with clients, follow Talib’s principles as outlined in Part 1 by Peper (2023) which suggests that to improve health first remove the unnatural which in this case are the ultra-processed foods, simple carbohydrates, exposure to pesticides and herbicides (Taleb, 2014). The approach is beneficial for prevention and treatment. This recommendation to optimize health is both very simple and very challenging. The simple recommendation is to eat only organic foods and as much variety as possible as recommended by Professor Michael Pollan in his books, Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and Food Rules (Pollan, 2006; Pollan, 2011).
Do not eat foods that contain herbicides and pesticide residues or are ultra-processed. Although organic foods especially vegetable and fruits are often much more expensive, you have choice: You can pay more now to optimize health or pay later to treat disease. Be safe and not sorry. This recommendation is similar to the quote, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food,” that has been attributed falsely since the 1970s to Hippocrates, the Greek founder of western medicine (5th Century, BC) (Cardenas, 2013).
There are many factors that interfere with implementing these suggestions; since, numerous people live in food deserts (no easy access to healthy unprocessed foods ) or food swamps (a plethora of fast food outlets) and 54 million Americans are food insecure (Ney, 2022). In addition, we and our parents have been programmed by the food industry advertising to eat the ultra- processed foods and may no longer know how to prepare healthy foods such as exemplified by a Mediterranean diet. Recent research by Bayles et al (2022) has shown that eating a Mediterranean diet improves depression significantly more than the befriending control group. In addition, highly processed foods and snacks are omnipresent, often addictive and more economical.
Remember that clients are individuals and almost all research findings are based upon group averages. Even when the data implies that a certain intervention is highly successful, there are always some participants for whom it is very beneficial and some for whom it is ineffective or even harmful. Thus, interventions need to be individualized for which there is usually only very limited data. In most cases, the original studies did not identify the characteristics of those who were highly successful or those who were unsuccessful. In addition, when working with specific individuals with ADHD, anxiety, depression, etc. there are multiple possible causes.
Before beginning specific clinical treatment such as neurofeedback and/or medication, we recommend the following:
- “Grandmother assessment” that includes and assessment of screen time, physical activity, outdoor sun exposure, sleep rhythm as outlined in Part 1 by Peper (2023). Then follow-up with a dietary assessment that investigates the prevalence of organic/non organic foods, ingestion of fast foods, ultra-processed foods, soft drinks, high simple carbohydrate and sugar, salty/sugary/fatty snacks, fruits, vegetables, and eating patterns (eating with family or by themselves in front of screens). Be sure to include an assessment of emotional reactivity and frequency of irritability and “hangryness”.
- If the assessment suggest low level of organic whole foods and predominance of ultra- refined foods, it may be possible that the person is deficient in vitamins and minerals. Recommend that the child is tested for the vitamin deficiencies. If vitamin deficiencies identified, recommend to supplement the diet with the necessary vitamins and mineral and encourage eating foods that naturally include these substances (Henry & CNS, 2023). If there is a high level of emotional reactivity and “hangryness,” a possible contributing factor could be hypoglycemic rebound from a high simple carbohydrate (sugar) intake or not eating breakfast combined with hyperventilation (Engel et al., 1947; Barr et al., 2019). Recommend eliminating simple carbohydrate breakfast and fast food snacks and substitute organic foods that include complex carbohydrates, protein, fats, vegetables and fruit. Be sure to eat breakfast.
- Implement “Grandmother Therapy”. Encourage the family and child to change their diet to eating a whide variety of organic foods (vegetables, fruits, some fish, meat and possibly dairy) and eliminate simple carbohydrates and sugars. This diet will tend to reduce nutritional deficits and may eliminate the need for supplements.
- Concurrent with the stabilization of the physiology begin psychophysiological treatment strategies such as neurofeedback biofeedback and cognitive behavior therapy.
Relevant blogs
Author Disclosure
Authors have no grants, financial interests, or conflicts to disclose.
References
Arnold, L, Lofthouse, N., & Hurt, E. (2012). Artificial food colors and attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms: conclusions to dye for. Neurotherapeutics, 9(3), 599-609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-012-0133-x
Arab, A. & Mostafalou, S. (2022). Neurotoxicity of pesticides in the context of CNS chronic diseases. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 32(12), 2718-2755. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2021.1987396
Barr, E.A., Peper, E., & Swatzyna, R.J. (2019). Slouched Posture, Sleep Deprivation, and Mood Disorders: Interconnection and Modulation by Theta Brain Waves. NeuroRegulation, 6(4), 181–189. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.4.181
Bayes. J., Schloss, J., Sibbritt, D. (2022). The effect of a Mediterranean diet on the symptoms of depression in young males (the “AMMEND: A Mediterranean Diet in MEN with Depression” study): a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 116(2), 572-580. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqac106
Bjørling-Poulsen, M., Andersen, H.R. & Grandjean, P. Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ Health 7, 50 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-7-50
Bommersbach, T.J., McKean, A.J., Olfson, M., Rhee, T.G. (2023). National Trends in Mental Health–Related Emergency Department Visits Among Youth, 2011-2020. JAMA, 329(17):1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.4809
Bouchard, M.F., Bellinger, D.C., Wright, R.O., & Weisskopf, M.G. (2010). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and urinary metabolites of organophosphate pesticides. Pediatrics, 125(6), e1270-7. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-3058
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Cardenas, D. (2013). Let not thy food be confused with thy medicine: The Hippocratic misquotation. e-Spen Journal, 8(6), 3260-3262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnme.2013.10.002
CDC, (2023). Quick Facts on the Risks of E-cigarettes for Kids, Teens, and Young Adults. CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 23, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/Quick-Facts-on-the-Risks-of-E-cigarettes-for-Kids-Teens-and-Young-Adults.html
Chang, J.C., Su, K.P., Mondelli, V. et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Youths with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials and Biological Studies. Neuropsychopharmacol. 43, 534–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.160
Chhabra, R., Kolli, S., & Bauer, J.H. (2013). Organically Grown Food Provides Health Benefits to Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE, 8(1): e52988. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052988
Davis, D. R., Epp, M. D., & Riordan, H. D. (2004). Changes in USDA food composition data for 43 garden crops, 1950 to 1999. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 23(6), 669-682. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719409
Derbyshire, E. (2017). Do Omega-3/6 Fatty Acids Have a Therapeutic Role in Children and Young People with ADHD? J Lipids. 6285218. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6285218
Del-Ponte, B., Quinte, G.C., Cruz, S., Grellert, M., & Santos, I. S. Dietary patterns and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 252, 160-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.04.061
Durukan, İ., Kara, K., Almbaideen, M., Karaman, D., & Gül, H. (2018). Alexithymia, depression and anxiety in parents of children with neurodevelopmental disorder: Comparative study of autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics International, 60(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.13510
Effatpanah, M., Rezaei, M., Effatpanah, H., Effatpanah, Z., Varkaneh, H.K., Mousavi. S.M., Fatahi, S., Rinaldi, G., & Hashemi, R. (2019). Magnesium status and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res, 274, 228-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.02.043
Engel, G.L., Ferris, E.B., & Logan, M. (1947). Hyperventilation; analysis of clinical symptomatology. Ann Intern Med, 27(5), 683-704. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-27-5-683
EPA. (2023). Glyphosate. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/glyphosate
European Commission. (2023). EU legislation on MRLs.Food Safety. Assessed April 1, 2023. https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/maximum-residue-levels/eu-legislation-mrls_en#:~:text=A%20general%20default%20MRL%20of,e.g.%20babies%2C%20children%20and%20vegetarians
Faraone, S.V. & Larsson, H. (2019). Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry, 24(4), 562-575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0
Fernandez-Cornejo, J. Nehring, R, Osteen, C., Wechsler, S., Martin, A., & Vialou, A. (2014). Pesticide use in the U.S. Agriculture: 21 Selected Crops, 1960-2008. Economic Information Bulletin Number 123, United State Department of Agriculture. https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/43854/46734_eib124.pdf
Gomes, G. N., Vidal, F. N., Khandpur. N., et al. (2023). Association Between Consumption of Ultraprocessed Foods and Cognitive Decline. JAMA Neurol, 80(2),142–150. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.4397
Hemamy, M., Heidari-Beni, M., Askari, G., Karahmadi, M., & Maracy, M. (2020). Effect of Vitamin D and Magnesium Supplementation on Behavior Problems in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Int J Prev Med, 11(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_546_17
Henry, K. (2023). An Integrative Medicine Approach to ADHD. Rupa Health. Accessed September 30, 2023. https://www.rupahealth.com/post/an-integrative-medicine-approach-to-adhd
Henry, K. & CNS, L.A. (2023). Natural treatments for ADHD. Webinar Presentation by IntegrativePractitioner.com and sponsored by Rupa Health, June 6, 2023 https://divcom-events.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/divcom-events/recording/e29cefcae6c1103bb7f3aa780efee435/playback?
Hemamy, M., Pahlavani, N., Amanollahi, A. et al. (2021). The effect of vitamin D and magnesium supplementation on the mental health status of attention-deficit hyperactive children: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr, 21, 178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-021-02631-1
Konofal, E., Lecendreux, M., Arnulf, I., & Mouren, M. (2004). Iron Deficiency in Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 158(12), 1113–1115. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.158.12.1113
Kotsi, E., Kotsi, E. & Perrea, D.N. (2019). Vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a meta-analysis. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord, 11, 221–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-018-0276-7
LaChance, L.R. & Ramsey, D. (2018). Antidepressant foods: An evidence-based nutrient profiling system for depression. World J Psychiatr, 8(3): 97-104. World J Psychiatr., 8(3): 97-104. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v8.i3.97
Landaas, E.T., Aarsland, T.I., Ulvik, A., Halmøy, A., Ueland. P.M., & Haavik, J. (20166). Vitamin levels in adults with ADHD. BJPsych Open, 2(6), 377-384. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjpo.bp.116.003491
Linday, L.A. (2010). Cod liver oil, young children, and upper respiratory tract infections. J Am Coll Nutr, 29(6), 559-62. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2010.10719894
Leoci, R. & Ruberti, M. (2021) Pesticides: An Overview of the Current Health Problems of Their Use. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 9, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2021.98001
Lustig, R.H. (2021). Metaboical: The lure and the lies of processed food, nutrition, and modern medicine. New York: Harper Wave. https://www.amazon.com/Metabolical-processed-poisons-people-planet/dp/1529350077
MacInerney, E. K., Swatzyna, R. J., Roark, A. J., Gonzalez, B. C., & Kozlowski, G. P. (2017). Breakfast choices influence brainwave activity: Single case study of a 12-year-old female. NeuroRegulation, 4(1), 56–62. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.4.1.56
McCann, D., Barrett, A., Cooper, A., Crumpler, D., Dalen, L., Grimshaw, K., et al. (2007). Food additives and hyperactive behavior in 3-year old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet, 370(9598), 1560-1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3
Mengying, L.I, Fallin, A, D., Riley,A., Landa, R., Walker, S.O., Silverstein, M., Caruso, D., et al. (2016). The Association of Maternal Obesity and Diabetes With Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities. Pediatrics, 137(2), e20152206. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-2206
Mousain-Bosc, M., Roche, M., Polge, A., Pradal-Prat, D., Rapin, J., & Bali, J.P. (2006). Improvement of neurobehavioral disorders in children supplemented with magnesium-vitamin B6. I. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders. Magnes Res. 19(1), 46-52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16846100/#:~:text=In%20almost%20all%20cases%20of,increase%20in%20Erc%2DMg%20values.
Ney, J. (2022). Food Deserts and Inequality. Social Policy Data Lab. Updated: Jan 24, 2022. Accessed September, 23, 2023. https://www.socialpolicylab.org/post/grow-your-blog-community
Peper, E. (2023a). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. the peperperspective July 2, 2023. Accessed august 8, 2024, https://peperperspective.com/2023/07/04/reflections-on-the-increase-in-autism-adhd-anxiety-and-depression-part-1-bonding-screen-time-and-circadian-rhythms/
Peper, E. (2023b). Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. NeuroRegulation, 10(2), 134-138. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.10.2.134
Pollan, M. (2006). Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals and Food Rules. New York Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Omnivores-Dilemma-Natural-History-Meals/dp/1594200823/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?_
Pollan, M. (2011). Food rules. New York Penguin Press. https://www.amazon.com/Food-Rules-Eaters-Michael-Pollan/dp/B00VSBILFG/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?
Pongpitakdamrong, A., Chirdkiatgumchai, V., Ruangdaraganon, N., Roongpraiwan, R., Sirachainan, N., Soongprasit, M., & Udomsubpayakul, U. (2022). Effect of Iron Supplementation in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Iron Deficiency: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, 43(2), 80-86., https://doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0000000000000993
Porto, A. & Abu-Alreesh, S. (2022). Vitamin D for babies, children & adolescents. Health Living. Healthychildren.org. Accessed September 24, 2023. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/nutrition/Pages/vitamin-d-on-the-double.aspx#
Poudineh, M., Parvin, S., Omidali, M., Nikzad, F., Mohammadyari, F., Sadeghi Poor Ranjbar, F., F., Nanbakhsh, S., & Olangian-Tehrani, S. (2023). The Effects of Vitamin Therapy on ASD and ADHD: A Narrative Review. CNS & Neurological Disorders – Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets – CNS & Neurological Disorders), (22), 5, 2023, 711-735. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527321666220517205813
Puigbò, P., Leino, L. I., Rainio, M. J., Saikkonen, K., Saloniemi, I., & Helander, M. (2022). Does Glyphosate Affect the Human Microbiota?. Life, 12(5), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050707
Ríos-Hernández, A., Alda, J.A., Farran-Codina, A., Ferreira-García, E., & Izquierdo-Pulido, M. (2017). The Mediterranean Diet and ADHD in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics, 139(2):e20162027. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2027
Ryu, S.A., Choi, Y.J., An, H., Kwon, H.J., Ha, M., Hong, Y.C., Hong, S.J., & Hwang, H.J. (2022). Associations between Dietary Intake and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Scores by Repeated Measurements in School-Age Children. Nutrients, 14(14), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142919
Sagiv, S.K., Kogut, K., Harley, K., Bradman, A., Morga, N., & Eskenazi, B. (2021). Gestational Exposure to Organophosphate Pesticides and Longitudinally Assessed Behaviors Related to Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Executive Function, American Journal of Epidemiology, 190(11), 2420–2431. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwab173
Swanson, N.L., Leu, A., Abrahamson, J., & Wallet, B. (2014). Genetically engineered crops, glyphosate and the deterioration of health in the United States of America. Journal of Organic Systems, 9(2), 6-17. https://www.organic-systems.org/journal/92/JOS_Volume-9_Number-2_Nov_2014-Swanson-et-al.pdf
Swatzyna, R. J., Boutros, N. N., Genovese, A. C., MacInerney, E. K., Roark, A. J., & Kozlowski, G. P. (2018). Electroencephalogram (EEG) for children with autism spectrum disorder: Evidential considerations for routine screening. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 28(5), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-018-1225-x
Taleb, N. N. (2014). Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder (Incerto). New York: Random House Publishing Group. https://www.amazon.com/Antifragile-Things-That-Disorder-Incerto/dp/0812979680/ref=tmm_pap_swatch_0
Tohidi, S., Bidabadi, E., Khosousi, M.J., Amoukhteh, M., Kousha, M., Mashouf, P., Shahraki, T. (2021). Effects of Iron Supplementation on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children Treated with Methylphenidate. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci, 19(4), 712-720. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2021.19.4.712
Unal, D. Çelebi, F., Bildik,H.N., Koyuncu, A., & Karahan, S. (2019). Vitamin B12 and haemoglobin levels may be related with ADHD symptoms: a study in Turkish children with ADHD, Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 29(4), 515-519. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750573.2018.1459005
USDA. (2019). Fish oil, cod liver. FoodData Central. USDA U.S> Department of Agriculture. Published 4/1/2019. Accessed September 24, 2024. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173577/nutrients
Van Tulleken, C. (2023). Ultra-Processed People. The Science Behind Food That Isn’t Food. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. https://www.amazon.com/Ultra-Processed-People-Science-Behind-Food/dp/1324036729/ref=asc_df_1324036729/?
Wahab, S., Muzammil, K., Nasir, N., Khan, M.S., Ahmad, M.F., Khalid, M., Ahmad, W., Dawria, A., Reddy, L.K.V., & Busayli, A.M. (2022). Advancement and New Trends in Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Food: A Comprehensive Review. Plants (Basel), 11(9), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091106
Wang. Y., Huang, L., Zhang, L., Qu, Y., & Mu, D. (2017). Iron Status in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One, 12(1):e0169145. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169145
Wilson, L. (2015). Mothers, beware: Your lifestyle choices will even affect your grandkids.
News Corp Australia Network. Accessed Jun 24, 2024. https://www.news.com.au/lifestyle/parenting/kids/mothers-beware-your-lifestyle-choices-will-even-affect-your-grandkids/news-story/3f326f457546cfb32af5c409f335fb56
Woo, H.D.,; Kim, D.W., Hong, Y.-S., Kim, Y.-M.,Seo, J.-H.,; Choe, B.M., Park, J.H.,; Kang, J.-W., Yoo, J.-H.,; Chueh, H.W., et al. (2014). Dietary Patterns in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Nutrients, 6, 1539-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6041539
Zhong, C., Tessing, J., Lee, B.K., Lyall, K. Maternal Dietary Factors and the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review of Existing Evidence. Autism Res,13(10),1634-1658. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2402
TechStress: Building Healthier Computer Habits
Posted: August 30, 2023 Filed under: ADHD, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, cognitive behavior therapy, computer, digital devices, education, emotions, ergonomics, Evolutionary perspective, Exercise/movement, health, laptops, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, screen fatigue, stress management, Uncategorized, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: cellphone, fatigue, gaming, mobile devices, screens 5 CommentsBy Erik Peper, PhD, BCB, Richard Harvey, PhD, and Nancy Faass, MSW, MPH
Adapted by the Well Being Journal, 32(4), 30-35. from the book, TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey, and Nancy Faass.

Every year, millions of office workers in the United States develop occupational injuries from poor computer habits—from carpal tunnel syndrome and tension headaches to repetitive strain injury, such as “mouse shoulder.” You’d think that an office job would be safer than factory work, but the truth is that many of these conditions are associated with a deskbound workstyle.
Back problems are not simply an issue for workers doing physical labor. Currently, the people at greatest risk of injury are those with a desk job earning over $70,000 annually. Globally, computer-related disorders continue to be on the rise. These conditions can affect people of all ages who spend long hours at a computer and digital devices.
In a large survey of high school students, eighty-five percent experienced tension or pain in their neck, shoulders, back, or wrists after working at the computer. We’re just not designed to sit at a computer all day.
Field of Ergonomics
For the past twenty years, teams of researchers all over the world have been evaluating workplace stress and computer injuries—and how to prevent them. As researchers in the fields of holistic health and ergonomics, we observe how people interact with technology. What makes our work unique is that we assess employees not only by interviewing them and observing behaviors, but also by monitoring physical responses.
Specifically, we measure muscle tension and breathing, in the moment, in real-time, while they work. To record shoulder pain, for example, we place small sensors over different muscles and painlessly measure the muscle tension using an EMG (electromyograph)—a device that is employed by physicians, physical therapists, and researchers. Using this device, we can also keep a record of their responses and compare their reactions over time to determine progress.
What we’ve learned is that people get into trouble if their muscles are held in tension for too long. Working at a computer, especially at a stationary desk, most people maintain low-level chronic tension for much of the day. Shallow, rapid breathing is also typical of fine motor tasks that require concentration, like data entry.
Muscle tension and breathing rate usually increase during data entry or typing without our awareness.
When these patterns are paired with psychological pressure due to office politics or job insecurity, the level of tension and the risk of fatigue, inflammation, pain, or injury increase. In most cases, people are totally unaware of the role that tension plays in injury. Of note, the absolute level of tension does not predict injury—rather, it is the absence of periodic rest breaks throughout the day that seems to correlate with future injuries.
Restbreaks
All of life is the alternation between movement and rest, inhaling and exhaling, sleeping and waking. Performing alternating tasks or different types of activities and movement is one way to interrupt the couch potato syndrome—honoring our evolutionary background.
Our research has confirmed what others have observed: that it’s important to be physically active, at least periodically, throughout the day. Alternating activity and rest recreate the pattern of our ancestors’ daily lives. When we alternate sedentary tasks with physical activity, and follow work with relaxation, we function much more efficiently. In short, move your body more.
Better Computer Habits: Alternate Periods of Rest and Activity
As mentioned earlier, our workstyle puts us out of sync with our genetic heritage. Whether hunting and gathering or building and harvesting, our ancestors alternated periods of inactivity with physical tasks that required walking, running, jumping, climbing, digging, lifting, and carrying, to name a few activities. In contrast, today many of us have a workstyle that is so immobile we may not even leave our desk for lunch.
As health researchers, we have had the chance to study workstyles all over the world. Back pain and strain injuries now affect a large proportion of office workers in the US and in high-tech firms worldwide. The vast majority of these jobs are sedentary, so one focus of the research is on how to achieve a more balanced way of working.
A recent study on exercise looked at blood flow to the brain. Researchers Carter and colleagues found that if people sit for four hours on the job, there’s a significant decrease in blood flow to the brain. However, if every thirty or forty minutes they get up and move around for just two minutes, then brain blood flow remains steady. The more often you interrupt sitting with movement, the better.
It may seem obvious that to stay healthy, it’s important to take breaks and be physically active from time to time throughout the day. Alternating activity and rest recreate the pattern of our ancestors’ daily lives. The goal is to alternate sedentary tasks with physical activity and follow work with relaxation. When we keep this type of balance going, most people find that they have more energy, are more productive, and can be more effective.
Genetics: We’re Hardwired Like Ancient Hunters

Despite a modern appearance, we carry the genes of our forebearers—for better and for worse. (Art courtesy of Peter Sis). Reproduced from Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books.
In the modern workplace, most of us find ourselves working indoors, in small office spaces, often sitting at a computer for hours at a time. In fact, the average Westerner spends more than nine hours per day sitting indoors, yet we’re still genetically programmed to be physically active and spend time outside in the sunlight most of the day, like the nomadic hunters and gatherers of forty thousand years ago.
Undeniably, we inherently conserve energy in order to heal and regenerate. This aspect of our genetic makeup also helps burn fewer calories when food is scarce. Hence the propensity for lack of movement and sedentary lifestyle (sitting disease).
In times of famine, the habit of sitting was essential because it reduced calorie expenditure, so it enabled our ancestors to survive. In a prehistoric world with a limited food supply, less movement meant fewer calories burned. Early humans became active when they needed to search for food or shelter. Today, in a world where food and shelter are abundant for most Westerners, there is no intrinsic drive to initiate movement.
It is also true that we have survived as a species by staying active. Chronic sitting is the opposite of our evolutionary pattern in which our ancestors alternated frequent movement while hunting or gathering food with periods of rest. Whether they were hunters or farmers, movement has always been an integral aspect of daily life. In contrast, working at the computer—maintaining static posture for hours on end—can increase fatigue, muscle tension, back strain, and poor circulation, putting us at risk of injury.
Quit a Sedentary Workstyle
Almost everyone is surprised by how quickly tension can build up in a muscle, and how painful it can become. For example, we tend to hover our hands over the keyboard without providing a chance for them to relax. Similarly, we may tighten some of the big muscles of our body, such as bracing or crossing our legs.
What’s needed is a chance to move a little every few minutes—we can achieve this right where we sit by developing the habit of microbreaks. Without regular movement, our muscles can become stiff and uncomfortable. When we don’t take breaks from static muscle tension, our muscles don’t have a chance to regenerate and circulate oxygen and necessary nutrients.
Build a variety of breaks into your workday:
- Vary work tasks
- Take microbreaks (brief breaks of less than thirty seconds)
- Take one-minute stretch breaks
- Fit in a moving break
Varying Work Tasks
You can boost physical activity at work by intentionally leaving your phone on the other side of the desk, situating the printer across the room, or using a sit-stand desk for part of the day. Even a few minutes away from the desk makes a difference, whether you are hand delivering documents, taking the long way to the bathroom, or pacing the room while on a call.
When you alternate the types of tasks and movement you do, using a different set of muscles, this interrupts the contractions of muscle fibers and allows them to relax and regenerate. Try any of these strategies:
- Alternate computer work with other activities, such as offering to do a coffee run
- Schedule walking meetings with coworkers
- Vary keyboarding and hand movements
Ultimately, vary your activities and movements as much as possible. By changing your posture and making sure you move, you’ll find that your circulation and your energy improve, and you’ll experience fewer aches and pains. In a short time, it usually becomes second nature to vary your activities throughout the day.
Experience It: “Mouse Shoulder” Test
You can test this simple mousing exercise at the computer or as a simulation. If you’re at the computer, sit erect with your hand on the mouse next to the keyboard. To simulate the exercise, sit with erect posture as if you were in front of your computer and hold a small object you can use to imitate mousing.
With the mouse (or a sham mouse), simulate drawing the letters of your name and your street address, right to left. Be sure each letter is very small (less than half an inch in height). After drawing each letter, click the mouse.
As part of the exercise, draw the letters and numbers as quickly as possible for ten to fifteen seconds. What did you observe? In almost all cases, you may note that you tightened your mousing shoulder and your neck, stiffened your trunk, and held your breath. All this occurred without awareness while performing the task. Over time, this type of muscle tension can contribute to discomfort, soreness, pain, or eventual injury.
Microbreaks
If you’ve developed an injury—or have chronic aches and pains—you’ll probably find split-second microbreaks invaluable. A microbreak means taking brief periods of time that last just a few seconds to relax the tension in your wrists, shoulders, and neck.
For example, when typing, simply letting your wrists drop to your lap for a few seconds will allow the circulation to return fully to help regenerate the muscles. The goal is to develop a habit that is part of your routine and becomes automatic, like driving a car. To make the habit of microbreaks practical, think about how you can build the breaks into your workstyle. That could mean a brief pause after you’ve completed a task, entered a column of data, or before starting typing out an assignment.
For frequent microbreaks, you don’t even need to get up—just drop your hands in your lap or shake them out, move your shoulders, and then resume work. Any type of shaking or wiggling movement is good for your circulation and kind of fun.
In general, a microbreak may be defined as lasting one to thirty seconds. A minibreak may last roughly thirty seconds to a few minutes, and longer large-movement breaks are usually greater than a few minutes. Popular microbreaks:
- Take a few deep breaths
- Pause to take a sip of water
- Rest your hands in your lap
- Stretch
- Let your arms drop to your sides
- Shake out your hands (wrists and fingers)
- Perform a quick shoulder or neck roll
Often, we don’t realize how much tension we’ve been carrying until we become more mindful of it. We can raise our awareness of excess tension—this is a learned skill—and train ourselves to let go of excess muscle tension. As we increase our awareness, we’re able to develop a new, more dynamic workstyle that better fits our goals and schedule.
One-Minute Stretch Breaks

We all benefit from a brief break, even with the best of posture (left). One approach is to totally release your muscles (middle). That release can be paired with a series of brief stretches (right). Reproduced from Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books.
The typical mini-stretch break lasts from thirty seconds to a few minutes, and ideally you want to take them several times per hour. Similar to microbreaks, mini-stretch breaks are especially important for people with an injury or those at risk of injury. Taking breaks is vital, especially if you have symptoms related to computer stress or whenever you’re working long hours at a sedentary job. To take a stretch break:
Begin with a big stretch, for example, by reaching high over your head then drop your hands in your lap or to your sides.
Look away from the monitor, staring at near and far objects, and blink several times. Straighten your back and stretch your entire backbone by lifting your head and neck gently, as if there were an invisible string attached to the crown of your head.
Stretch your mind and body. Sitting with your back straight and both feet flat on the floor, close your eyes and listen to the sounds around you, including the fan on the computer, footsteps in the hallway, or the sounds in the street.
Breathe in and out over ten seconds (breathe in for four or five seconds and breathe out for five or six seconds), making the exhale slightly longer than the inhale. Feel your jaw, mouth, and tongue muscles relax. Feel the back and bottom of the chair as your body breathes all around you. Envision someone in your mind’s eye who is kind and reassuring, who makes you feel safe and loved, and who can bring a smile to your face inwardly or outwardly.
Do a wiggling movement. When you take a one-minute break, wiggling exercises are fast and easy, and especially good for muscle tension or wrist pain. Wiggle all over—it feels good, and it’s also a great way to improve circulation.
Building Exercise and Movement into Every Day
Studies show that you get more benefit from exercising ten to twenty minutes, three times a day, than from exercising for thirty to sixty minutes once a day. The implication is that doing physical activities for even a few minutes can make a big difference.
Dunstan and colleagues have found that standing up three times an hour and then walking for just two minutes reduced blood sugar and insulin spikes by twenty-five percent.Fit in a Moving Break
Fit in a Moving Break
Once we become conscious of muscle tension, we may be able to reverse it simply by stepping away from the desk for a few minutes, and also by taking brief breaks more often. Explore ways to walk in the morning, during lunch break, or right after work. Ideally, you also want to get up and move around for about five minutes every hour.
Ultimately, research makes it clear that intermittent movement, such as brief, frequent stretching throughout the day or using the stairs rather than elevator, is more beneficial than cramming in a couple of hours at the gym on the weekend. This explains why small changes can have a big impact—it’s simply a matter of reminding yourself that it’s worth the effort.
Workstation Tips
Your ability to see the display and read the screen is key to reducing neck and eye strain. Here are a few strategic factors to remember:
Monitor height: Adjust the height of your monitor so the top is at eyebrow level, so you can look straight ahead at the screen.
Keyboard height: The keyboard height should be set so that your upper arms hang straight down while your elbows are bent at a 90-degree angle (like the letter L) with your forearms and wrists held horizontally.
Typeface and font size: For email, word processing, or web content, consider using a sans serif typeface. Fonts that have fewer curved lines and flourishes (serifs) tend to be more readable on screen.
Checking your vision: Many adults benefit from computer glasses to see the screen more clearly. Generally, we do not recommend reading glasses, bifocals, trifocals, and progressive lenses as they tend to allow clear vision at only one focal length. To see through the near-distance correction of the lens requires you to tilt your head back. Although progressive lenses allow you to see both close up and at a distance, the segment of the lens for each focal length is usually too narrow for working at the computer.
Wearing progressive lenses requires you to hold your head in a fixed position to be in focus. Yet you may be totally unaware that you are adapting your eye and head movements to sustain your focus. When that is the case, most people find that special computer glasses are a good solution.
Consider computer glasses if you must either bring your nose to the screen to read the text, wear reading glasses and find that their focal length is inappropriate for the monitor distance, wear bi- or trifocal glasses, or are older than forty.
Computer glasses correct for the appropriate focal distance to the computer. Typically, monitor distance is about twenty-three to twenty-eight inches, whereas reading glasses correct for a focal length of about fifteen inches. To determine your individual, specific focal length, ask a coworker to measure the distance from the monitor to your eyes. Provide this personal focal distance at the eye exam with your optometrist or ophthalmologist and request that your computer glasses be optimized for that distance.
Remembering to blink: As we focus on the screen, our blinking rate is significantly reduced. Develop the habit of blinking periodically: at the end of a paragraph, for example, or when sending an email.
Resting your eyes: Throughout the day, pause and focus on the far distance to relax your eyes. When looking at the screen, your eyes converge, which can cause eyestrain. Each time you look away and refocus, that allows your eyes to relax. It’s especially soothing to look at green objects such as a tree that can be seen through a window.
Minimizing glare: If the room is lit with artificial light, there may be glare from your light source if the light is right in front of you or right behind you, causing reflection on your screen. Reflection problems are minimized when light sources are at a 90-degree angle to the monitor (with the light coming from the side). The worst situations occur when the light source is either behind or in front of you.
An easy test is to turn off your monitor and look for reflections on the screen. Everything that you see on the monitor when it’s turned off is there when you’re working at the monitor. If there are bright reflections, they will interfere with your vision. Once you’ve identified the source of the glare, change the location of the reflected objects or light sources, or change the location of the monitor.
Contrast: Adjust the light contrast in the room so that it is neither too bright nor too dark. If the room is dark, turn on the lights. If it is too bright, close the blinds or turn off the lights. It is exhausting for your eyes to have to adapt from bright outdoor light to the lighting of your computer screen. You want the light intensity of the screen to be somewhat similar to that in the room where you’re working. You also do not want to look from your screen to a window lit by intense sunlight.
Don’t look down at phone: According to Kenneth Hansraj, MD, chief of spine surgery at New York Spine Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine, pressure on the spine increases from about ten pounds when you are holding your head erect, to sixty pounds of pressure when you are looking down. Bending forward to look at your phone, your head moves out of the line of gravity and is no longer balanced above your neck and spine. As the angle of the face-forward position increases, this intensifies strain on the neck muscles, nerves, and bones (the vertebrae).
The more you bend your neck, the greater the stress since the muscles must stretch farther and work harder to hold your head up against gravity. This same collapsed head-forward position when you are seated and using the phone repeats the neck and shoulder strain. Muscle strain, tension headaches, or neck pain can result from awkward posture with texting, craning over a tablet (sometimes referred to as the iPad neck), or spending long hours on a laptop.
A face-forward position puts as much as sixty pounds of pressure on the neck muscles and spine.
Repetitive strain of neck vertebrae (the cervical spine), in combination with poor posture, can trigger a neuromuscular syndrome sometimes diagnosed as thoracic outlet syndrome. According to researchers Sharan and colleagues, this syndrome can also result in chronic neck pain, depression, and anxiety.
When you notice negative changes in your mood or energy, or tension in your neck and shoulders, use that as a cue to arch your back and look upward. Think of a positive memory, take a mindful breath, wiggle, or shake out your shoulders if you’d like, and return to the task at hand.
Strengthen your core: If you find it difficult to maintain good posture, you may need to strengthen your core muscles. Fitness and sports that are beneficial for core strength include walking, sprinting, yoga, plank, swimming, and rowing. The most effective way to strengthen your core is through activities that you enjoy.
Final Thoughts
If these ideas resonate with you, consider lifestyle as the first step. We need to build dynamic physical activity into our lives, as well as the lives of our children. Being outside is usually an uplift, so choose to move your body in natural settings whenever possible, whatever form that takes. Being outside is the factor that adds an energetic dimension. Finally, share what you learn, and help others learn and grow from your experiences.
If you spend time in front of a computeror using a mobile device, read the book, TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. It provides practical, easy-to-use solutions for combating the stress and pain many of us experience due to technology use and overuse. The book offers extremely helpful tips for ergonomic use of technology, it
goes way beyond that, offering simple suggestions for improving muscle health that seem obvious once you read them, but would not have thought of yourself: “Why didn’t I think of that?” You will learn about the connection between posture and mood, reasons for and importance of movement breaks, specific movements you can easily perform at your desk, as well as healthier ways to utilize technology in your everyday life.
See the book, TechStress-How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey and Nancy Faass. Available from: https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X/

Additional resources
Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythm
Posted: July 4, 2023 Filed under: ADHD, behavior, computer, digital devices, education, emotions, Evolutionary perspective, health, laptops, screen fatigue, Uncategorized | Tags: anxiety, autism, bonding, circadian rhythms, depression, nature, still face experiment 10 Comments
Adapted from: Peper, E. Reflections on the increase in Autism, ADHD, anxiety and depression: Part 1-bonding, screen time, and circadian rhythms. NeuroRegulation,10(2), 134-138. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.10.2.134
Over the past two decades, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of autism, Attention-Deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, depression, and pediatric suicidal behavior. Autism rates have risen from 1 in 150 children in 2000 to 1 in 36 children in 2020 (CDC, 2023), while ADHD rates have increased from 6% in 1997 to approximately 10% in 2018 (CDC, 2022). The rates of anxiety among 18-25 year-olds have also increased from 7.97% in 2008 to 14.66% in 2018 (Goodwin et al., 2020), and depression rates for U.S. teens ages 12-17 have increased from 8% in 2007 to 13% in 2017 (Geiger & Davis, 2019; Walrave et al., 2022). Pediatric suicide attempts have also increased by 163% from 2009 to 2019 (Arakelyan et al., 2023), and during the COVID-19 pandemic, these rates have increased by more than 25% (WHO, 2022; Santomauro et al., 2021). In addition, the prevalence of these disorders has tripled for US adults during the pandemic compared to before (Ettman et al., 2020).
The rapid increase of these disorders is not solely due to improved diagnostic methods, genetic factors or the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic amplified pre-existing increasing trends. More likely, individuals who were at risk had their disorders triggered or amplified by harmful environmental and behavioral factors. Conceptually, Genetics loads the gun; epigenetics, behavior, and environment pull the trigger.
While behavioral strategies such as neurofeedback, Cognitive Behavior Therapy, biofeedback, meditation techniques, and pharmaceuticals can treat or ameliorate these disorders, the focus needs to be on risk reduction. In some ways, treatment can be likened to closing the barn doors after the horses have bolted.
Evolutionary perspective to reduce risk factors
Nassim Taleb (2012) in his book, Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder (Incerto), provides an evolutionary perspective and offers simple rules of health by reducing risk factors:
- Assume that anything that was not part of our evolutionary past is probably harmful.
- Remove the unnatural/unfamiliar (e.g. smoking/ e-cigarettes, sugar, digital media).
- We do not need evidence of harm to claim that a drug or an unnatural procedure is dangerous. If evidence of harm does not exist, it does not mean harm does not exist.
- Only resort to medical techniques when the health payoff is very large (to save a life), exceeds its potential harm, such as incontrovertibly needed surgery or life-saving medicine (penicillin).
- Avoid the iatrogenics and negative side effects of prescribed medication.
Writer and scholar Taleb’s suggestions are reminiscent of the perspective described by the educator Joseph C. Pearce (1993) in his book, Evolution’s End. Pearce argued that modern lifestyles have negatively affected the secure attachment and bonding between caregivers and infants. The lack of nurturing and responsive caregiving in early childhood may lead to long-term emotional and psychological problems. He points out that we have radically adapted behaviors that differ from those that evolved over thousands of generations and that allowed us to thrive and survive. In the last 100 years, babies have often been separated from their mothers at birth or early infancy by being put in a nursery or separate room, limited or no breastfeeding with the use of formula, exposure to television for entertainment, lack of exploratory play outdoors, and the absence of constant caretakers in high-stress and unsafe environments.
As Pearce pointed out, “If you want true learning, learning that involves the higher frontal lobes – the intellectual, creative brain – then again, the emotional environment must be positive and supportive. This is because at the first sign of anxiety the brain shifts its functions from the high, prefrontal lobes to the old defenses of the reptilian brain… These young people need audio-vocal communication, nurturing, play, body movement, eye contact, sweet sounds and close heart contact on a physical level” (Mercogliano & Debus, 1999).
To optimize health, eliminate or reduce those factors that have significantly changed or were not part of our evolutionary past. The proposed recommendations are based upon Talib’s perspective that anything that was not part of our evolutionary past is probably harmful; thus, it is wise to remove the unnatural/unfamiliar and adopt the precautionary principle, which states that if evidence of harm does not exist, it does not mean harm does not exist (Kriebel et al., 2010).
This article is the first of a three-part series. Part 1 focuses on increasing reciprocal communication between infant and caretaker, reducing screen time, and re-establishing circadian rhythms; Part 2 focuses on reducing exposure to neurotoxins, eliminating processed foods, and supporting the human biome; and Part 3 focuses on respiration and movement.
Part 1- Increase bonding, reduce screen time, and re-establish circadian rhythms
Increase bonding between infant and caretaker
Infants develop emotional communication through reciprocal interactions with their caregivers, during which the caregiver responds to the infant’s expressions. When this does not occur, it can be highly stressful and detrimental to the infant’s development. Unfortunately, more and more babies are emotionally and socially isolated while their caregivers are focussed on, and captured by, the content on their digital screens. Moreover, infants and toddlers are entertained (babysat) by cellphones and tablets instead of dynamically interacting with their caretakers. Screens do not respond to the child’s expressions; the screen content is programmed to capture the infant’s attention through rapid scene changes. Without reciprocal interaction, babies often become stressed, as shown by the research of developmental psychologist Professor Edward Tronick, who conducted the “Still Face” experiment (Tronick & Beeghly, 2011; Weinberg et al, 2008).
The “Still Face” experiment illustrated what happens when caregivers are not responding to infants’ communication. The caregivers were asked to remain still and unresponsive to their babies, resulting in the infants becoming increasingly distressed and disengaged from their surroundings. Not only does this apply to infants but also to children, teenagers and older individuals. Watch the short Still Face experiment, which illustrates what happens when the caretaker is not responding to the infant’s communication.
Recommendation. Do not use cellphone and digital media while being with an infant in the first two years of life. It is important for caregivers to limit their cellphone use and prioritize reciprocal interactions with their infants for healthy emotional and psychological development.
Reduce screen time (television, social media, streaming videos, gaming)[1]
From an evolutionary perspective, screen time is an entirely novel experience. Television, computers, and cellphones are modern technologies that have significantly impacted infants’ and young people’s development. To grow, infants, toddlers, and children require opportunities to explore the environment through movement, touch, and play with others, which is not possible with screens. Research has shown that excessive screen time can negatively affect children’s motor development, attention span, socialization skills, and contribute to obesity and other health problems (Hinkley et al., 2014; Carson et al., 2016; Mark, 2023).
When four-year-olds watch fast-paced videos, they exhibit reduced executive functions and impulse control, which may be a precursor for ADHD, compared to children who engage in activities such as drawing (Lillard & Peterson, 2011; Mark, 2023).
Furthermore, excessive screen time and time spent on social media are causal in increasing depression in young adults-–as was discovered when Facebook became available at selected universities. Researchers compared the mental health of students at similar universities where Facebook was or was not available and observed how the students’ mental health changed when Facebook became available (Braghieri et al., 2022). Their research showed that “College-wide access to Facebook led to an increase in severe depression by 7% and anxiety disorders by 20%. In total, the negative effect of Facebook on mental health appeared to be roughly 20% the magnitude of what is experienced by those who lose their job” (Walsh, 2022).
Exposure to digital media has also significantly reduced our attention span from 150 seconds in 2004 to an average of 44 seconds in 2021. The shortening of attention span may contribute to the rise of ADHD and anxiety (Mark, 2022, p. 96).
Recommendations: Reduce time spent on social media, gaming, mindlessly following one link after the other, or watching episode after episode of streaming videos. Instead, set time limits for screen use, turn off notifications, and prioritize in-person interactions with friends, family and colleagues while engaging in collaborative activities. Encourage children to participate in physical and social activities and to explore nature.
To achieve this, follow the guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendation on screen time (Council on Communications and Media, 2016), which suggest these limits on screen time for children of different age groups:
- Children under 18 months of age should avoid all screen time, except for video chatting with family and friends.
- Children aged 18-24 months should have limited screen time, and only when watched together with a caretaker.
- Children aged 2 to 5 years should have no more than one hour of screen time per day with parental supervision.
- For adolescents, screen and social media time should be limited to no more than an hour a day.
In our experience, when college students reduce their time spent on social media, streaming videos, and texting, they report that it is challenging; however, they then report an increase in well-being and performance over time (Peper et al., 2021). It may require more effort to provide children with actual experiential learning and entertainment than allowing them to use screens, but it is worthwhile. Having children perform activities and play outdoors–in a green nature environment–appears to reduce ADHD symptoms (Louv, 2008; Kuo & Taylor, 2004).
Reestablish circadian (daily) rhythms
Our natural biological and activity rhythms were regulated by natural light until the 19th century. It is hard to imagine not having light at night to read, to work on the computer, or to answer email. However, light not only illuminates, but also affects our physiology by regulating our biological rhythms. Exposure to light at night can interfere with the production of melatonin, which is essential for sleep. Insufficient sleep affects 30% of toddlers, preschoolers, and school-age children, as well as the majority of adolescents. The more media is consumed at bedtime, the more bedtime is delayed and total sleep time is reduced (Hale et al., 2018). Reduced sleep is a contributing factor to increased ADHD symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity (Cassoff et al., 2012).
Recommendations: Support the circadian rhythms. Avoid screen time one hour before bedtime. This will reduce exposure to blue light and reduce sympathetic arousal triggered by the content on the screen or reactions to social media and emails. Sleep in total darkness, and establish a regular bedtime and waking time to avoid “social jetlag,” which can negatively affect health and performance (Caliandro et al., 2021). Implement sleep hygiene strategies such as developing a bedtime ritual to improve sleep quality (Stager et al., 2023; Suni, 2023). Thus, go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, including weekends. Avoid large meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime. Consistency is key to success.
Conclusion
To optimize health, eliminate or reduce those factors that have significantly changed or were not part of our evolutionary past, and explore strategies that support behaviors that have allowed the human being to thrive and survive. Improve clinical outcomes and optimize health by enhancing reciprocal communication interactions, reducing screen time and re-establishing the circadian rhythm.
References
Arakelyan, M., Freyleue, S., Avula, D., McLaren, J.L., O’Malley, A.J., & Leyenaar, J.K. (2023). Pediatric Mental Health Hospitalizations at Acute Care Hospitals in the US, 2009-2019. JAMA, 329(12), 1000–1011. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.1992
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Caliandro, R., Streng, A.A., van Kerkhof, L.W.M., van der Horst, G.T.J., & Chaves, I. (2021). Social Jetlag and Related Risks for Human Health: A Timely Review. Nutrients, 13(12), 4543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124543
Carson, V., Tremblay, M.S., Chaput, J.P., & Chastin, S.F. (2016). Associations between sleep duration, sedentary time, physical activity, and health indicators among Canadian children and youth using compositional analyses. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab, 41(6 Suppl 3), S294-302. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2016-0026
Cassoff, J., Wiebe, S.T., & Gruber, R. (2012). Sleep patterns and the risk for ADHD: a review. Nat Sci Sleep, 4, 73-80. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSS.S31269
CDC. (2022). Attention-Deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): ADHD through the years. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Assessed March 27, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/timeline.html
CDC. (2023). Data & Statistics on Autism Spectrum Disorder. CDC Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Assessed March 25, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html
Council on Communications and Media. (2016). Media and young minds. Pediatrics, 138(5), e20162591. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2591
Ettman, C.K., Abdalla, S.M., Cohen, G.H., Sampson, L., Vivier, P.M.,& Galea, S. (2020), Prevalence of Depression Symptoms in US Adults Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open, 3(9):e2019686. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19686
Geiger, A.W. & Davis, L. (2019). A growing number of American teenagers-particularly girls-are facing depression. Pew Research Center. Accessed March 28, 2023.
Goodwin, R.D., Weinberger, A.H., Kim, J.H., Wu. M., & Galea, S. (2020). Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008-2018: Rapid increases among young adults. J Psychiatr Res. 130, 441-446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.08.014
Hale, L., Kirschen, G/W., LeBourgeois, M.K., Gradisar, M., Garrison, M.M., Montgomery-Downs, H., Kirschen, H., McHale, S.M., Chang, A.M., & Buxton, O.M. (2018). Youth Screen Media Habits and Sleep: Sleep-Friendly Screen Behavior Recommendations for Clinicians, Educators, and Parents. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am, 27(2),229-245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2017.11.014
Hinkley, T., Verbestel, V., Ahrens, W., Lissner, L., Molnár, D., Moreno, L.A., Pigeot, I., Pohlabeln, H., Reisch, L.A., Russo, P., Veidebaum, T., Tornaritis, M., Williams, G., De Henauw, S., De Bourdeaudhuij, I; IDEFICS Consortium. (2014). Early childhood electronic media use as a predictor of poorer well-being: a prospective cohort study. JAMA Pediatr,. May;168(5):485-92. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.94
Kriebel, D., Tickner, J., Epstein, P., Lemons, J., Levins, R., Loechler, E.L., Quinn, M., Rudel, R., Schettler, T., Stoto, M. (2001). The precautionary principle in environmental science. Environ Health Perspect, 109(9):871-6. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.01109871
Kuo. F.E. & Taylor, A.F. (2004). A potential natural treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: evidence from a national study. Am J Public Health. 94(9),1580-6. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.94.9.1580
Lillard, A.S. & Peterson, J. The immediate impact of different types of television on young children’s executive function. Pediatrics, 128(4), 644-9. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-1919
Louv, R. (2008). Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children from Nature-Deficit Disorder. Algonquin Books. Chapel Hill, NC: Algonquin Books
Mark, G. (2023). Attention Span: A Groundbreaking Way to Restore Balance, Happiness and Productivity. Toronto, Canada: Hanover Square Press.
Mercogliano, C. & Debus, K. (1999). Nurturing Heart-Brain Development Starting With Infants 1999 Interview with Joseph Chilton Pearce. Journal of Family Life, 5(1). https://www.michaelmount.co.za/nurturing-heart-brain-development-starting-with-infants-1999-interview-with-joseph-chilton-pearce/
Pearce, J.C. (1993). Evolutions’s End. New York: HarperOne.
Peper, E., Wilson, V., Martin, M., Rosegard, E., & Harvey, R. (2021). Avoid Zoom fatigue, be present and learn. NeuroRegulation, 8(1), 47–56. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.8.1.47
Santomauro, D.F., Mantilla Herrera, A.M., Shadid, J., Zheng, P., Ashbaugh, C., Pigott, D.M., Abbafati, C., Adolph, C., …. (2021). Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet, 398(103121700-1712., https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02143-7
Stager, L.M., Caldwell, A., Bates, C., & Laroche, H. (2023). Helping kids get the sleep they need. Society of Behavioral Medicine. Accessed March 29, 2023 https://www.sbm.org/healthy-living/helping-kids-get-the-sleep-they-need?gclid=Cj0KCQjww4-hBhCtARIsAC9gR3ZM7v9VSvqaFkLnceBOH1jIP8idiBIyQcqquk5y_RZaNdUjAR9Wpx4aAhTBEALw_wcB
Suni, E. (2023). Sleep hygiene- What it is, why it matters, and how to revamp your habits to get better nightly sleep. Sleep Foundation. Accessed March 29, 2023. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-hygiene
Taleb, N. N. (2012). Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder (Incerto) Random House Publishing Group. (Kindle Locations 5906-5908).
Tronick, E. & Beeghly, M. (2011).Infants’ meaning-making and the development of mental health problems. Am Psychol, 66(2),107-19. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021631
Walrave, R., Beerten, S.G., Mamouris, P. et al. Trends in the epidemiology of depression and comorbidities from 2000 to 2019 in Belgium. BMC Prim. Care 23, 163 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-022-01769-w
Walsh, D. (2022 September 14). Study: Social media use linked to decline in mental health. MIT Management Ideas Made to Matter. Accessed March 28, 2023. https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/study-social-media-use-linked-to-decline-mental-health#:~:text=College%2Dwide%20access%20to%20Facebook,with%20either%20psychotherapy%20or%20antidepressants
Weinberg, M.K., Beeghly, M., Olson, K.L., & Tronick, E. (2008). A Still-face Paradigm for Young Children: 2½ Year-olds’ Reactions to Maternal Unavailability during the Still-face. J Dev Process, 3(1):4-22. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22384309/
WHO (2022). COVID-19 pandemic triggers 25% increase in prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide. World Health Organization. Assessed march 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/news/item/02-03-2022-covid-19-pandemic-triggers-25-increase-in-prevalence-of-anxiety-and-depression-worldwide
[1] The critique of social media does not imply that there are no benefits. If used judiciously, it is a powerful tool to connect with family and friends or access information.



