Breathe Away Menstrual Pain- A Simple Practice That Brings Relief *
Posted: November 22, 2025 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, cognitive behavior therapy, education, emotions, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: dysmenorrhea, health, meditation, menstrual cramps, mental-health, mindfulness, wellness 2 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. Harvey, R., Chen, & Heinz, N. (2025). Practicing diaphragmatic breathing reduces menstrual symptoms both during in-person and synchronous online teaching. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, Published online: 25 October 2025. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09745-7
“Once again, the pain starts—sharp, deep, and overwhelming—until all I can do is curl up and wait for it to pass. There’s no way I can function like this, so I call in sick. The meds take the edge off, but they don’t really fix anything—they just mask it for a little while. I usually don’t tell anyone it’s menstrual pain; I just say I’m not feeling well. For the next couple of days, I’m completely drained, struggling just to make it through.
Many women experience discomfort during menstruation, from mild cramps to intense, even disabling pain. When the pain becomes severe, the body instinctively responds by slowing down—encouraging rest, curling up to protect the abdomen, and often reaching for medication in hopes of relief. For most, the symptoms ease within a day or two, occasionally stretching into three, before the body gradually returns to balance.
Another helpful approach is to practice slow abdominal breathing, guided by a breathing app FlowMD. In our study led by Mattia Nesse, PhD, in Italy, the response of one 22-year-old woman illustrated the power of this simple practice.
“Last night my period started, so I was a bit discouraged because I knew I’d get stomach pain, etc. On the other hand, I said, “Okay, let’s see if the breathing works,” and it was like magic — incredible. I’ll need to try it more times to understand whether it consistently has the same effect, but right now it truly felt magical. Just 3 minutes of deep breathing with the app were enough, and I’m not saying I don’t feel any pain anymore, but it has decreased a lot, so thank you! Thank you again for this tool… I’m really happy!”
The Silent Burden of Menstrual Pain
Menstrual pain, or dysmenorrhea, affects most women at some point in their lives — often silently. For many, the monthly cycle brings not only physical discomfort but also shame, fatigue, and interruptions to work or school. It is one of the leading causes of absenteeism and reduced productivity worldwide (Itani et al., 2022; Thakur & Pathania, 2022). In addition, the estimated health cost ranged from US $1367 to US$ 7043 per year (Huang et al., 2021). Yet, despite its prevalence, most women are never taught how to use their own physiology to ease these symptoms.
The Study (Peper et al, 2025)
Seventy-five university women participated across two upper-division Holistic Health courses. Forty-nine practiced 30 minutes per day of breathing and relaxation over five weeks as well as practicing the moment they anticipated or felt discomfort; twenty-six served as a comparison group without a specific daily self-care routine. Students rated change in menstrual symptoms on a scale from –5 (“much worse”) to +5 (“much better”). For the detailed steps in training, see the blog: https://peperperspective.com/2023/04/22/hope-for-menstrual-cramps-dysmenorrhea-with-breathing/ (Peper et al., 2023).
What changed
The results were striking. Women who practiced breathing and relaxation showed significant decrease in menstrual symptoms compared to the non-intervention group (p = 0.0008) as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Decrease in menstrual symptoms as compared to the control group after implementing slow diaphragmatic breathing.
Why does breathing and posture change have a beneficial effect?
When you stay curled up, your abdomen becomes compressed, leaving little room for the lower belly to relax or for the diaphragm to move freely. The result? Tension builds, and pain often increases.
To reverse this, create space for relaxation. Gently loosen your waist and let your abdomen expand as you inhale. Uncurl your body—lengthen your spine and open your chest, as shown in Figure 2. With each easy breath, you invite calm and allow your body to shift from tension to ease.
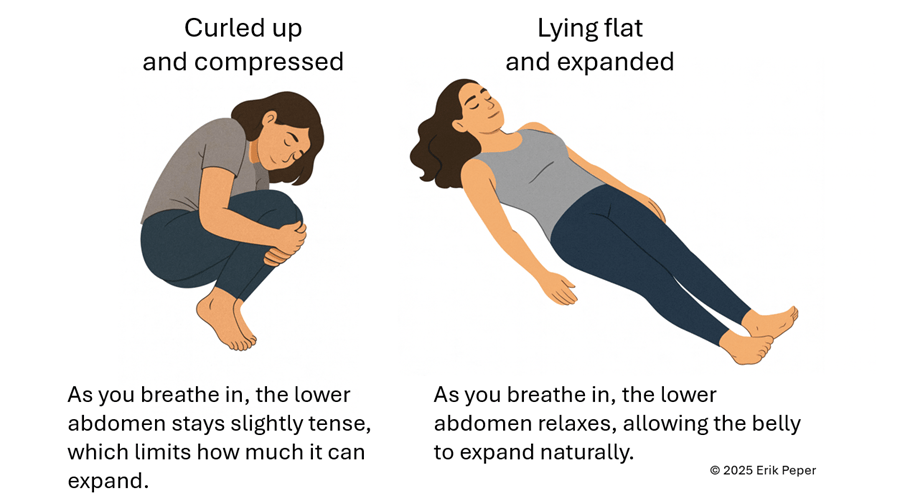
Figure 2. Curling up compresses the abdomen and prevents relaxation of the lower belly. In contrast, lying flat with the body gently expanded allows the abdomen to move freely with each breath, which can help reduce menstrual discomfort.
In contrast, slow abdominal or diaphragmatic breathing activates the body’s natural relaxation response. It quiets the stress-driven sympathetic nervous system, calms the mind, and improves circulation in the abdominal area. With each slow breath in, the abdomen gently expands while the pelvic floor and abdominal muscles relax. As you exhale, these muscles naturally tighten slightly, helping to massage and move blood and lymph through the abdominal region. This rhythmic movement supports healing and ease, as illustrated in Figure 3.
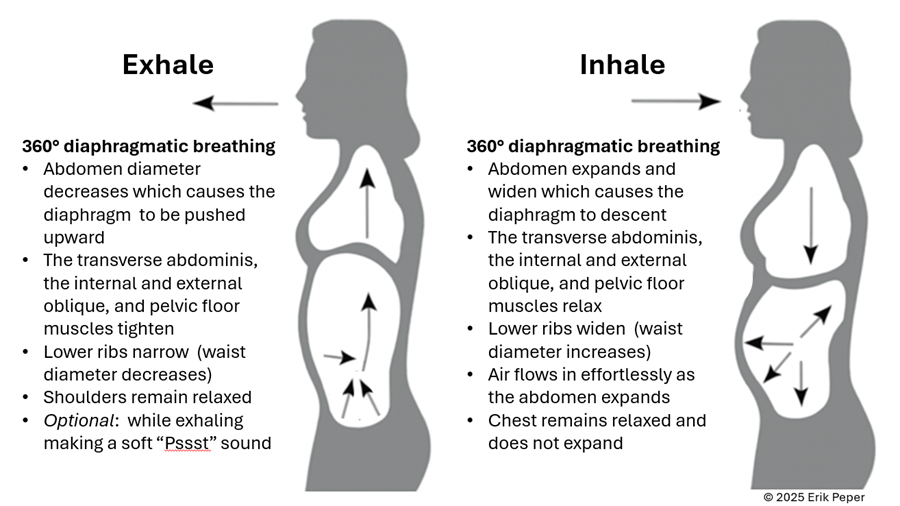
Figure 3. The dynamic process of diaphragmatic breathing.
The process of slower, lower diaphragmatic breathing
When lying down, rest comfortably on your back with your legs slightly apart. Allow your abdomen to rise naturally as you inhale and fall as you exhale. As you breathe out, imagine the air flowing through your abdomen, down your legs, and out through your feet. To deepen this sensation, you can ask a partner to gently stroke from your abdomen down your legs as you exhale—helping you sense the flow of release through your body.
Gently focus on slow, effortless diaphragmatic breathing. With each inhalation, your abdomen expands, and the lower belly softens. As you exhale, the abdomen gently goes down pushing the diaphragm upward and allowing the air to leave easily. Breathing slowly—about six breaths per minute—helps engage the body’s natural relaxation response.
If you notice that your breath is staying high in your chest instead of expanding through the abdomen, your symptoms may not improve and can even increase. One participant experienced this at first. After learning to let her abdomen expand with each inhalation while keeping her shoulders and chest relaxed, her next menstrual cycle was markedly easier and far less uncomfortable. The lesson is clear: technique matters.
“During times of pain, I practiced lying down and breathing through my stomach… and my cramps went away within ten minutes. It was awesome.” — 22-year-old college student
“Whenever I felt my cramps worsening, I practiced slow deep breathing for five to ten minutes. The pain became less debilitating, and I didn’t need as many painkillers.” — 18-year-old college student
These successes point out that it’s not just breathing — it’s how you breathe by providing space for the abdomen to expand during inhalation.
Practice: How to Do Diaphragmatic Breathing
- Find a quiet space. Lie on your back or sit comfortably erect with your shoulders relaxed.
- Place one hand on your chest and one on your abdomen.
- Inhale slowly through your nose for about 3–4 seconds. Let your abdomen expand as you breathe in — your chest should remain relaxed.
- Exhale gently through your mouth for 4—6 seconds, allowing the abdomen to fall or constrict naturally.
- As you exhale imagine the air moving down your arms, through your abdomen, down your legs, and out your feet
- Practice daily for 20 minutes and also for 5–10 minutes during the day when menstrual discomfort begins.
- Add warmth. Placing a warm towel or heating pad over your abdomen can enhance relaxation while lying on your back and breathing slowly.
With regular practice and implementing it during the day when stressed, this simple method can reduce cramps, promote calm, and reconnect you with your body’s natural rhythm.
Implement the ABCs during the day
The ABC sequence—adapted from the work of Dr. Charles Stroebel, who developed The Quieting Reflex (Stroebel, 1982)—teaches a simple way to interrupt stress reactions in real time. The moment you notice discomfort, pain, stress, or negative thoughts, interrupt the cycle with a simple ABC strategy:
A — Adjust your posture
Sit or stand tall, slightly arch your lower back and allowing the abdomen to expand while you inhale and look up. This immediately shifts your body out of the collapsed “defense posture’ and increases access to positive thoughts (Tsai et all, 2016; Peper et al., 2019)
B — Breathe
Allow your abdomen to expand as you inhale slowly and deeply. Let it get smaller as you exhale. Gently make a soft hissing sound as you exhale while helps the abdomen and pelvic floor to tighten. Then allow the abdomen to relax and widen which without effort draws the air in during inhalation. As you exhale, stay tall and imagine the air flowing through you and down your legs and out your feet.
C — Concentrate
Refocus your attention on what you want to do and add a gentle smile. This engages positive emotions, the smile helps downshift tension.
The video clip guides you through the ABCs process.
Integrate the breathing during the day by implementing your ABCs
When students practice relaxation technique and this method, they reported greater reductions in symptoms compared with a control group. By learning to notice tension and apply the ABC steps as soon as stress arises, they could shift their bodies and minds toward calm more quickly, as shown in Figure 4.
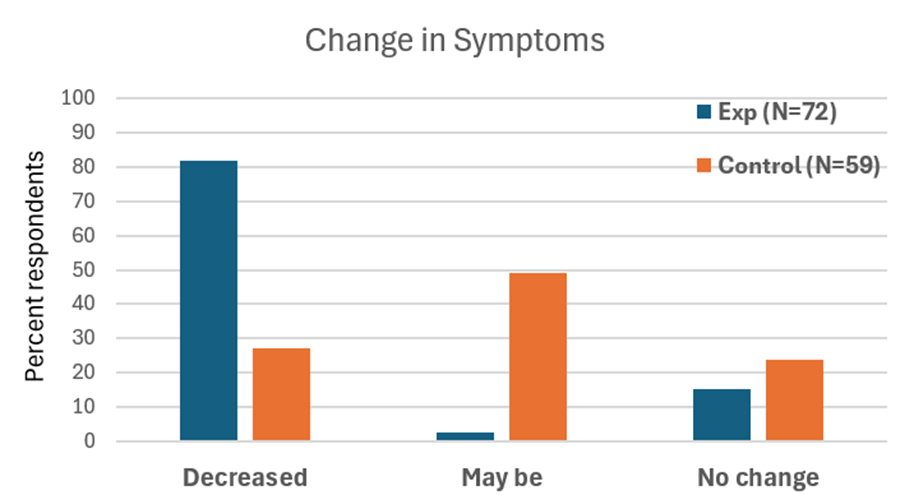
Figure 4. Change in symptoms after practicing a sequential relaxation and breathing techniques for four weeks.
Takeaway
Menstrual pain doesn’t have to be endured in silence or masked by medication alone. By practicing 30 minutes of slow diaphragmatic breathing daily and many times during the day, women may be able to reduce pain, stress, and discomfort — while building self-awareness and confidence in their body’s natural rhythms thereby having the opportunity to be more productive.
We recommend that schools and universities include self-care education—especially breathing and relaxation practices—as part of basic health curricula as this approach is scalable. Teaching young women to understand their bodies, manage stress, and talk openly about menstruation can profoundly improve well-being. It not only reduces physical discomfort but also helps dissolve the stigma that still surrounds this natural process,
Remember: Breathing is free—available anytime, anywhere and is helpful in reducing pain and discomfort. (Peper et al., 2025; Joseph et al., 2022)
See the following blogs for more in-depth information and practical tips on how to learn and apply diaphragmatic breathing:
REFERENCES
Itani, R., Soubra, L., Karout, S., Rahme, D., Karout, L., & Khojah, H.M.J. (2022). Primary Dysmenorrhea: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Updates. Korean J Fam Med, 43(2), 101-108. https://doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.21.0103
Huang, G., Le, A. L., Goddard, Y., James, D., Thavorn, K., Payne, M., & Chen, I. (2022). A systematic review of the cost of chronic pelvic pain in women. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada, 44(3), 286–293.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogc.2021.08.011
Joseph, A. E., Moman, R. N., Barman, R. A., Kleppel, D. J., Eberhart, N. D., Gerberi, D. J., Murad, M. H., & Hooten, W. M. (2022). Effects of slow deep breathing on acute clinical pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, 27, 2515690X221078006. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515690X221078006
Peper, E., Booiman, A. & Harvey, R. (2025). Pain-There is Hope. Biofeedback, 53(1), 1-9. http://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-53.01.16
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N., & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Chen, S., & Heinz, N. (2025). Practicing diaphragmatic breathing reduces menstrual symptoms both during in-person and synchronous online teaching. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. Published online: 25 October 2025. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09745-7
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153-169. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.1533-1
Stroebel, C. (1982). The Quieting Reflex. New York: Putnam Pub Group. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-Quieting-Charles-M-D-Stroebel/dp/0399126570/
Thakur, P. & Pathania, A.R. (2022). Relief of dysmenorrhea – A review of different types of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. MaterialsToday: Proceedings.18, Part 5, 1157-1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.207
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I. M. (2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23-27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
*Edited with the help of ChatGPT 5
Pragmatic techniques for monitoring and coaching breathing
Posted: December 14, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, emotions, meditation, mindfulness, neurofeedback, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, Uncategorized | Tags: art, books, Breathing rate, coaching, FlowMD app, nasal breathing, personal-development, self-monitoring, writing 4 CommentsDaniella Matto, MA, BCIA BCB-HRV , Erik Peper, PhD, BCB, and Richard Harvey, PhD
Adapted from: Matto, D., Peper, E., & Harvey, R. (2025). Monitoring and coaching breathing patterns and rate. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. https://townsendletter.com/monitoring-and-coaching-breathing-patterns-and-rate/
This blog aims to describe several practical strategies to observe and monitor breathing patterns to promote effortless diaphragmatic breathing. The goal of these strategies is to foster effortless, whole-body diaphragmatic breathing that promote health.
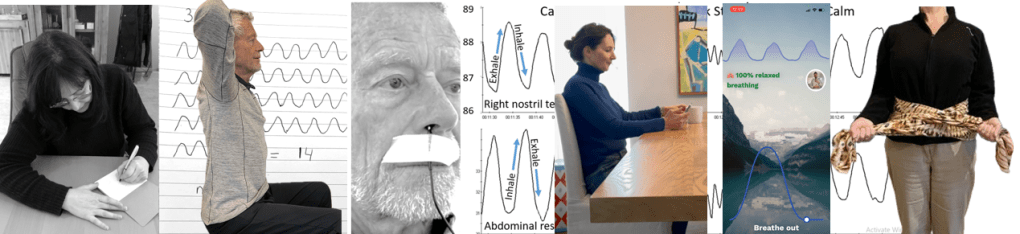
Breathing is usually covert and people are not usually aware of their breathing rate (breaths per minute) or pattern (abdominal or thoracic, breath holding or shallow breathing) unless they have an illness such as asthma, emphysema or are performing physical activity (Boulding et al, 2015)). Observing breathing is challenging; awareness of respiration often leads to unaware changes in the breath pattern or to an attempt to breathe perfectly (van Dixhoorn, 2021). Ideally breathing patterns should be observed/monitored when the person is unaware of their breathing pattern and the whole body participates (van Dixhoorn, 2008). A useful strategy is to have the person perform a task and then ask, “What happened to your breathing?”. For example, ask a person to simulate putting a thread through the eye of a needle or quickly look to the extreme right and left while keeping their head still. In almost all cases, the person holds their breath (Peper et al., 2002).
Teaching effortless slow diaphragmatic breathing is a precursor of Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback and is based on slow paced breathing (Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014; Steffen et al., 2017; Shaffer and Meehan, 2020). Mastering effortless diaphragmatic breathing is a powerful tool in the treatment of a variety of physical, behavioural, and cognitive conditions; however, to integrate this method into clinical or educational practice is easier said than done. Clients with dysfunctional breathing patterns often have difficulty following a breath pacer or mastering effortless breathing at a slower pace.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a few simple strategies that can be used to observe and monitor breathing patterns, provide economic strategies for observation and training, and suggestions to facilitate effortless diaphragmatic breathing.
Strategies to observe and monitor breathing pattern
Observation of the breathing patterns
- Is the breathing through the nose or mouth? Nose is usually better (Watso et al., 2023; Nestor, 2020).
- Does the abdomen expand during inhalation and constricts during exhalation or does the chest expand and rise during inhalation and fall during exhalation? Abdominal movement is usually better.
- Is exhalation flow softly or explosively like a sigh? Slow flow exhalation is preferred.
- Is the breath held or continues during activities? In most cases continued breathing is usually better.
- Does the person gasp before speaking or allows to speak while normally exhaling?
- What is the breathing rate (breaths per minute)? When sitting peacefully less than 14 breaths/minute is usually better and about 6 breaths per minute to optimize HRV
Physiological monitoring.
- Monitoring breathing with strain gauges around the abdomen and chest, and heart rate is the most common approach to identify the location of breath, the breathing pattern and heart rate variability. The strain gauges are placed around the chest and abdomen and heart rate is monitored with a blood volume pulse amplitude sensor from the finger. representative recording shows the effect of thoughts on breathing, heartrate and pulse amplitude of which the participant is totally unaware as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Physiological recording of breathing patterns with strain gauges.
- Monitoring breathing with a thermistor placed at the entrance of the nostril that has the most airflow (nasal patency) (Jovanov et al., 2001; Lerman et al., 2016). When the person exhales through the nose, the thermistor temperature increases and decreases when they inhale. A representative recording of a person being calm, thinking a stressful thought. and being calm. Although there were significant changes as indicated by the change in breathing patterns, the person was unaware of the changes as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Use of a thermistor to monitor breathing from the dominant nostril compared to the abdominal expansion as monitored by a strain gauge around the abdomen.
- Additional physiological monitoring approaches. There are many other physiological measures can be monitored to such as end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2), a non-invasive measurement of the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhaled breath (Meuret et al., 2008; Meckley, 2013); scalene/trapezius EMG to identify thoracic breathing (Peper & Tibbett, 1992; Peper & Tibbets, 1994); low abdominal EMG to identify transfers and oblique tightening during exhalation and relaxation during inhalation (Peper et al., 2016; and heart rate to monitor cardiorespiratory synchrony (Shaffer & Meehan, 2020). Physiological monitoring is useful; since, the clinician and the participant can observe the actual breathing pattern in real time, how the pattern changes in response the cognitive and physical tasks, and used for feedback training. The recorded data can document breathing problems and evidence of mastery.
The challenges of using physiological monitoring arethat the equipment may be expensive, takes skill to operate and interpret the data, and is usually located in the office and not at home.
Economic strategies for observation and training breathing
To complement the physiological monitoring and allow observations outside the office and at home, some of the following strategies may be used to observe breathing pattern (rate and expansion of the breath in the body), and suggestion to facilitate effortless diaphragmatic breathing. These exercises make excellent homework for the client. Practicing awareness and internal self-regulation by the client outside the clinic contributes enormously to the effect of biofeedback training (Wilson et al., 2023),
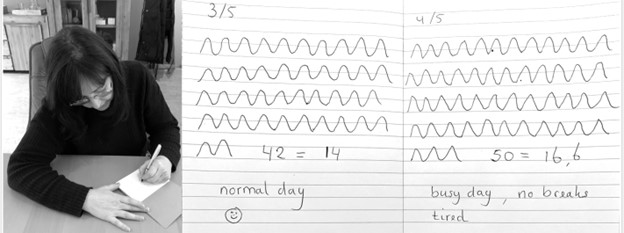
Observe breathing rate: Draw the breathing pattern
Take a piece of paper, a pen and a timer, set to 3 minutes. Start the timer. Upon inhalation draw the line up and upon exhalation draw the line down, creating a wave. When the timer stops, after 3 minutes, calculate the breathing rate per minute by dividing the number of waves by 3 as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Drawing the breathing pattern for three minutes during two different days.
From these drawings, the breathing rate become evident. Many individuals are often surprised to discover that their breathing rate increased during periods of stress, such as a busy day with no breaks, compared to their normal days.
Monitoring and training diaphragmatic breathing
The scarf technique for abdominal feedback
Many participants are unaware that they are predominantly breathing in their chest and their abdomen expansion is very limited during inhalation. Before beginning, have participant loosen their belt and or stand upright since sitting collapsed/slouched or having the waist constriction such as a belt of tight constrictive clothing that inhibits abdominal expansion during inhalation.
Place the middle part of a long scarf or shawl on your lower back, take the ends in both hands and cross the ends: your left hand is holding the right part of the scarf, and the right hand is holding the left end of the scarf. Give a bit of a pull, so you can feel any movement of the scarf. When breathing more abdominally you will feel a pull at the ends of the scarf as you lower back, and flanks will expand as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Using a scarf as feedback.
FlowMD app
A recent cellphone app, FlowMD, is unique because it uses the cellphone camera to detect the subtle movements of the chest and abdomen (FlowMD, 2024). It provides real time feedback of the persons breathing pattern. Using this app, the person sits in front of their cellphone camera and after calibration, the breathing pattern is displayed as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5. Training breathing with FlowMD,.
Suggestions to optimize abdominal breathing that may lead to a slower breath rate when the client practices the technique
Beach pose
By locking the upper chest and sitting up straight it is often easier to breathe so that the abdomen can expand and constrict. Place your hands behind your head and Interlock your finger of both hands, pull your elbows back and up. The person can practice this either laying down on their back or sitting straight up at the edge of the chair as shown in Figure 6.
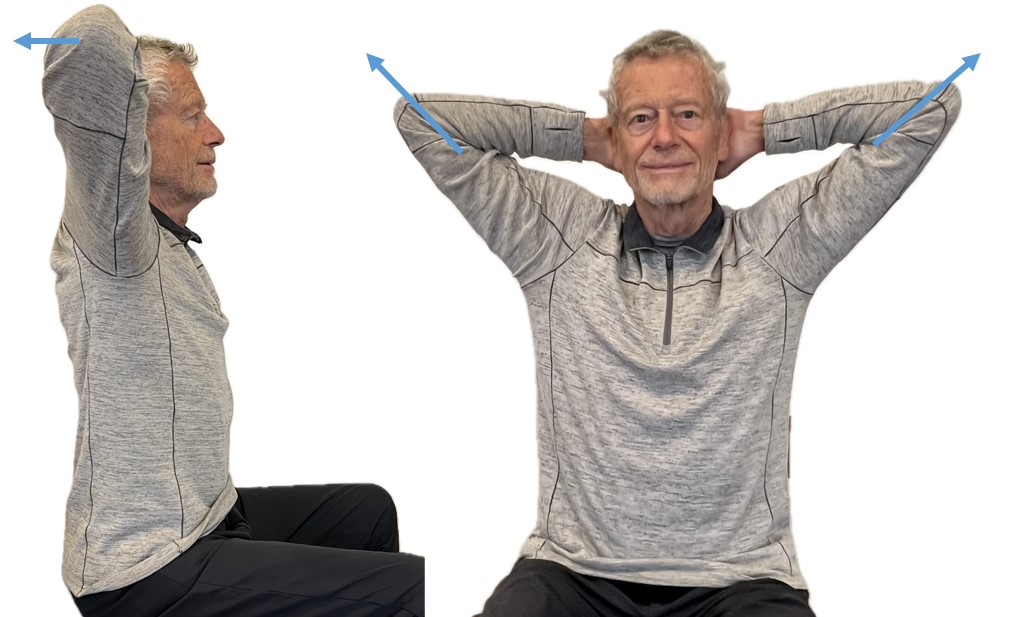

Figure 6. Sitting erect with the shoulders pulled back and up to allow abdominal expansion and constriction as the breathing pattern.
Observe the effect of posture on breathing
Have the person sit slouched/collapsed like a letter C and take a few slow breath, then have them sit up in a tall and erect position and take a few slow breaths. Usually they will observe that it is easier to breathe slower and lower and tall and erect.
Using your hands for feedback to guide natural breathing
Holding your hands with index fingers and thumbs touching the lower abdomen. When inhaling the fingers and thumbs separate and when exhaling they touch again (ensuring a full exhale and avoiding over breathing). The slight increase in lower abdominal muscle tension during the exhalation and relaxation during inhalation and the abdominal wall expands can also be felt with fingertips as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Using your hands and finger for feedback to guide the natural breathing of expansion and constriction of the abdomen. Reproduced by permission from Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49.
Coaching suggestions
There are many strategies to observe, teach and implement effortless breathing (Peper et al., 2024).. Even though breathing is natural and babies and young children breathe diaphragmatically as their large belly expands and constricts. Yet, in many cases the natural breathing shifts to dysfunctional breathing for multiple reasons such as chronic triggering defense reactions to avoiding pain following abdominal surgery (Peper et al, 2015). When participants initially attempt to relearn this natural pattern, it can be challenging especially, if the person habitually breathes shallowly, rapidly and predominantly in their chest.
When initially teaching effortless breathing, have the person exhale more air than normal without the upper chest compressing down and instead allow the abdomen comes in and up thereby exhaling all the air. If the person is upright then allow inhalation to occur without effort by letting the abdominal wall relaxes and expands. Initially inhale more than normal by expanding the abdomen without lifting the chest. Then exhale very slowly and continue to breathe so that the abdomen expands in 360 degrees during inhalation and constricts during exhalation. Let the breathing go slower with less and less effort. Usually, the person can feel the anus dropping and relaxing during inhalation.
Another technique is to ask the person to breathe in more air than normal and then breathe in a little extra air to completely fill the lungs, before exhaling fully. Clients often report that it teaches them to use the full capacity of the lungs.
The goal is to breath without effort. Indirectly this can be monitored by finger temperature. If the finger temperature decreases, the participant most likely is over-breathing or breathing with too much effort, creating sympathetic activity; if the finger temperature increases, breathing occurs slower and usually with less effort indicating that the person’s sympathetic activation is reduced.
Conclusion
There are many strategies to monitor and coach breathing. Relearning diaphragmatic breathing can be difficult due to habitual shallow chest breathing or post-surgical adaptations. Initial coaching may involve extended exhalations, conscious abdominal expansion, and gentle inhalation without chest movement. Progress can be monitored through indirect physiological markers like finger temperature, which reflects changes in sympathetic activity. The integration of these techniques into clinical or educational practice enhances self-regulation, contributing significantly to therapeutic outcomes. In this article we provided a few strategies which may be useful for some clients.
Additional blogs on breathing
https://peperperspective.com/2015/09/25/resolving-pelvic-floor-pain-a-case-report/
REFERENCES
Boulding, R., Stacey, R., & Niven, N. (2016). Dysfunctional breathing: a review of the literature and proposal for classification. European Respiratory Review, 25(141),: 287-294. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0088-2015
FlowMD. (2024). FlowMD app. Accessed December 13, 2024. https://desktop.flowmd.co/
Jovanov, E., Raskovic, D., & Hormigo, R. (2001). Thermistor-based breathing sensor for circadian rhythm evaluation. Biomedical sciences instrumentation, 37, 493–497. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11347441/
Lehrer, P. & Gevirtz R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work? Front Psychol, 5,756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
Lerman, J., Feldman, D., Feldman, R. et al. Linshom respiratory monitoring device: a novel temperature-based respiratory monitor. (2016). Can J Anesth/J Can Anesth, 63, 1154–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-016-0694-y
Meckley, A. (2013). Balancing Unbalanced Breathing: The Clinical Use of Capnographic Biofeedback. Biofeedback, 41(4), 183–187. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-41.4.02
Meuret, A. E., Wilhelm, F. H., Ritz, T., & Roth, W. T. (2008). Feedback of end-tidal pCO2 as a therapeutic approach for panic disorder. Journal of psychiatric research, 42(7), 560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.06.005
Nestor, J. (2020). Breath: The New Science of a Lost Art. New York: Riverhead Books. https://www.amazon.com/Breath-New-Science-Lost-Art/dp/0735213615/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Peper, E., Gibney, K.H., & Holt, C.F. (2002). Make Health Happen. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. https://he.kendallhunt.com/product/make-health-happen-training-yourself-create-wellness
Peper, E., Oded, Y., Harvey, R., Hughes, P., Ingram, H., & Martinez, E. (2024). Breathing for health: Mastering and generalizing breathing skills. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. November 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/suggestions-for-mastering-and-generalizing-breathing-skills/
Peper, E., & Tibbetts, V. (1992). Fifteen-month follow-up with asthmatics utilizing EMG/incentive inspirometer feedback. Biofeedback and self-regulation, 17(2), 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000104
Peper, E. & Tibbetts, V. (1994). Effortless diaphragmatic breathing. Physical Therapy Products. 6(2), 67-71. https://biofeedbackhealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/peper-and-tibbets-effortless-diaphragmatic.pdf
Shaffer, F. and Meehan, Z.M. (2020). A Practical Guide to Resonance Frequency Assessment for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.570400
Steffen, P.R., Austin, T., DeBarros, A., and Brown, T. (2017). The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood. Front Public Health, 5, 222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2017.00222
van Dixhoorn, J.V. (2008). Whole-body breathing. Biofeedback, 36,54–58. https://www.euronet.nl/users/dixhoorn/L.513.pdf
van Dixhoorn, J.V. (2021). Functioneel ademen-Adem-en ontspannings oefeningen voor gevorderden. Amersfoort: Uiteveriy Van Dixhoorn. https://www.bol.com/nl/nl/p/functioneel-ademen/9300000132165255/
Watso, J. C., Cuba, J.N., Boutwell, S.L, Moss, J…(2023). Acute nasal breathing lowers diastolic blood pressure and increases parasympathetic contributions to heart rate variability in young adults. American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology.
325I(6), R797-R80. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00148.2023
Wilson, V., Somers, K. & Peper, E. (2023). Differentiating Successful from Less Successful Males and Females in a Group Relaxation/Biofeedback Stress Management Program. Biofeedback, 51(3), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.5298/608570
[1] Correspondence should be addressed to:
Erik Peper, Ph.D., Institute for Holistic Health Studies, San Francisco State University, 1600 Holloway Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94132 Tel: 415 338 7683 Email: epeper@sfsu.edu web: www.biofeedbackhealth.org blog: www.peperperspective.com
Suggestions for mastering and generalizing breathing skills
Posted: October 30, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, CBT, cellphone, cognitive behavior therapy, emotions, ergonomics, healing, health, mindfulness, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: abdominal beathing, anxiety, diaphragmatic braething, health, hyperventilation, meditation, mental-health, mindfulness, mouth breathing, Toning 3 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E., Oded, Y., Harvey, R., Hughes, P., Ingram, H., & Martinez, E. (2024). Breathing for health: Mastering and generalizing breathing skills. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. November 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/suggestions-for-mastering-and-generalizing-breathing-skills/

Breathing techniques are commonly employed with complimentary treatments, biofeedback, neurofeedback or adjunctive therapeutic strategies to reduce stress and symptoms associated with excessive sympathetic arousal such as anxiety, high blood pressure, insomnia, or gastrointestinal discomfort. Even though it seems so simple, some participants experience difficulty in mastering effortless breathing and/or transferring slow breathing skills into daily life. The purpose of this article is to describe: 1) factors that may interfere with learning slow diaphragmatic breathing (also called cadence or paced breathing, HRV or resonant frequency breathing along with other names), 2) challenges that may occur when learning diaphragmatic breathing, and 3) strategies to generalize the effortless breathing into daily life.
Background
A simple two-item to-do list could be: ‘Breathe in, breathe out.’ Simple things are not always easy to master. Mastering and implementing effortless ‘diaphragmatic’ or ‘abdominal belly’ breathing may be simple, yet not easy. Breathing is a dynamic process that involves the diaphragm, abdominal, pelvic floor and intercostal muscles that can include synchronizing the functions of the heart and lungs and may result in cardio-respiratory synchrony or coupling, as well as ‘heart-rate variability breathing training (Codrons et al., 2014; Dick et al., 2014; Elstad et al., 2018; Maric et al., 2020; Matic et al., 2020). Improving heart-rate variability is a useful approach to reduce symptoms of stress and promotes health and reduce anxiety, asthma, blood pressure, insomnia, gastrointestinal discomfort and many other symptoms associated with excessive sympathetic activity (Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014; Xiao et al., 2017; Jerath et al., 2019; Chung et al., 2021; Magnon et al., 2021; Peper et al., 2022).
Breathing can be effortful and In some cases people have dysfunctional breathing patterns such as breath holding, rapid breathing (hyperventilation), shallow breathing and lack of abdominal movement. This usually occurs without awareness and may contribute to illness onset and maintenance. When participants learn and implement effortless breathing, symptoms often are reduced. For example, when college students are asked to practice effortless diaphragmatic breathing twenty-minutes a day for one week, as well as transform during the day dysfunction breathing patterns into diaphragmatic breathing, they report a reduction in shallow breathing, breath holding,, and a decrease of symptoms as shown in Fig 1 (Peper et al, 2022).

Figure 1. Percent of people who reported that their initial symptoms improved after practicing slow diaphragmatic breathing for twenty minutes per day over the course of a week (reproduced from: Peper et al, 2022).
Most students became aware of their dysfunctional breathing and substituted slow, diaphragmatic breathing whenever they realized they were under stress; however, some students had difficulty mastering ‘effortless’ (e.g., automated, non-volitional) slow, diaphragmatic breathing that allowed abdominal expansion during inhalation.
Among those had more difficulty, they tended to have almost no abdominal movement (expansion during inhalation and abdominal constriction during exhalation). They tended to breathe shallowly as well as quickly in their chest using the accessory muscles of breathing (sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major and minor, serratus anterior, latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior superior).
The lack of abdominal movement during breathing reduced the movement of lymph as well as venous blood return in the abdomen; since; the movement of the diaphragm (the expansion and constriction of the abdomen) acts a pump. Breathing predominantly in the chest may increase the risk of anxiety, neck, back and shoulder pain as well as increase abdominal discomfort, acid reflux, irritable bowel, dysmenorrhea and pelvic floor pain (Banushi et al., 2023; Salah et al., 2023; Peper & Cohen, 2017; Peper et al., 2017; Peper et al., 2020, Peper et al., 2023). Learning slow, diaphragmatic or effortless breathing at about six breaths per minute (resonant frequency ) is also an ‘active ingredient’ in heartrate variability (HRV) training (Steffen et al., 2017; Shaffer & Meehan, 2020).
1. Factors that interfere with slow, diaphragmatic breathing
Difficulty allowing the skeletal and visceral muscles in the abdomen to expand or constrict in ‘three-dimensions’ (e.g., all around you in 360 degrees) during inhalation or exhalation. Whereas internal factors under volitional control and will mediate breathing practices, external factors can restrict and moderate the movement of the muscles. For example:
Clothing restrictions (designer jeans syndrome). The clothing is too tight around the abdomen; thereby, the abdomen cannot expand (MacHose & Peper, 1991; Peper et al., 2016). An extreme example were the corsets worn in the late 19th century that was correlated with numerous illnesses.
Suggested solutions and recommendations: Explain the physiology of breathing and how breathing occurs by the diaphragmatic movement. Discuss how babies and dogs breathe when they are relaxed; namely, the predominant movement is in the abdomen while the chest is relaxed. This would also be true when a person is sitting or standing tall. Discuss what happens when the person is eating and feels full and how they feel better when they loosen their waist constriction. When their belt is loosened or the waist button of their pants is undone, they usually feel better.
Experiential practice. If the person is wearing a belt, have the person purposely tighten their belt so that the circumference of the stomach is made much smaller. If the person is not wearing a belt, have them circle their waist with their hands and compress it so that the abdomen can not expand. Have them compare breathing with the constricted waist versus when the belt is loosened and then describe what they experienced.
Most participants will feel it is easier to breathe and much more comfortable when the abdomen is not constricted.
Previous abdominal injury. When a person has had abdominal surgery (e.g., Cesarean section, appendectomy, hernia repair, or episiotomy), they unknowingly may have learned to avoid pain by not moving (relaxing or tensing) the abdomen muscles (Peper et al., 2015; Peper et al., 2016). Each time the abdomen expands or constricts, it would have pulled on the injured area or stitches that would have cause pain. The body immediately learns to limit movement in the affected area to avoid pain. The reduction in abdominal movement becomes the new normal ‘feeling’ of abdominal muscle inactivity and is integrated in all daily activities. This is a process known as ‘learned disuse’ (Taub et al., 2006). In some cases, learned disuse may be combined with fear that abdominal movement may cause harm or injury such as after having a kidney transplant. The reduction in abdominal movement induces shallow thoracic breathing which could increase the risk of anxiety and would reduce abdominal venous and lymph circulation that my interfere with the healing.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss the concept of learned disuse and have participant practice abdominal movement and lower and slower breathing.
Experiential practices: Practicing abdominal movements
Sit straight up and purposely exhale while pulling the abdomen in and upward and inhale while expanding the abdomen. Even with these instructions, some people may continue to breathe in their chest. To limit chest movement, have the person interlock their hands and bring them up to the ceiling while going back as far as possible. This would lock the shoulders and allows the abdomen to elongate and thereby increase the diaphragmatic movement by allowing the abdomen to expand. If people initially have held their abdomen chronically tight then the initial expansion of abdomen by relaxing those muscle occurs with staccato movement. When the person becomes more skilled relaxing the abdominal muscles during inhalation the movement becomes smoother.
Make a “psssssst” sound while exhaling. Sit tall and erect and slightly pull in and up the abdominal wall and feel the anus tightening (pulling the pelvic floor up) while making the sound. Then allow inhalation to occur by relaxing the stomach and feeling the anus go down.
Use your hands as feedback. Sit up straight, placing one hand on the chest and another on the abdomen. While breathing feel the expansion of the abdomen and the contraction of the abdomen during exhalation. Use a mirror to monitor the chest-muscle movement to ensure there is limited rising and falling in this area.
Observe the effect of collapsed sitting. When sitting with the lower back curled, there is limited movement in the lower abdomen (between the pubic region and the umbilicus/belly button) and the breathing movement is shallower without any lower pelvic involvement (Kang et al., 2016). This is a common position of people who are working at their computer or looking at their cellphone.
Experiential practice: looking at your cellphone
Sit in a collapsed position and look down at your cellphone. Look at the screen and text as quickly as possible.
Compare this to sitting up and then lift the cell phone at eye level while looking straight ahead at the cellphone. Look at the screen and text as quickly as possible.
Observe how the position effected your breathing and peripheral awareness. Most likely, your experience is similar those reported by students. Close to 85%% of students who complete this activity reported that their breathing was shallower sitting slouched versus erect and about 85% of the students reported that their peripheral awareness and vision improved when sitting erect (Peper et al., 2024).
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Be aware how posture affect breathing. While sitting, place a rolled-up towel against the lower back so that the person sits more erect which would allow the abdomen to expand when inhaling.
Self-image, self-esteem, and confidence. Participants may hold their abdomen in because they want to look slim (sometimes labeled as the “hourglass syndrome” associate expanding the abdomen as unattractive (PTI, 2023). A flat abdomen is culturally reinforced by social media and fashion models and encouraged in some activities such as ballet. On the other hand, some people purposely puff up their chest to increase size and dominance (Cohen & Leung, 2009).
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss the benefits of diaphragmatic breathing including its ability to reduce anxiety in social settings that may enhance confidence. Similar to an earlier suggestion, have the person explore clothing with a looser waist that still supports feelings of attractiveness and power.
Feeling anxious, fearful or threatened. The normal physiological stress reaction is a slight gasp with the tightening of the abdomen muscles for protection when a stressor occurs (Gilbert, 1998; Ekerholt & Bergland., 2008). The stressor can be an actual physical event, social situation or thoughts and emotions. Shallow breathing is a natural self-protective response. This pattern is often maintained until one feels ‘safe’ enough to relax, which for many can have a duration of the entire day or until finding the relative safety of sleep.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss how the physiological stress reaction is a normal response pattern that the person most likely learned in early childhood for self-protection. This pattern is often observed in clients who are emotionally sensitive and/or react excessively to a variety of stimuli. Note that some people have learned not to show their reactivity on their face or in the overt behaviors, yet they continue to breathe shallowly as a telltale sign of ‘distress.’ People who breath shallowly may experience this response as burdensome. Discuss with them how to reframe their sensitivity as a gift; namely, they are more aware of other people’s reactions and emotions. They just need to learn how not to respond automatically. Encourage awareness of their breath-holding and shallow breathing. Follow this by teaching them to replace the dysfunctional breathing with slow, diaphragmatic breathing at 6-breaths-per-minute. A possible training sequence is the following:
- Teach slow, diaphragmatic breathing
- Practice evoking a stressor and the moment the client senses the stress response, shallow breaths or holds their breath have them shift to slow, diaphragmatic breathing.
- If the person slouches in response to stress, the moment they become aware of slouching, have then sit erect, look up and then breathe diaphragmatically. (Peper et al., 2019)
Experiential practice: Transform stressful thoughts by looking up, breathing, and changing thoughts.
Evoke a stressor and then attempt to reframe the experience (cognitive behavior therapy or CBT approach).
Compare this to evoking a stressor, then shift to an upright position while looking up, take a few slow, diaphragmatic breaths, and reframe the experience.
In almost all cases, when the client shifts position, looks up and then reframes, the stress reaction is significantly reduced and it is much easier to reframe the experiences positively compared to when only attempting to reframe the experience (Peper et al., 2019).
Diaphragmatic breathing feels abnormal. How you breathe habitually is what feels normal unless there is overt illness such as asthma or emphysema. Any new pattern usually feels abnormal. When the person shifts their breathing pattern, such as in a transition from habitual shallow chest breathing to slower diaphragmatic abdominal breathing, it feels strange and wrong.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss the concept that habitual patterns are normal (e.g., a person who typically slouches when standing straight may experience that they are going to fall backwards). Emphasize the importance of making a shift in posture and leaning into the discomfort of the new experience. Often after practicing slow diaphragmatic breathing, the person may report feeling much more relaxed (e.g., sensing heaviness and warmth) with their fingers increasing in temperature.
2. Challenges that may occur when learning diaphragmatic breathing
Ideally, breathing is an effortless diaphragmatic process as described by the phrase, “it breathes me” (Luthe & Schultz, 1970; Luthe, 1979); however, some participants struggle to achieve this type of breathing. The following are common challenges and possible solutions:
Distraction and internal dialogue. Many people struggle with thoughts jumping from one area to another. Some people refer to this mental state as “monkey mind.”
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Validate that distraction and internal dialogue are normal and require continual managing and practice to overcome. Experimental Practice: Have the person train focus during diaphragmatic breathing techniques by focusing on 1 item in the room. Remind them that when thoughts arise, note them briefly instead of engaging with them and then refocus on the item. Start with increments of time and increase with practice.
Effect of gravity on breathing. In the vertical position, exhalation occurs when the abdomen constricts (slight tightening of the transverse and oblique abdominal muscles and the pelvic floor) pushes the diaphragm up, allowing the air to go out. It needs to push against gravity.
In the vertical position, inhalation occurs when the abdominal muscles and pelvic floor muscles relax and the abdomen widens in all directions (360 degrees) which causes the diaphragm to descend as it is being pulled down by gravity. This process allows effortless inhalation. The experience is the opposite when lying supine on one’s back. While lying down, gravity pulls on the abdomen that cause the diaphragm to go upward allowing the air to flow out during exhalation. Inhalation takes work because as the diaphragm descends it has to push the abdominal content upward against gravity.
Experiential practice: Erect versus supine
- Vertical position. Begin by exhaling completely by pulling the abdomen in and up while staying erect and not pressing/contracting the chest downward. At the end of exhalation, allow the abdomen to relax (pop out) and feel how the air is sucked in without trying to inhale
- Horizontal position. Begin by lying down, with the face pointing up. Inhale by expanding your abdomen and pushing your abdomen upward against gravity. Then let exhalation occur while totally relaxing as gravity pushes the abdomen downward, which pushes the diaphragm upward into the chest allowing the air to flow out. Optionally, place a small bag of rice/beans (e.g., approximately one to five pound or. One-half to two kilograms) on your lower abdomen while lying down. When you inhale, push the weight upward and away from you by allowing the stomach, but not the chest, to expand. Allow exhalation to occur as the weight pushes your abdomen down and upward into your chest. The weight is useful as it allows the mind to focus more easily on the task of feeling the movement of the abdomen.
Over breathing/hyperventilation. Even breathing at about six breaths per minute can cause hyperventilation can occur. Hyperventilation occurs when a person is breathing in excess of the metabolic needs of the body and thereby eliminating more carbon dioxide. The result is respiratory alkalosis and an elevated blood pH as the dissolved carbon dioxide (pCO2) in the blood is reduced (Folgering, 1999).
The most common symptoms of over breathing are colder sweaty hands and light-headedness. If this starts to occur, focus on decreasing the airflow during exhalation by exhaling through pursed lips making the sound, “Pssssssst.” While making this sound, make the sound softer with less airflow. Alternatively, have them imagine a holding a dandelion flower a few inches from their lips and blow so softly the seeds do not blow away. The blowing away of the seed is the feedback that you are blowing to hard as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Dandelion seeds as feedback when the person is blowing with too much effort. Alternatively, we recommend that the client imagine smelling the scent/fragrance of a flower that usually causes nose inhalation and then exhale gently through pursed lips ast if the air flows over a candle and, the flame does not move back and forth.
Mouth breathing. Mouth breathing contributes to disturbed sleep, snoring, sleep apnea, dry mouth upon waking, fatigue, allergies, ear infections, attention deficit disorders, crowded miss-aligned teeth, and poorer quality of life (Kahn & Ehrlich, 2018). Even the risk of ear infections in children is 2.4 time higher for mouth breathers than nasal breathers (van Bon et al, 1989) and nine and ten year old children who mouth breath have significantly poorer quality of life and have higher use of medications (Leal et al, 2016).
Breathing through the nose is associated with deeper and slower breathing rate than mouth breathing. Nose breathing reduces airway irritation since the nose filters, humidifies, warms/cools the inhaled air as well as reduces the air turbulence in the upper airways. The epithelial cells of the nasal cavities produce nitric oxide that are carried into the lungs when inhaling during nasal breathing (Lundberg & Weitzberg, 1999). The nitric oxide contributes to healthy respiratory function by promoting vasodilation, aiding in airway clearance, exerting antimicrobial effects, and regulating inflammation (McKeown, 2019; Allen, 2024). Note that alternate nostril breathing, such as breathing in one nostril for 5-seconds and out of the other for 5-seconds is another technique which some people find beneficial.
Slower breathing approaches also facilitates sympathetic parasympathetic balance and reduces airway irritation. If the person breathes habitually through their mouth, refer them to health care provider to explore factors that may contribute to mouth breathing such as enlarged tonsils and adenoids or deviated septum. In addition, explore environmental factors that could contribute nasal inflammation such as allergies or foods such as dairy (Al-Raby, 2016).
Performance anxiety. Many participants are concerned about their performance. The direct instructions such as “follow the graphic” causes the person to try hard to breathe with too much effort. Explore some of the following indirect strategies to interrupt ongoing cognitive judgements and self-talk.
- Toning or humming (Peper et al., 2019a). While exhaling, have the person hum a sound with their mouth closed. Let the sound go for about 6 seconds, relax, inhale and hum again. Toning is very similar except you verbalize a tone such as “Oammm.” (For detailed instructions on toning, see: Anziani & Peper (2021)).
- Stroking down arms and legs during exhalation. Have a partner gently stroke down your arms from your shoulder past your fingertips as you are exhaling. The downward stroking is in rhythm with the exhalation. As the arm is being stroked, attend to the sensations going down the arms. Be sure that the toucher exhales at the same time and the stroking down the arm takes about six seconds. After being stroked for a few times, have the person imagine that each time they exhale they feel a flow down through their arms and out their fingers.
- Repeat the same process while stroking down the legs from the side of their hips to their toes.
- Finally, have the person imagine/feel the sensation streaming down their legs with each exhalation.
- Many participants will report that they sense a steaming going down their arms, that they hands warm up, and their thought have stopped.
- Integrated body movement with breathing especially flexion and contraction (Meehan & Shaffer, 2023). Integrate the normal response of flexion that induces exhalation and extension evokes inhalation. Be careful that the flexion movement does not encourage participants to compress their chest during exhalation, which tends to encourage chest breathing. Have the person focus on their head staying tall and erect. Have the person sit straight up with their feet slight apart and their hands palm down on their lap. Allow inhaling to initiate as the person simultaneously arches their lower back expanding the stomach, separating the knees and turning the hands palm up. Initiate exhalation while simultaneously bringing the knees together, turning the palms face down on the thighs and rolling the pelvic back slightly rounding the lower back. Do the movements smoothly while keeping the legs and shoulders relaxed.
Flooded by emotions. Although very rare, at times when the person allows the abdomen to relax, they may experience by the emotions from a past trauma as the habitual bracing patterns are relaxed.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Validate these emotions for the person. Explain that this is a normal process that may occur if past trauma has occurred. Clients who have had past trauma often experience hypervigilance, which may interfere with the relaxation response that occurs during more optimal states of breathing. Transitioning to a more optimal rest state may be uncomfortable for a person who has experienced trauma because it reduces hypervigilance. This can feel uncomfortable as hypervigilance in these cases serves a protective role, even if it is an illusory feeling of protection from future harm. Since persistent hypervigilance can interfere with the relaxation response, the benefits of allowing a relaxation response to occur through slower breathing should be highlighted. Grounding techniques as described by Peper et al (2024a) can be useful to become centered.
3. Strategies to generalize the effortless breathing into daily life.
Generalizing the skill occurs after having mastered diaphragmatic breathing in different positions (sitting, standing, lying down, and while performing tasks). It is important to remember that our breathing patterns are conditioned with our behavior. Become aware how breathing affects cognitions and emotions and how emotions and cognitions affects breathing. The following are some strategies that may facilitate learning and generalizing the slower breathing skills.
Observing how our behavior affects our breathing: Anything that may evoke the alarm or defense reaction tends to cause the person gasp and/or hold their breath. For example, when a person is sitting peacefully, make an unexpected noise behind their back or movement in their periphery of vision. In most cases they will gasp or hold their breath. Usually, they are unaware of this process unless they are asked what happened to their breathing. The major reason for the breath holding is that the stimuli triggers an alarm/defense reaction and when we hold our breath our hearing is more acute (we can hear approaching danger earlier). The problem is that we give this response when there is no actual, immediate or present threat.
Experiential practice. Sit comfortably. Now as quickly as possible without rotating the head, look with your eyes to the extreme right and then left and back and forth as if trying to identify danger at the periphery. Do this for a few eye movements. Almost everyone holds their breath when doing this exercise. For generalizing the skill, ask the person to observe during the day situations in which they hold their breath, ask them if it was necessary and encourage them to start diaphragmatic breathing.
Observing how breathing affects our thoughts and emotions. Breathing patterns are intrinsically linked to our emotions and thoughts as illustrated in the many language phrases such as sigh of relief, full of hot air, waiting with bated breath. At the same time, our breathing patterns also affect our thoughts. For instance, when we breathe shallowly and more rapidly, we can induce feelings of fear or anxiety. If we gasp, we can experience thought stopping.
Experiential practices: Incomplete exhalation: Observe what happens when you exhale less than you inhale. Begin by exhaling only 70% of the air you inhaled, then inhale and exhale again only 70% of the air you just inhaled continue this for 30 seconds. Many people will experience the onset of anxiety symptoms, lightheadedness, dizziness, neck and shoulder tension, etc. (Peper & MacHose, 1993). If you experience symptoms during this exercise and you have experienced these symptoms in the past, it is likely that unknowingly breathing in a dysfunctional pattern could have evoked them. Therefore, practicing effortless breathing may interrupt and reduce the symptoms. Do this practice while observing the person carefully and immediately interrupt and distract the person if they start feeling dizzy, too anxious, or trigger the beginning of a panic attack or PTSD symptoms.
Experiential practice: Gasp or sniff-hold sniff. Observe what happens when you are performing a cognitive task and you rapidly gasp or do sniff-hold-sniff again before exhaling. Begin by sequentially subtracting mentally, the number 7 from 146 (e.g., 146, 139, 132….). Do this as rapidly as possible and do not make a mistake. While doing the subtracting, take a rapid gasp (such as one is triggered by surprise or fear), alternatively, take a quick sniff through your nose, hold your breath and take another sniff on top of the first one, then exhale. Whereas subtrating numbers is a skill most adults can perform, the ‘time pressure’ along with the direction to avoid mistakes may be the ‘immediate’ source of strain. Whether it was the time pressure, the direction to avoid mistakes or the direction to gasp, observe what happened to your thinking process. In almost all cases, your higher-order thoughts (doing the sequential subtraction under time pressure while gasping) have disappeared, replaced by the immediate thoughts of ‘performance anxiety.’
If you blank out on exams or experience anxiety, gasping and breath holding may be one of the factors that increases symptoms and affects your performance. If you are aware that you are holding your breath or gasped, use that as the cue to shift to slow diaphragmatic breathing and you may find that your performance improves. Therefore, observe when and where you were blanking out, gasping and/or holding your breathing then substitute slow, effortless diaphragmatic breathing.
How to develop awareness and interrupting of dysfunctional breathing response. Most participants are unaware of their somatic responses until symptoms occur. Being aware of the initiation of a somatic response may assist you in identifying triggers and interrupting the developing process. A significant component of the training is symptom prescription rehearsal.
Symptom prescription is a practice in which the participant simulates/acts out the psychophysiological pattern associated with their symptoms. They amplify the body pattern until they feel the onset of the actual symptoms. The moment the person feels the beginning of the symptom, they stop the practice and initiate slow breathing and relaxation. After practicing the symptom rehearsal, they are instructed to become aware of the onset of the symptom and then use that signal to trigger the effortless breathing while looking up and shifting the body into an upright sitting position (Peper et al., 2019). Gasping and breath holding are normal responses to unexpected stimuli; however, they may trigger sympathetic activation even when there is no actual danger.
Experiential practice: Developing awareness on neck and shoulder tension:
Sit comfortably and practice effortless breathing for a minute. Take a fearful gasp and observe what happens in your body (e.g., slight neck and upper chest tension, light headedness, slight radiating pain into the eye, etc.). Shift back to effortless breathing until all symptoms /sensations have disappeared.
- Now gasp with less effort and observe the first sensations, use the awareness of first sensations to trigger the effortless breathing and continue to breathe until symptoms have disappeared
- Continue this practice. Reduce the gasping effort each time.
- After having developed the initial somatic sensation then during the day observe what triggers this response and immediately shift to slower diaphragmatic breathing. After you have shifted to effortless breathing, reflect on the trigger. Was it necessary to react? If yes, explore strategies to resolve the issue.
The same process can be done to assist with desensitization to painful memories or stressful events. Each time the person becomes aware of their somatic reaction to an evoked memory or stressful event, they shift to effortless diaphragmatic breathing. If they find that it is difficult to interrupt the emotional memories and it triggers more and more negative thoughts and associations, use the sniff-hold-sniff technique and follow that with box-breathing or any of the other quick somatic rescue techniques (Peper et al., 2024a). Box-breathing in this context could include a brief breath-holding. A typical box-breathing technique is to breath in for a count of four, hold for a count of four, breath out for a count of four, then breath in again for a count of four, continuing the figurative 4-4-4-4 count of breathing.
Practice slower diaphragmatic breathing during the day. Implement effortless diaphragmatic breathing through regeneration and interrupting the stress response.
- Support regeneration. Each day set aside 10 to 20 minutes to practice slow effortless diaphragmatic breathing at about 6-breaths-per-minute. In the beginning 10 to 20 minutes may be too long, thus in some cases have the person practice a few times a day for two minutes and slowly build up to 10 or more minutes. The practice is not just a mechanical process of breathing it includes mindfulness training. Namely, as you are breathing each time you exhale imagine a flow doing down your arms and legs and as you inhale an energy coming into you. Whenever your attention drifts bring it back to the breathing.
- Integrate breathing with daily activities. Practice slower breather before eating, after putting the seat belt on in the car, or whenever a notification pops up on the cell phone.
- Set reminders and alarms on your phone to check how you are feeling and breathing. Leave notes on nearby furniture such as a nightstand, on the shower door, and/or on the kitchen table as reminders to be mindful of your breath. If stressed or breathing shallowly, take a moment to breathe slowly.
- Interrupt the stress response. During the day when you are aware that you shallow breathe, are holding your breath, feel anxious, experience neck and shoulder tightness, or worry and use that as a cue to shift position by sitting or standing more erect, looking upward and take a few slow diaphragmatic breaths.
- Use cue condition to facilitate this process. Each time you begin the practice smell a specific aroma or do some behavioral movement and then do the breathing. After a while the aroma or behavioral movement will become the classically conditioned cue to trigger the effortless breathing.
- Use role rehearsal and conditioning to generalize the skill. Generalizing the skills often takes more time than what may be expected. In a culture where instant relief is expected— implied message associated with medication— self-mastery techniques are different and challenging as they take time to master the skill and implement them during daily life. The process of mastery is similar to learning to play a musical instrument or sports. Learning to play the violin requires practice as well as practice with failures along the way until one is ready for more challenging musical pieces, recitals, or performances.
A useful strategy to implement the learning is role rehearsal in the office, at home at work, and in real life. It is usually much easier to practice these skills in a safe space such as your own room or, with a therapist compared to with other people or, at work. To generalize the skill most efficiently, it can be helpful to practice in a safe environment while imagining being in the actual stressful location This process is illustrated by the strategy to reduce social anxiety and menstrual cramps.
Social anxiety when seeing my supervisor. Master effortless breathing in a safe environment. Role rehearsal in imagery. If you observed that you held your breath when your supervisor is around, begin with imagery when your supervisor is not present. Sit, comfortably. Let go of muscle tension and breathe effortlessly, evoking a scenario where your supervisor is walking by and continue to breathe slowly as you imagine the scene. Role rehearsal in action. Ask another person to role-play your supervisor. Sit, comfortably. Let go of muscle tension and breathe effortlessly. Have this person walk into the room in a similar way that your supervisor would. Imagine that person is your supervisor while practicing your effortless breathing. Repeat until the effortless breathing is more automatic. Practice many times in real life. Whenever the rehearsed situation occurs, implement slower paced breathing.
Menstrual cramps that causes most women to curl up and breathe shallowly when experiencing menstrual cramps (Peper et al., 2023). Master effortless breathing in a safe environment. Practice breathing lying down. While lying down, breathe diaphragmatically by having a three-to-five-pound weight such as a bag of rice or hot water pad on your abdomen. If you have a partner, have the person stroke your legs from the abdomen to your toes while you exhale. Role rehearse experiencing pain and then practice lower diaphragmatic breathing. Namely, tighten your abdomen as if you have discomfort, then focus on relaxing the buttocks and sensing the air flowing down your legs and out your feet as you exhale. Practice in real life. A few days before you expected menstruation, practice slow diaphragmatic breathing several times for at least 5-10 minutes during the day. When your menstruation starts practice the slower and lower breathing while imagining the air flowing down the abdomen, through the legs and out the feet.
Summary/Conclusion
Breathing is the mind-body bridge. It usually occurs without awareness and breathing changes affect our thought, emotions and body. Mastering and implementing slower breathing during the day takes time and practice. By observing when breathing patterns change, participants may identify internal and external factors that affect breathing which provides an opportunity to implement effortless diaphragmatic breathing to optimize health as well as resolve some of the triggers. As one 20-year-old, female student reported,
The biggest benefit from learning diaphragmatic breathing was that it gave me the feeling of safety in many moments. My anxiety tended to make me feel unsafe in many situations but homing in and mastering diaphragmatic breathing helped tremendously. I shifted from constant chest breathing to acknowledging it and in turn, reminding myself to breathe with my diaphragm.
References
Allen, R. (2024). The health benefits of nose breathing. Nursing in General Practice. http://hdl.handle.net/10147/559021
Al-Rabia, M.W. (2016). Food-induced immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic rhinitis. J Microsc Ultrastruct, 4(2), 69-75. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1016/j.jmau.2015.11.004
Anziani, M. & Peper, E. (2021). Healing from paralysis-Music (toning) to activate health. Peperperspective –ideas on illness, health and well-being from Erik Peper. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://peperperspective.com/2021/11/22/healing-from-paralysis-music-toning-to-activate-health/
Banushi, B., Brendle, M., Ragnhildstveit, A., Murphy, T., Moore, C., Egberts, J., & Robison, R. (2023). Breathwork Interventions for Adults with Clinically Diagnosed Anxiety Disorders: A Scoping Review. Brain Sci. 13(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020256
Chung, A.H., Gevirtz, R.N., Gharbo, R.S. et al. (2021).Pilot Study on Reducing Symptoms of Anxiety with a Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Wearable and Remote Stress Management Coach. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 46, 347–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-021-09519-x
Cohen, D. & Leung, A.K.Y. (2009). The hard embodiment of culture. European Journal of Social Psychology, 9, 1278–1289 https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.671
Codrons, E., Bernardi, N. F., Vandoni, M., & Bernardi, L. (2014). Spontaneous group synchronization of movements and respiratory rhythms. PloS one, 9(9), e107538. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107538
Dick, T. E., Mims, J. R., Hsieh, Y. H., Morris, K. F., & Wehrwein, E. A. (2014). Increased cardio-respiratory coupling evoked by slow deep breathing can persist in normal humans. Respiratory physiology & neurobiology, 204, 99-111. https://doil.org/10.1016/j.resp.2014.09.013
Ekerholt, K. & Bergland, A. (2008). Breathing: A sign of life and a unique area for reflection and action. Physical therapy, 88(7), 832-840. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20070316
Elstad, M., O’Callaghan, E. L., Smith, A. J., Ben-Tal, A., & Ramchandra, R. (2018). Cardiorespiratory interactions in humans and animals: rhythms for life. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 315(1), H6-H17. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00701.2017
Folgering, H. (1999). The pathophysiology of hyperventilation syndrome. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis, 54(4), 365-72. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10546483/
Gilbert, C. (1998). Emotional sources of dysfunctional breathing. Journal of bodywork and movement therapies, 2(4), 224-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-8592(98)80019-3
Jerath, R., Beveridge, C., & Barnes, V.A. (2019). Self-Regulation of Breathing as an Adjunctive Treatment of Insomnia. Front Psychiatry, 9(780). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00780
Kahn, S. & Ehrlich, P.R. (2018). Jaws. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. https://www.amazon.com/Jaws-Hidden-Epidemic-Sandra-Kahn/dp/1503604136/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?_encoding=UTF8&qid=1685135054&sr=1-1
Kang, K.W., Jung, S.I., Lee, do Y., Kim, K., & Lee, N.K. (2016) Effect of sitting posture on respiratory function while using a smartphone. J Phys Ther Sci, 28(5), 1496-8. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.1496
Leal, R.B., Gomes, M.C., Granville-Garcia, A.F., Goes, P.S.A., & de Menezes, V.A. (2016). Impact of Breathing Patterns on the Quality of Life of 9- to 10-year-old Schoolchildren. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 30(5):e147-e152. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4363
Lehrer, P.M. & Gevirtz, R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work? Front Psychol. 5, 756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
Lundberg, J.O. & Weitzberg, E. (1999). Nasal nitric oxide in man. Thorax. (10):947-52. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.54.10.947
Luthe, W. (1979). About the Methods of Autogenic Therapy. In: Peper, E., Ancoli, S., Quinn, M. (eds). Mind/Body Integration. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2898-8_12
Luthe, W. & Schultz, J. H. (1970). Autogenic therapy: Medical applications. New York: Grune and Stratton. https://www.amazon.com/Autogenic-Therapy-II-Medical-Applications/dp/B001J9W7L6
MacHose, M., & Peper, E. (1991). The effect of clothing on inhalation volume. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 16(3), 261–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000020
Magnon. V., Dutheil, F., & Vallet, G.T. (2021). Benefits from one session of deep and slow breathing on vagal tone and anxiety in young and older adults. Sci Rep. 11(1),19267. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98736-9
Maric, V., Ramanathan, D., & Mishra, J. (2020). Respiratory regulation & interactions with neuro-cognitive circuitry. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 112, 95-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.02.001
Matić, Z., Platiša, M. M., Kalauzi, A., & Bojić, T. (2020). Slow 0.1 Hz breathing and body posture induced perturbations of RRI and respiratory signal complexity and cardiorespiratory coupling. Frontiers in physiology, 11, 24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00024
McKeown, P. (2021). The Breathing Cure: Develop New Habits for a Healthier, Happier, and Longer Life. Boca Raton, Fl “Humanix Books. https://www.amazon.com/BREATHING-CURE-Develop-Healthier-Happier/dp/1630061972/
Meehan, Z.M. & Shaffer, F. (2023). Adding Core Muscle Contraction to Wrist-Ankle Rhythmical Skeletal Muscle Tension Increases Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia and Low-Frequency Power. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 48(1), 127-134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-022-09568-w
McKeown, P. (2021). The breathing cure: Develop new habits for a healthier, happier, and longer life. Humanix Books. https://www.amazon.com/BREATHING-CURE-Develop-Healthier-Happier/dp/1630061972/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N. & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E. & Cohen, T. (2017). Inhale to Breathe Away Pelvic Floor Pain and Enjoy Intercourse. Biofeedback, 45 (1), 21–24. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.1.04
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Cuellar, Y., & Membrila, C. (2022). Reduce anxiety. NeuroRegulation, 9(2), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.9.2.91
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153-169. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.153
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Rosegard, E. (2024). Increase attention, concentration and school performance with posture feedback. Biofeedback, 52(2). https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-52.02.07 or https://www.researchgate.net/publication/383151816_WHAT_ABOUT_THIS_Increase_Attention_Concentration_and_School_Performance_with_Posture_Feedback
Peper, E. & MacHose, M. (1993). Symptom prescription: Inducing anxiety by 70% exhalation. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 18(3), 133-138. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999790
Peper, E., Mason, L., Harvey, R., Wolski, L, & Torres, J. (2020). Can acid reflux be reduced by breathing? Townsend Letters-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine, 445/446, 44-47. https://www.townsendletter.com/article/445-6-acid-reflux-reduced-by-breathing/
Peper, E., Mason, L., Huey, C. (2017). Healing irritable bowel syndrome with diaphragmatic breathing. Biofeedback. 45(4), 83–87. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.4.04
Peper, E., Oded, Y., & Harvey, R. (2024a). Quick somatic rescue techniques when stressed. Biofeedback, 52(1), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.5298/982312
Peper, E., Pollack, W., Harvey, R., Yoshino, A., Daubenmier, J. & Anziani, M. (2019a). Which quiets the mind more quickly and increases HRV: Toning or mindfulness? NeuroRegulation, 6(3), 128-133. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.12
Peper, E., Swatzyna, R., & Ong, K. (2023). Mouth breathing and tongue position: a risk factor for health. Biofeedback. 51(3), 74–78 https://doi.org/10.5298/912512
PTI. (2023 August 3). Often suck your stomach in to look slimmer in pictures? It can lead to ‘hourglass syndrome.’ The Economic Times Panache. Accessed March 26, 2024. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/magazines/panache/often-suck-your-stomach-in-to-look-slimmer-in-pictures-it-can-lead-to-hourglass-syndrome/articleshow/102392681.cms?from=mdr
Salah, H.M., Goldberg, L.R., Molinger, J., Felker, G.M., Applefeld, W., Rassaf, T., Tedford, R.J., Mirro, M., Cleland, J.GF., & Fudim, M. (2022). Diaphragmatic Function in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 80(17), 1647-1659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.08.760
Shaffer, F. & Meehan, Z.M. (2020). A Practical Guide to Resonance Frequency Assessment for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback. Frontiers in Neuroscience,14. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.570400
Steffen, P.R., Austin, T., DeBarros, A., & Brown, T. (2017). The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood. Front Public Health, 5, 222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2017.00222
Taub, E., Uswatte, G., Mark, V. W., Morris, D. M. (2006). The learned nonuse phenomenon: Implications for rehabilitation. Europa Medicophysica, 42(3), 241-256. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17039223/
van Bon, M.J., Zielhuis, G.A., Rach, G.H., & van den Broek, P. (1989). Otitis media with effusion and habitual mouth breathing in Dutch preschool children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, (2), 119-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-5876(89)90087-6
Xiao, M., Zi-Qi, Y., Gong, Z.Q., Zhang, H., Duan, N.Y., Shi, Y.T,, Wei, G.X., Li, Y.F. (2017).The Effect of Diaphragmatic Breathing on Attention, Negative Affect and Stress in Healthy Adults. Front Psychol. 8(874). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00874
Cellphones affects social communication, vision, breathing, and health: What to do!
Posted: September 4, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, cellphone, computer, digital devices, educationj, ergonomics, health, laptops, Neck and shoulder discomfort, posture, screen fatigue, self-healing, stress management, techstress, Uncategorized, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: communication, myopia, pedestrian deaths, peripheral vision, text neck 7 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. & Harvey, R. (2024). Cell phones affects social communication, vision, breathing, and mental and physical health: What to do! TownsendLetter-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine,September 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/smartphone-affects-social-communication-vision-breathing-and-mental-and-physical-health-what-to-do/

Abstract
Smartphones are an indispensable part of our lives. Unfortunately too much of a ‘good thing’ regarding technology can work against us, leading to overuse, which in turn influences physical, mental and emotional development among current ‘Generation Z’ and ‘Millennial’ users (e.g., born 1997-2012, and 1981-1996, respectively). Compared to older technology users, Generation Z report more mental and physical health problems. Categories of mental health include attentional deficits, feelings of depression, anxiety social isolation and even suicidal thoughts, as along with physical health complaints such as sore neck and shoulders, eyestrain and increase in myopia. Long duration of looking downward at a smartphone affects not only eyestrain and posture but it also affects breathing which burden overall health. The article provides evidence and practices so show how technology over use and slouching posture may cause a decrease in social interactions and increases in emotional/mental and physical health symptoms such as eyestrain, myopia, and body aches and pains. Suggestions and strategies are provided for reversing the deleterious effects of slouched posture and shallow breathing to promote health.
We are part of an uncontrolled social experiment
We, as technology users, are all part of a social experiment in which companies examine which technologies and content increase profits for their investors (Mason, Zamparo, Marini, & Ameen, 2022). Unlike University research investigations which have a duty to warn of risks associated with their projects, we as participants in ‘profit-focused’ experiments are seldom fully and transparently informed of the physical, behavioral and psychological risks (Abbasi, Jagaveeran, Goh, & Tariq, 2021; Bhargava, & Velasquez, 2021). During university research participants must be told in plain language about the risks associated with the project (Huh-Yoo & Rader, 2020; Resnik, 2021). In contrast for-profit technology companies make it possible to hurriedly ‘click through’ terms-of-service and end-user-license-agreements, ‘giving away’ our rights to privacy, then selling our information to the highest bidder (Crain, 2021; Fainmesser, Galeotti, & Momot, 2023; Quach et al., 2022; Yang, 2022).
Although some people remain ignorant and or indifferent (e.g., “I don’t know and I don’t care”) about the use of our ‘data,’ an unintended consequence of becoming ‘dependent’ on technology overuse includes the strain on our mental and physical health (Abusamak, Jaber & Alrawashdeh, 2022; Padney et al., 2020). We have adapted new technologies and patterns of information input without asking the extent to which there were negative side effects (Akulwar-Tajane, Parmar, Naik & Shah, 2020; Elsayed, 2021). As modern employment shifted from predominantly blue-collar physical labor to white collar information processing jobs, people began sitting more throughout the day. Workers tended to look down to read and type. ‘Immobilized’ sitting for hours of time has increased as people spend time working on a computer/laptop and looking down at smartphones (Park, Kim & Lee, 2020). The average person now sits in a mostly immobilized posture 10.4 hours/day and modern adolescents spent more than two thirds of their waking time sitting and often looking down at their smartphones (Blodgett, et al., 2024; Arundell et al., 2019).
Smartphones are an indispensable part of our lives and is changing the physical and mental emotional development especially of Generation Z who were born between 1997-2012 (Haidt, 2024). They are the social media and smartphone natives (Childers & Boatwright, 2021). The smartphone is their personal computer and the gateway to communication including texting, searching, video chats, social media (Hernandez-de-Menendez, Escobar Díaz, & Morales-Menendez, 2020; Nichols, 2020; Schenarts, 2020; Szymkowiak et al., 2021). It has 100,000 times the processing power of the computer used to land the first astronauts on the moon on July 20, 1969 according to University of Nottingham’s computer scientist Graham Kendal (Dockrill, 2020). More than one half of US teens spend on the average more than 7 hours on daily screen time that includes watching streaming videos, gaming, social media and texting and their attention span has decreased from 150 seconds in 2004 to an average of 44 seconds in 2021 (Duarte, F., 2023; Mark, 2022, p. 96).
For Generation Z, social media use is done predominantly with smartphones while looking down. It has increased mental health problems such as attentional deficits, depression, anxiety suicidal thoughts, social isolation as well as decreased physical health (Haidt, 2024; Braghieri et al., 2023; Orsolini, Longo & Volpe, 2023; Satılmış, Cengız, & Güngörmüş, 2023; Muchacka-Cymerman, 2022; Fiebert, Kistner, Gissendanner & DaSilva, 2021; Mohan et al., 2021; Goodwin et al., 2020).
The shift in communication from synchronous (face-to-face) to asynchronous (texting) has transformed communications and mental health as it allows communication while being insulated from the other’s reactions (Lewis, 2024). The digital connection instead of face-to-face connection by looking down at the smart phone also has decreased the opportunity connect with other people and create new social connections, with three typical hypotheses examining the extent to which digital technologies (a) displace/ replace; (b) compete/ interfere with; and/or, (c) complement/ enhance in-person activities and relationships (Kushlev & Leitao, 2020).
As described in detail by Jonathan Haidt (2024), in his book, The Anxious Generation, the smartphone and the addictive nature of social media combined with the reduction in exercise, unsupervised play and childhood independence was been identified as the major factors in the decrease in mental health in your people (Gupta, 2023). This article focuses less on distraction such as attentional deficits, or dependency leading to tolerance, withdrawal and cravings (e.g., addiction-like symptoms) and focuses more on ‘dysregulation’ of body awareness (posture and breathing changes) and social communication while people are engaged with technology (Nawaz,Bhowmik, Linden & Mitchell, 2024).
The excessive use of the smartphones is associated with a significant reduction of physical activity and movement leading to a so-called sedentarism or increases of sitting disease (Chandrasekaran & Ganesan, 2021; Nakshine, Thute, Khatib, & Sarkar, 2022). Unbeknown to the smartphone users their posture changes, as they looks down at their screen, may also affect their mental and physical health (Aliberti, Invernizzi, Scurati & D’lsanto, 2020).
(1) Explore how looking at your smartphone affects you (adapted from: Peper, Harvey, & Rosegard, 2024)
For a minute, sit in your normal slouched position and look at your smartphone while intensely reading the text or searching social media. For the next minute sit tall and bring the cell phone in front of you so you can look straight ahead at it. Again, look at your smartphone while intensely reading the text or searching social media.
Compare how the posture affects you. Most likely, your experience is similar to the findings from students in a classroom observational study. Almost all experienced a reduction in peripheral awareness and breathed more shallowly when they slouched while looking at their cellphone.
Decreased peripheral awareness and increased shallow breathing that affects physical and mental health and performance. The students reported looking down position reduces the opportunity of creating new social connections. Looking down my also increases the risk for depression along with reduced cognitive performance during class (Peper et al., 2017; Peper et al., 2018).
(2) Explore how posture affects eye contact (adapted from the exercise shared by Ronald Swatzyna, 2023)[2]
Walk around your neighborhood or through campus either looking downwards or straight ahead for 30 minutes while counting the number of eye contacts you make.
Most likely, when looking straight ahead and around versus slouched and looking down you had the same experience as Ronald Swatzyna (2023), Licensed Clinical Social Worker. He observed that when he walked a three-mile loop around the park in a poor posture with shoulders forward in a head down position, and then reversed direction and walked in good posture with the shoulders back and the head level, he would make about five times as many eye contacts with a good posture compared to the poor posture.
Anecdotal observations, often repeated by many educators, suggest before the omnipresent smartphone, students would look around and talk to each other before a university class began. Now, when Generation Z students enter an in-person class, they sit down, look down at their phone and tend not to interact with other students.
(3) Experience the effect of face-to-face in-person communication
During the first class meeting, ask students to put their cellphones away, meet with three or four other students for a few minutes, and share a positive experience that happened to them last week as well as what they would like to learn in the class. After a few minutes, ask them to report how their energy and mood changed.
In our observational class study with 24 junior and senior college students in the in-person class and 54 students in the online zoom class, almost all report that that their energy and positive mood increased after they interacted with each other. The effects were more beneficial for the in-person small group sharing than the online breakout groups sharing on Zoom as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Change in subjective energy and mood after sharing experiences synchronously in small groups either in-person or online.
Without direction of a guided exercise to increase social connections, students tend to stay within their ‘smartphone bubble’ while looking down (Bochicchio et al., 2022). As a result, they appear to be more challenged to meet and interact with other people face-to-face or by phone as is reflected in the survey data that Generation Z is dating much less and more lonely than the previous generations (Cox et al., 2023).
What to do:
- Put the smartphone away so that you do not see it in social settings such as during meals or classes. This means that other people can be present with you and the activity of eating or learning.
- Do not permit smartphones in the classroom including universities unless it is required for a class assignment.
- In classrooms and in the corporate world, create activities that demands face-to-face synchronous communication.
- Unplug from the audio programs when walking and explore with your eyes what is going on around you.
(4) Looking down increases risk of injury and death
Looking down at a close screen reduces peripheral awareness and there by increases the risk of accidents and pedestrian deaths. Pedestrian deaths are up 69% since 2011 (Cova, 2024) and have consistently increased since the introduction of the iPhone in 2007 as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Increase in pedestrian death since the introduction of the iphone (data plotted from https://www.iihs.org/topics/fatality-statistics/detail/pedestrians)
In addition, the increase use of mobile phones is also associated with hand and wrist pain from overuse and with serious injuries such as falls and texting while driving due to lack of peripheral awareness. McLaughlin et al (2023) reports an increase in hand and wrist injuries as well serious injuries related to distracted behaviors, such as falls and texting while driving. The highest phone related injuries (lacerations) as reported from the 2011 to 2020 emergency room visits were people in the age range from 11–20 years followed by 21–30 years.
What to do:
- Do not walk while looking at your smartphone. Attend to the environment around you.
- Unplug from the audio podcasts when walking and explore with your eyes what is going on around you.
- Sit or stop walking when answering the smartphone to reduce the probability of an accident.
- For more pragmatic suggestions, see the book, TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics, by Peper, Harvey and Faass (2020).
(5) Looking at screens increases the risk of myopia
Looking at a near screen for long periods of time increases the risk of myopia (near sightedness) which means that distant vision is more blurry. Myopia has increased as children predominantly use computers or, smartphones with smaller screen at shorter distances. By predominantly focusing on nearby screens without allowing the eye to relax remodels the eyes structure. Consequently, myopia has increase in the U.S. from 25 percent in the early 1970s to nearly 42 percent three decades later (OHSU, 2022).
Looking only at nearby screens, our eyes converge and the ciliary muscles around the lens contract and remain contracted until the person looks at the far distance. The less opportunity there is to allow the eyes to look at distant vision, the more myopia occurs. in Singapore 80 per cent of young people aged 18 or below have nearsightedness and 20 % of the young people have high myopia as compared to 10 years ago (Singapore National Eye Centre, 2024). The increase in myopia is a significant concern since high myopia is associated with an increased risk of vision loss due to cataract, glaucoma, and myopic macular degeneration (MMD). MMD is rapidly increasing and one of the leading causes of blindness in East Asia that has one of the highest myopia rates in the world (Sankaridurg et al., 2021).
What to do:
- Every 20 minutes stop looking at the screen and look at the far distance to relax the eyes for 20 seconds.
- Do not allow young children access to cellphones or screens. Let them explore and play in nature where they naturally alternate looking at far and near objects.
- Implement the guided eye regenerating practices descrubed in the article, Resolve eyestrain and screen fatigue, by Peper (2021).
- Read Meir Schneider’s (2016) book, Vision for Life, for suggestions how to maintain and improve vision.
(6) Looking down increases tech neck discomfort
Looking down at the phone while standing or sitting strains the neck and shoulder muscles because of the prolonged forward head posture as illustrated in the YouTube video, Tech Stress Symptoms and Causes (DeWitt, 2018). Using a smartphone while standing or walking causes a significant increase in thoracic kyphosis and trunk (Betsch et al., 2021). When the head is erect, the muscle of the neck balance a weight of about 10 to 12 pounds or, approximately 5 kilograms; however, when the head is forward at 60 degrees looking at your cell phone the forces on the muscles are about 60 pound or more than 25 kilograms, as illustrated in Figure 4 (Hansraj, 2014).

Figure 4. The head forward position puts as much as sixty pounds of pressure on the neck muscles and spine (by permission from Dr. Kenneth Hansraj, 2014).
This process is graphically illustrated in the YouTube video, Text Neck Symptoms and Causes Video, produced by Veritas Health (2020).
What to do:
- Keep the phone in front of you so that you do not slouch down by having your elbow support on the table.
- Every ten minutes stretch, look up and roll your shoulders backwards.
- Wear a posture feedback device such as the UpRight Go 2 to remind you when you slouch to change posture and activity (Peper et al., 2019; Stuart, Godfrey & Mancini, 2022).
- Take Alexander Technique lessons to improve your posture (Cacciatore, Johnson, & Cohen, 2020; AmAT, 2024; STAT, 2024).
(7) Looking down increases negative memory recall and depression
In our previous research, Peper et al. (2017) have found that recalling hopeless, helpless, powerless, and defeated memories is easier when sitting in a slouched position than in an upright position. Recalling positive memories is much easier when sitting upright and looking slightly upward than sitting slouched position. If attempting to recall positive memories the brain has to work hard as indicated by an significantly higher amplitudes of beta2, beta3, and beta4 EEG (i.e., electroencephalograph) when sitting slouched then when sitting upright (Tsai et al., 2016).
Not only does the postural position affect memory recall, it also affects mental math under time-pressure performance. When students sit in a slouched position, they report that is much more difficult to do mental math (serial 7ths) than when in the upright position (Peper et al., 2018). The effect of posture is most powerful for the 70% of students who reported that they blanked out on exams, were anxious, or worried about class performance or math. For the 30% who reported no performance anxiety, posture had no significant effect. When students become aware of slouching thought posture feedback and then interrupt their slouching by sitting up, they report an increase in concentration, attention and school performance (Peper et al., 2024).
How we move and walk also affects our subjective energy. In most cases, when people sit for a long time, they report feeling more fatigue; however, if participants interrupt sitting with short movement practices they report becoming less fatigue and improved cognition (Wennberg et al., 2016). The change in subjective energy and mood depends upon the type of movement practice. Peper & Lin (2012) reported that when students were asked to walk in a slow slouching pattern looking down versus to walk quickly while skipping and looking up, they reported that skipping significantly increased their subjective energy and mood while the slouch walking decreased their energy. More importantly, student who had reported that they felt depressed during the last two years had their energy decrease significantly more when walking very slowly while slouched than those who did not report experiencing depression. Regardless of their self-reported history of depression, when students skipped, they all reported an increase in energy (Peper & Lin, 2012; Miragall et al., 2020).
What to do:
- Walk with a quick step while looking up and around.
- Wear a posture feedback device such as the UpRight Go 2 to remind you when you slouch to change posture and activity (Peper et al., 2019; Roggio et al., 2021).
- When sitting put a small pillow in the mid back so that you can sit more erect (for more suggestions, see the article by Peper et al., 2017a, Posture and mood: Implications and applications to therapy).
- Place photo and other objects that you like to look a slightly higher on your wall so that you automatically look up.
(8) Shallow breathing increases the risk for anxiety
When slouching we automatically tend to breathe slightly faster and more shallowly. This breathing pattern increases the risk for anxiety since it tends to decrease pCO2 (Feinstein et al., 2022; Meuret, Rosenfield, Millard & Ritz, 2023; Paulus, 2013; Smits et al., 2022; Van den Bergh et al., 2013). Sitting slouched also tends to inhibit abdominal expansion during the inhalation because the waist is constricted by clothing or a belt –sometimes labeled as ‘designer jean syndrome’ and may increase abdominal symptoms such as acid reflux and irritable bowel symptoms (Engeln & Zola, 2021; Peper et al., 2016; Peper et al., 2020). When students learn diaphragmatic breathing and practice diaphragmatic breathing whenever they shallow breathe or hold their breath, they report a significant decrease in anxiety, abdominal symptoms and even menstrual cramps (Haghighat et al., 2020; Peper et al., 2022; Peper et al., 2023).
What to do:
- Loosen your belt and waist constriction when sitting so that the abdomen can expand.
- Learn and practice effortless diaphragmatic breathing to reduce anxiety.
Conclusion
There are many topics related to postural health and technology overuse that were addressed in this article. Some topics are beyond the scope of the article, and therefore seen as limitations. These relate to diagnosis and treatment of attentional deficits, or dependency leading to tolerance, withdrawal and cravings (e.g., addiction-like symptoms), or of modeling relationships between factors that contribute to the increasing epidemic of mental and physical illness associated with smartphone use and social media, such as hypotheses examining the extent to which digital technologies (a) displace/ replace; (b) compete/ interfere with; and/or, (c) complement/ enhance in-person activities and relationships. Typical pharmaceutical ‘treat-the-symptom’ approaches for addressing ‘tech stress’ related to technology overuse includes prescribing ‘anxiolytics, pain-killers and muscle relaxants’ (Kazeminasab et al., 2022; Kim, Seo, Abdi, & Huh, 2020). Although not usually included in diagnosis and treatment strategies, suggesting improving posture and breathing practices can significantly affect mental and physical health. By changing posture and breathing patterns, individuals may have the option to optimize their health and well-being.
See the book, TechStress-How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey and Nancy Faass. Available from: https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X/

Explore the following blogs for more background and useful suggestions
References
Abbasi, G. A., Jagaveeran, M., Goh, Y. N., & Tariq, B. (2021). The impact of type of content use on smartphone addiction and academic performance: Physical activity as moderator. Technology in Society, 64, 101521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101521
Abusamak, M., Jaber, H. M., & Alrawashdeh, H. M. (2022). The effect of lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic on digital eye strain symptoms among the general population: a cross-sectional survey. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, 895517. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.895517
Akulwar-Tajane, I., Parmar, K. K., Naik, P. H., & Shah, A. V. (2020). Rethinking screen time during COVID-19: impact on psychological well-being in physiotherapy students. Int J Clin Exp Med Res, 4(4), 201-216. https://doi.org/10.26855/ijcemr.2020.10.014
Aliberti, S., Invernizzi, P. L., Scurati, R., & D’Isanto, T. (2020). Posture and skeletal muscle disorders of the neck due to the use of smartphones. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise , 15 (3proc), S586-S598. https://www.jhse.ua.es/article/view/2020-v15-n3-proc-posture-skeletal-muscle-disorders-neck-smartpho; https://air.unimi.it/retrieve/handle/2434/774436/1588570/HSE%20-%20Posture%20and%20skeletal%20muscle%20disorders.pdf
AmSAT. (2024). American Society for the Alexander Technique. Accessed July 27, 2024. https://alexandertechniqueusa.org/
Arundell, L., Salmon, J., Koorts, H. et al. (2019). Exploring when and how adolescents sit: cross-sectional analysis of activPAL-measured patterns of daily sitting time, bouts and breaks. BMC Public Health 19, 653. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-6960-5
Bhargava, V. R., & Velasquez, M. (2021). Ethics of the attention economy: The problem of social media addiction. Business Ethics Quarterly, 31(3), 321-359. https://doi.org/10.1017/beq.2020.32
Betsch, M., Kalbhen, K., Michalik, R., Schenker, H., Gatz, M., Quack, V., Siebers, H., Wild, M., & Migliorini, F. (2021). The influence of smartphone use on spinal posture – A laboratory study. Gait Posture, 85, 298-303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.02.018
Blodgett, J.M., Ahmadi, M.N., Atkin, A.J., Chastin, S., Chan, H-W., Suorsa, K., Bakker, E.A., Hettiarcachchi, P., Johansson, P.J., Sherar,L. B., Rangul, V., Pulsford, R.M…. (2024). ProPASS Collaboration , Device-measured physical activity and cardiometabolic health: the Prospective Physical Activity, Sitting, and Sleep (ProPASS) consortium, European Heart Journal, 45(6) 458–471, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad717
Bochicchio, V., Keith, K., Montero, I., Scandurra, C., & Winsler, A. (2022). Digital media inhibit self-regulatory private speech use in preschool children: The “digital bubble effect”. Cognitive Development, 62, 101180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogdev.2022.101180
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social Media and Mental Health (July 28, 2022). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Cacciatore, T. W., Johnson, P. M., & Cohen, R. G. (2020). Potential mechanisms of the Alexander technique: Toward a comprehensive neurophysiological model. Kinesiology Review, 9(3), 199-213. https://doi.org/10.1123/kr.2020-0026
Chandrasekaran, B., & Ganesan, T. B. (2021). Sedentarism and chronic disease risk in COVID 19 lockdown–a scoping review. Scottish Medical Journal, 66(1), 3-10. https://doi.org/10.1177/0036933020946336
Childers, C., & Boatwright, B. (2021). Do digital natives recognize digital influence? Generational differences and understanding of social media influencers. Journal of Current Issues & Research in Advertising, 42(4), 425-442. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641734.2020.1830893
Cox, D.A., Hammond, K.E., & Gray, K. (2023). Generation Z and the Transformation of American Adolescence: How Gen Z’s Formative Experiences Shape Its Politics, Priorities, and Future. Survey Center of American Life, November 23, 2023. Accessed July 4, 2024. https://www.americansurveycenter.org/research/generation-z-and-the-transformation-of-american-adolescence-how-gen-zs-formative-experiences-shape-its-politics-priorities-and-future/
Crain, M. (2021). Profit over privacy: How surveillance advertising conquered the internet. U of Minnesota Press. https://www.amazon.com/Profit-over-Privacy-Surveillance-Advertising/dp/1517905044
Cova, E. (2024). Pedestrian fatalities at historic high. Smart Growth America (data from U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT). Accessed July 2, 2024. https://smartgrowthamerica.org/pedestrian-fatalities-at-historic-high/
Duarte, F. (2023). Average Screen Time for Teens (2024). Exploding Topics. Accessed July 5, 2024. https://explodingtopics.com/blog/screen-time-for-teens#average
DeWitt, D. (2018). How Does Text Neck Cause Pain? Spine-Health October 26, 2018. Accessed July 5, 2024. https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/neck-pain/how-does-text-neck-cause-pain
Dockrill, P. (2020). Your laptop charger is more powerful than Apollo11’s computer, says apple developer. Science Alert, Janural 12, 2020. Accessed July 4, 2024. https://www.sciencealert.com/apollo-11-s-computer-was-less-powerful-than-a-usb-c-charger-programmer-discovers
Elsayed, W. (2021). Covid-19 pandemic and its impact on increasing the risks of children’s addiction to electronic games from a social work perspective. Heliyon, 7(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08503
Engeln, R., & Zola, A. (2021). These boots weren’t made for walking: gendered discrepancies in wearing painful, restricting, or distracting clothing. Sex roles, 85(7), 463-480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-021-01230-9
Fainmesser, I. P., Galeotti, A., & Momot, R. (2023). Digital privacy. Management Science, 69(6), 3157-3173. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2022.4513
Feinstein, J. S., Gould, D., & Khalsa, S. S. (2022). Amygdala-driven apnea and the chemoreceptive origin of anxiety. Biological psychology, 170, 108305. https://10.1016/j.biopsycho.2022.108305
Fiebert, I., Kistner, F., Gissendanner, C., & DaSilva, C. (2021). Text neck: An adverse postural phenomenon. Work, 69(4), 1261-1270. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-213547
Goodwin, R. D., Weinberger, A. H., Kim, J. H., Wu. M., & Galea, S. (2020). Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008–2018: Rapid increases among young adults. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 130, 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.08.014
Gupta, N. (2023). Impact of smartphone overuse on health and well-being: review and recommendations for life-technology balance. Journal of Applied Sciences and Clinical Practice, 4(1), 4-12. https://doi.org/10.4103/jascp.jascp_40_22
Haghighat, F., Moradi, R., Rezaie, M., Yarahmadi, N., & Ghaffarnejad, F. (2020). Added Value of Diaphragm Myofascial Release on Forward Head Posture and Chest Expansion in Patients with Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-53279/v1
Haidt, J. (2024). The Anxious generation: How the great rewiring of childhood is causing an epidemic of mental illness. New York: Penguin Press. https://www.anxiousgeneration.com/book
Hansraj, K.K. (2014). Assessment of stresses in the cervical spine caused by posture and position of the head. Surg Technol Int. 25, 277-279. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25393825/
Hernandez-de-Menendez, M., Escobar Díaz, C. A., & Morales-Menendez, R. (2020). Educational experiences with Generation Z. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM), 14(3), 847-859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-020-00674-9
Huh-Yoo, J., & Rader, E. (2020). It’s the Wild, Wild West: Lessons learned from IRB members’ risk perceptions toward digital research data. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 4(CSCW1), 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1145/3392868
IIHS (2024). Fatality Facts 2022Pedestrians. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). Accessed July 2, 2024. https://www.iihs.org/topics/fatality-statistics/detail/pedestrians
Kazeminasab, S., Nejadghaderi, S. A., Amiri, P., Pourfathi, H., Araj-Khodaei, M., Sullman, M. J., … & Safiri, S. (2022). Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC musculoskeletal disorders, 23, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04957-4
Kim, K. H., Seo, H. J., Abdi, S., & Huh, B. (2020). All about pain pharmacology: what pain physicians should know. The Korean journal of pain, 33(2), 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2020.33.2.108
Kushlev, K., & Leitao, M. R. (2020). The effects of smartphones on well-being: Theoretical integration and research agenda. Current opinion in psychology, 36, 77-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.05.001
Lewis, H.R. (2024). Mechanical intelligence and counterfeit humanity. Harvard Magazine, 126(6), 38-40. https://www.harvardmagazine.com/2024/07/harry-lewis-computers-humanity#google_vignette
Mark, G. (2023). Attention Span: A Groundbreaking Way to Restore Balance, Happiness and Productivity. Toronto, Canada: Hanover Square Press. https://www.amazon.com/Attention-Span-Finding-Fighting-Distraction-ebook/dp/B09XBJ29W9
Mason, M. C., Zamparo, G., Marini, A., & Ameen, N. (2022). Glued to your phone? Generation Z’s smartphone addiction and online compulsive buying. Computers in Human Behavior, 136, 107404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107404
McLaughlin, W.M., Cravez, E., Caruana, D.L., Wilhelm, C., Modrak, M., & Gardner, E.C. (2023). An Epidemiological Study of Cell Phone-Related Injuries of the Hand and Wrist Reported in United States Emergency Departments From 2011 to 2020. J Hand Surg Glob, 5(2),184-188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2022.11.009
Meuret, A. E., Rosenfield, D., Millard, M. M., & Ritz, T. (2023). Biofeedback Training to Increase Pco2 in Asthma With Elevated Anxiety: A One-Stop Treatment of Both Conditions?. Psychosomatic medicine, 85(5), 440-448. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0000000000001188
Miragall, M., Borrego, A., Cebolla, A., Etchemendy, E., Navarro-Siurana, J., Llorens, R., … & Baños, R. M. (2020). Effect of an upright (vs. stooped) posture on interpretation bias, imagery, and emotions. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 68, 101560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101560
Mohan, A., Sen, P., Shah, C., Jain, E., & Jain, S. (2021). Prevalence and risk factor assessment of digital eye strain among children using online e-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: Digital eye strain among kids (DESK study-1). Indian journal of ophthalmology, 69(1), 140-144. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_2535_20
Muchacka-Cymerman, A. (2022). ‘I wonder why sometimes I feel so angry’ The associations between academic burnout, Facebook intrusion, phubbing, and aggressive behaviours during pandemic Covid 19. Polish Psychological Bulletin, 53(4). https://doi.org/10.24425/ppb.2022.143376
Nakshine, V. S., Thute, P., Khatib, M. N., & Sarkar, B. (2022). Increased screen time as a cause of declining physical, psychological health, and sleep patterns: a literary review. Cureus, 14(10). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.30051
Nawaz, S., Bhowmik, J., Linden, T., & Mitchell, M. (2024). Validation of a modified problematic use of mobile phones scale to examine problematic smartphone use and dependence. Heliyon, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24832
Nicholas, A. J. (2020). Preferred learning methods of generation Z. Faculty and Staff – Articles & Papers. Digital Commons @ Salve Regina. Salve Regina University. https://digitalcommons.salve.edu/fac_staff_pub/74
OHSU. (2022). Myopia on the rise, especially among children. Casey Eye Institute. Oregan Health and Science University. Accessed July 7, 2024. https://www.ohsu.edu/casey-eye-institute/myopia-rise-especially-among-children
Orsolini, L., Longo, G., & Volpe, U. (2023). The mediatory role of the boredom and loneliness dimensions in the development of problematic internet use. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054446
Pandey, R., Gaur, S., Kumar, R., Kotwal, N., & Kumar, S. (2020). Curse of the technology-computer related musculoskeletal disorders and vision syndrome: a study. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 8(2), 661. https://doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20200253
Park, J. C., Kim, S., & Lee, H. (2020). Effect of work-related smartphone use after work on job burnout: Moderating effect of social support and organizational politics. Computers in human behavior, 105, 106194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.106194
Paulus, M.P. (2013). The breathing conundrum-interoceptive sensitivity and anxiety. Depress Anxiety.30(4), 315-20. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22076
Peper, E. (2021). Resolve eyestrain and screen fatigue. Well Being Journal, 30(1), 24-28. https://wellbeingjournal.com/resolve-eyestrain-and-screen-fatigue/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N. & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Cuellar, Y., & Membrila, C. (2022). Reduce anxiety. NeuroRegulation, 9(2), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.9.2.91
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Mason, L. (2019). “Don’t slouch!” Improve health with posture feedback. Townsend Letter-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine, 436, 58-61. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337424599_Don%27t_slouch_Improve_health_with_posture_feedback
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Mason, L., & Lin, I.-M. (2018). Do better in math: How your body posture may change stereotype threat response. NeuroRegulation, 5(2), 67–74. http://dx.doi.org/10.15540/nr.5.2.67
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Rosegard, E. (2024). Increase attention, concentration and school performance with posture feedback. Biofeedback, 52(2). https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-52.02.07
Peper, E. & Lin, I-M. (2012). Increase or decrease depression-How body postures influence your energy level. Biofeedback, 40 (3), 126-130. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-40.3.01
Peper, E., Lin, I-M, & Harvey, R. (2017a). Posture and mood: Implications and applications to therapy. Biofeedback, 35(2), 42-48. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.03
Peper, E., Lin, I-M., Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback.45 (2), 36-41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E., Mason, L., Harvey, R., Wolski, L, & Torres, J. (2020). Can acid reflux be reduced by breathing? Townsend Letters-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine, 445/446, 44-47. https://www.townsendletter.com/article/445-6-acid-reflux-reduced-by-breathing/
Quach, S., Thaichon, P., Martin, K. D., Weaven, S., & Palmatier, R. W. (2022). Digital technologies: tensions in privacy and data. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 50(6), 1299-1323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-022-00845-y
Resnik, D. B. (2021). Standards of evidence for institutional review board decision-making. Accountability in research, 28(7), 428-455. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989621.2020.1855149
Roggio, F., Ravalli, S., Maugeri, G., Bianco, A., Palma, A., Di Rosa, M., & Musumeci, G. (2021). Technological advancements in the analysis of human motion and posture management through digital devices. World journal of orthopedics, 12(7), 467. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v12.i7.467
Sankaridurg, P., Tahhan, N., Kandel, H., Naduvilath, T., Zou, H., Frick,K.D., Marmamula, S., Friedman, D.S., Lamoureux, e. Keeffe, J. Walline, J.J., Fricke, T.R., Kovai, V., & Resnikoff, S. (2021) IMI Impact of Myopia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci, 62(5), 2. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.62.5.2
Satılmış, S. E., Cengız, R., & Güngörmüş, H. A. (2023). The relationship between university students’ perception of boredom in leisure time and internet addiction during social isolation process. Bağımlılık Dergisi, 24(2), 164-173. https://doi.org/10.51982/bagimli.1137559
Schenarts, P. J. (2020). Now arriving: surgical trainees from generation Z. Journal of surgical education, 77(2), 246-253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2019.09.004
Schneider, M. (2016). Vision for life. Ten Steps to Natural Eyesight Improvement. Berkeley: North Atlantic books. https://www.amazon.com/Vision-Life-Revised-Eyesight-Improvement/dp/1623170087
Singapore National Eye Centre. (2024). Severe myopia cases among children in Singapore almost doubled in past decade. CAN. Accessed July 4, 2024. https://www.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/myopia-children-cases-almost-double-glasses-eye-checks-4250266
Smits, J. A., Monfils, M. H., Otto, M. W., Telch, M. J., Shumake, J., Feinstein, J. S., … & Exposure Therapy Consortium. (2022). CO2 reactivity as a biomarker of exposure-based therapy non-response: study protocol. BMC psychiatry, 22(1), 831. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-022-04478-x
STAT (2024). The society of teachers of the Alexander Technique. Assessed July 27, 2024. https://alexandertechnique.co.uk/
Stuart, S., Godfrey, A., & Mancini, M. (2022). Staying UpRight in Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study of a novel wearable postural intervention. Gait & Posture, 91, 86-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.09.202
Swatzyna, R. (2023). Personal communications.
Szymkowiak, A., Melović, B., Dabić, M., Jeganathan, K., & Kundi, G. S. (2021). Information technology and Gen Z: The role of teachers, the internet, and technology in the education of young people. Technology in Society, 65, 101565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101565
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I. M.*(2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23-27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
Van den Bergh, O., Zaman, J., Bresseleers, J., Verhamme, P., Van Diest, I. (2013). Anxiety, pCO2 and cerebral blood flow, International Journal of Psychophysiology, 89 (1), 72-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.05.011
Veritas Health. (2020). Text Neck Symptoms and Causes Video. YouTube video, accessed August 29, 2024. https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/neck-pain/how-does-text-neck-cause-pain?source=YT
Wennberg, P., Boraxbekk, C., Wheeler, M., et al. (2016). Acute effects of breaking up prolonged sitting on fatigue and cognition: a pilot study. BMJ Open, 6, e009630. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009630
Yang, K. H. (2022). Selling consumer data for profit: Optimal market-segmentation design and its consequences. American Economic Review, 112(4), 1364-1393. https://www.aeaweb.org/articles/pdf/doi/10.1257/aer.20210616
[1] Correspondence should be addressed to: Erik Peper, Ph.D., Institute for Holistic Health Studies, Department of Recreation, Parks, Tourism and Holistic Health, San Francisco State University, 1600 Holloway Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94132 Email: epeper@sfsu.edu; web: www.biofeedbackhealth.org; blog: www.peperperspective.com
[2] I thank Ronald Swatzyna (2023), Licensed Clinical Social Worker for sharing this exercise with me. He discovered that a difference in the number of eye contacts depending how he walked. When he walked a 3.1 mile loop around the park in a poor posture- shoulders forward, head down position- and then reversed direction and walked in good posture with the shoulders back and the head level, that that he make about 5 times as many eye contacts with good posture compared to the poor posture. He observed that he make about five times as many eye contacts with good posture as compared to the poor posture.
Increase attention, concentration and school performance
Posted: August 15, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, digital devices, education, ergonomics, posture, screen fatigue, stress management, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: cellphone, concentration 5 CommentsReproduced from: Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Rosegard, E. (2024). Increase attention, concentration and school performance with posture feedback. Biofeedback, 52(2), 48-52. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-52.02.07

When I sit with good posture on my computer, I am significantly more engaged in what I’m doing. When I slouch on my computer I tend to procrastinate, go on my phone, and get distracted so it ends up taking much longer to do my work when my posture is bad.…I have ADHD and I struggle a lot with my mind wandering when I should be paying attention. Having good posture really helps me to lock in and focus.—22 year old male student.
Over the past two decades, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, and depression. ADHD rates have increased from 6% in 1997 to approximately 10% in 2018 (CDC, 2022). The rates of anxiety among 18–25 year-olds have also increased from 7.97% in 2008 to 14.66% in 2018 (Goodwin et al., 2020). Students are more distracted, stressed and exhausted (Hanscom, 2022; Hoyt et al., 2021). The more students are distracted, the lower their academic achievement (Feng et al., 2019). In our recent class survey of more than 100 junior and senior college students on the first day of class, 54% reported that they were tired and dreading the day when they woke up. When you are tired and stressed it is difficult to focus attention and have clarity of thought. Their self-report is similar to the mental health trends in the United States by age group in 2008–2019. Mental health of young people has significantly deteriorated over the last 15 years (Braghieri et al., 2021/2023).
The increase in psychological distress is most prevalent in people ages 18–29 and who were brought up with the cellphone (the iPhone was introduced in 2007) and social media. Now when students enter a class, they tend to sit down, look down at their cellphone while slouching, and they do not make contact with most other students unless instructed or reminded by the instructor. When instructed to talk to another student for less than 5 minutes (e.g., share something positive that happened to you this week), 93% of the students reported an increase in subjective energy and alertness (Peper, 2024).
As a group, students are social media and cell phone natives and thus have many distractions and stimuli to which they continuously respond. It is not surprising that the average attention span has decreased from 150 seconds in 2004 to 44 seconds in 2021 (Mark, 2023). More importantly, they now tend to sit in a slouched collapsed position, which facilitates access to hopeless, helpless, powerless and defeated thoughts and memories (Tsai et al., 2016; Peper et al., 2017) and reduces cognitive performance when performing mental math (Peper et al., 2018). Sitting slouched and looking down also reduces peripheral awareness and increases shallow thoracic breathing—a breathing pattern that increases the risk of anxiety. Experience this yourself.
For a minute, look at your cellphone while intensely reading the text or searching social media in the following two positions: sitting straight up and looking straight ahead at your cell phone or slouching and looking down at your cell phone, as shown in Figure 1. Most likely, your experience is similar to the findings from the classroom observational study in which half the students looked down and the other half looked straight ahead and then reversed their positions (Peper, unpublished). They then compared the subjective experience associated with the position. In the slouched position, most experienced a reduction in peripheral awareness and breathed more shallowly (see Figure 1).

Figure 1. Effect of slouching or looking straight ahead on vision and breathing.
The slouched position reduces social awareness and decreases awareness of external stimuli as illustrated in Steve Cutts’ superb animation, Mobile world (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wUW1wjlKvmY).
Given the constant stimulation, distractions and shortened attention span, it is more challenging to be calm and have clarity of mind when having to study or take an exam at school. As educators, we constantly explore ways to engage students and support their learning and especially share quick skills they can use to optimize performance (Peper& Wilson, 2021). In previous research, Harvey et al., 2020 showed that students who used posture feedback improved their health scores compared to the control group. The purpose of this paper is to share a 4-week class assignment by which numerous students reported an increase in attention, concentration, confidence, school performance and a decrease in stress.
Participants: 18 undergraduate students (7 males and 11 females, average age 22 [STDEV 2.2]) enrolled in an upper division class. As a report about an effort to improve the quality of a classroom activity, this report of findings was exempted from Institutional Review Board oversight.
Equipment: Wearable posture feedback device, UpRight Go 2, which the person wears on their neck and which provides vibratory feedback whenever they slouch, as shown in Figure 2. It is used in conjunction with the cellphone app that allows them to calibrate the feedback device.

Figure 2. Attachment of posture feedback device on neck or spine and the app to calibrate the device.
Procedure: Students attended the 3-hour weekly class that explored autogenic training, somatic awareness, psychobiology of stress, the role of posture, and the psychophysiology of respiration. The lectures included short experiential practices demonstrating the body-mind connections such as imagining a lemon to increase salivation, the effect of slouched versus erect posture on evoking positive/empowering or hopeless/helpless/powerless/defeated thoughts, and the effect of sequential 70% exhalation for 30 seconds on increasing anxiety (Tsai et al., 2016; Peper et al., 2017).
Each week for 4 weeks the students were assigned a self-practice that they would implement daily at home and record their experiences. At the end of the week, they reviewed their own log and summarized their own observations (benefits, difficulties). During the next class session, they met in small groups of 5 to 6 students to discuss their experiences and extract common themes.
The 4-week curriculum was sequenced as follows:
Week 1
- Lecture on the benefits/harms of posture with experiential practices (effect of slouching vs erect on access to hopeless/helpless/powerless thoughts versus optimistic and empowering thoughts; posture and arm strength (Peper, 2022).
- Homework assignments:
- Watch the great Ted Talk and one of the most viewed by Amy Cuddy (2013), “Your body language shapes who you are.”
- Keep a detailed log to monitor situations where they slouched and identify situations that were associated with slouching.
Week 2
- Lecture on psychophysiology and class discussion in which students shared their experiences of slouching; namely, what were the triggers, how it affected them and what they could do to change.
- Demonstration, explanation, and how to use the posture feedback device, UpRight Go 2.
- Homework assignment: Wear UpRight Go 2 during the day, use it in different settings (studying, walking, work), and keep a log. When it vibrates (slouching) observe what was going on and change your behavior such as when tired>get rest or do exercise; when depressed>change internal language; ergonomic issues>change the environment, posture>give yourself lower back support.
Week 3
- Class discussion on what to do when slouching is triggered by tiredness, negative and hopeless thoughts, ergonomics such as laptop placement and chair. Students meet in groups to share their experiences and what they did in response to the vibratory feedback.
- Homework assignment: Continue to wear the UpRight Go 2 during the day and keep a log.
Week 4
- Class discussion in groups of five students about their experiences of slouching, what to do and how it affects them.
- Homework assignment: Wear UpRight Go 2 during the day and keep a log. Submit a paper that describes their experience with the posture feedback from the UpRight Go 2 and fill out a short anonymous survey in which they rated their change in experience since using the posture feedback device on a scale from 3 (worse) to 0 (no change) to 3 (better) .
Results
All students reported that wearing the feedback device increased attention and concentration as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Amount of time using the UpRight Go 2:On the average the students used the device 4.8 days a week (STDEV 2.0) and 2.2 hours per day (STDEV 1.3).
Location of use:Although most students practiced sitting in front of their computer, they also reported using it while at work, playing pool or doing yoga and even while seeing a therapist.
Discussion
All the students reported that the posture feedback helped them to become more aware of slouching and when they then interrupted their slouching, they experienced an increase in energy and a decrease in stress. As a 21-year-old male student said: “I felt more engaged with whatever I was doing. I tend to … daydream and get distracted, but I experience much less of that when I sit with good posture.”
Many reported that it helped identify their emotions when they were feeling overwhelmed. Then they could sit up, shift their perspective, and many reported a decrease in back and neck pain as well as a decrease in tiredness. When participants wear non-invasive wearables that provide accurate feedback, they are often surprised what triggers are associated with feedback or how their performance improves when they respond to the feedback signal by changing their thoughts and behavior. This posture self-awareness project should be embedded in strategies that optimize the learning state as described by Peper & Wilson (2021).
To the students’ surprise, they were often unaware that they started to slouch, nor were they aware of how much this slouching was connected to their emotions, mental state or external factors. For example, one student reported that he wore the device while being in a therapy session. All of a sudden, it vibrated. At that moment, he realized that he was becoming anxious, although he and therapist were unaware. He then shared what happened with the therapist, and that helped the therapeutic process.
The benefits may not only be due to posture change but that the students became aware and interrupted their habitual pattern. This process is similar to that described by Charles Stroebel (1985) when he taught patients the Quieting Reflect that reduced numerous somatic symptoms ranging from headaches to hypertension.
The posture feedback intervention is both simple and challenging since it requires the participants to wear the device, identify factors that trigger the slouching, and interrupt their automatic patterns by changing posture and behavior whenever they felt the vibratory feedback. The awareness gave them the opportunity to change posture and thoughts. By shifting to an upright posture, they experienced that they could concentrate more and have increased energy. As a 19-year-old female student wrote: “My breathing was better and sitting in an upright position gave me more energy when doing tasks.”
Conclusion
We recommend that a 4-week home practice module that incorporates wearable posture feedback is offered to all students to enhance their well-being. With the posture feedback, participants can increase their awareness of slouching, identify situations that trigger slouch, and learn strategies to shift their posture, thoughts, emotions and external environment to optimize maintaining an empowered position. As a 20-year old male student reported, “The app helped me when I was feeling overwhelmed and then I would sit up. When I had it on, I did a lot of work. I was more concentrated.”
Explore the following blogs for more background and useful suggestions
References
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2023). Media and mental health (July 28, 2022). SSRN. (Original work published 2021). https://ssrn.com/abstract=3919760 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919760
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). ADHD through the years. Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Retrieved March 27, 2023, from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/timeline.html
Cuddy, A. (2012) Your body language may shape who you are. TED Talk. Retrieved March 16, 2024 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ks-_Mh1QhMc
Feng, S., Wong, Y. K., Wong, L. Y., & Hossain, L. (2019). The internet and Facebook usage on academic distraction of college students, Computers & Education, 134, 41-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j
Goodwin, R. D., Weinberger, A. H., Kim, J. H., Wu. M., & Galea, S. (2020). Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008–2018: Rapid increases among young adults. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 130, 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.08.014
Hanscom, N. (2022). Students, staff notice higher levels of student distraction this school year, reflect on potential causes. Retrieved September 28, 2023, from https://dgnomega.org/13162/feature/students-staff-notice-higher-levels-of-student-distraction-this-school-year-reflect-on-potential-causes/
Harvey, R., Peper, E., Mason, L., & Joy, M. (2020). Effect of posture feedback training on health. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 45(1), 59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-020-09457-0
Hoyt, L. T., Cohen, A. K., Dull, B., Castro, E. M., & Yazdani, N. (2021). “Constant stress has become the new normal”: Stress and anxiety inequalities among U.S. college students in the time of COVID-19. Journal of Adolescent Health. 68(2), 270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.10.030
Mark, G. (2023). Attention span: A groundbreaking way to restore balance, happiness and productivity. Hanover Square Press.
Peper, E. (2022, March 4). A breath of fresh air: Breathing and posture to optimize health. [Conference presentation at the 2nd Virtual Ergonomics Summit], Krista Burns, PhD. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PhV7Ulhs38s
Peper, E. (2024a). Change in energy and alertness after talking with each other versus looking at cellphone. Data collected from HH380 class fall 2023. Unpublished.
Peper, E. (2024b). Changes in vision and breathing when looking down or straight ahead at the cellphone. Data collected from HH380 class, Spring, 2024, San Francisco State University. Unpublished.
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Mason, L., & Lin, I.-M. (2018). Do better in math: How your body posture may change stereotype threat response. NeuroRegulation, 5(2), 67–74. http://dx.doi.org/10.15540/nr.5.2.67
Peper, E., Lin, I.-M., Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback.45(2), 36–41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E. & Wilson, V. (2021). Optimize the learning state: Techniques and habits. Biofeedback, 49(2), 46-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-49-2-04
Stroebel, C. F. (1985). QR: The Quieting Reflex. Berkley. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-Quieting-Charles-M-D-Stroebel/dp/0399126570
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I.-M.(2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23–27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
Quick Rescue Techniques When Stressed
Posted: February 4, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, CBT, cognitive behavior therapy, education, emotions, Evolutionary perspective, Exercise/movement, health, mindfulness, Neck and shoulder discomfort, posture, relaxation, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: alarm reaction, anxiety, box breathing, Breathing, conditioning, defense reaction, health, huming, Parasympathetic response, rumination, safety, sniff inhale, somatic practices, stress, sympathetic arousal, tactical breathing, Toning, yoga 9 CommentsErik Peper, PhD, Yuval Oded, PhD, and Richard Harvey, PhD
Adapted from Peper, E., Oded, Y, & Harvey, R. (2024). Quick somatic rescue techniques when stressed. Biofeedback, 52(1), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.5298/982312 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380481426

“If a problem is fixable, if a situation is such that you can do something about it, then there is no need to worry. If it’s not fixable, then there is no help in worrying. There is no benefit in worrying whatsoever.” ― Dalai Lama XIV
To implement the Dalai Lama’s quote is challenging. When caught up in an argument, being angry, extremely frustrated, or totally stressed, it is easy to ruminate, worry. It is much more challenging to remember to stay calm. When remembering the message of the Dalai Lama’s quote, it may be possible to shift perspective about the situation although a mindful attitude may not stop ruminating thoughts. The body typically continues to reacti to the torrents of thoughts that may occur when rehashing rage over injustices, fear over physical or psychological threats, or profound grief and sadness over the loss of a family member. Some people become even more agitated and less rational as illustrated in the following examples.
I had an argument with my ex and I am still pissed off. Each time I think of him or anticipate seeing them, my whole body tightened. I cannot stomach seeing him and I already see the anger in his face and voice. My thoughts kept rehashing the conflict and I am getting more and more upset.
A car cut right in front of me to squeeze into my lane. I had to slam on my brakes. What an idiot! My heart rate was racing and I wanted to punch the driver.
When threatened, we respond quickly in our thoughts and body with a defense reaction that may negatively affect those around us as well as ourselves. What can we do to interrupt negative stress reactions?
Background
Many approaches exist that allow us to become calmer and less reactive. General categories include techniques of cognitive reappraisal (seeing the situation from the other person’s point of view and labeling your own feelings and emotions) and stress management techniques. Practices that are beneficial include mindfulness meditation, benign humor (versus gallows humor), listening to music, taking a time out while implementing a variety of self-soothing practices, or incorporating slow breathing (e.g., heart rate variability and/or box breathing) throughout the day.
No technique fits all as we respond differently to our stressful life circumstances. For example, some people during stress react with a “tend and befriend stress response” (Cohen & Lansing, 2021; Taylor et al., 2000). This response appears to be mostly mediated by the hormone oxytocin acting in ways that sooth or calm the nervous system as an analgesic. These neurophysiological mechanisms of the soothing with the calming analgesic effects of oxytocin have been characterized in detail by Xin, et al. (2017).
The most common response is a fight/flight/freeze stress response that is mediated by excitatory hormones such as adrenalin and inhibitory neurotransmitters such as gamma amino butyric acid (GABA). There is a long history of fight/flight/freeze stress response research, which is beyond the scope of this blog with major theories and terms such as interior milleau (Bernard, 1872); homeostasis and fight/flight (Cannon, 1929); general adaptation syndrome (Selye, 1951); polyvagal theory (Porges, 1995); and, allostatic load (McEwen, 1998). A simplified way to start a discussion about stress reactions begins with the fight/flight stress response. When stressed our defense reactions are triggered. Our sympathetic nervous system becomes activated our mind and body stereotypically responds as illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1. An intense confrontation tends to evoke a stress response (reproduced from Peper et al., 2020).
The flight/fight response triggers a cascade of stress hormones or neurotransmitters (e.g., hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal cascade) and produces body changes such as the heart pounding, quicker breathing, an increase in muscle tension and sweating. Our body mobilizes itself to protect itself from danger. Our focus is on immediate survival and not what will occur in the future (Porges, 2021; Sapolsky, 2004). It is as if we are facing an angry lion—a life-threatening situation—and we feel threatened and unsafe.
Rather than sitting still, a quick effective strategy is to interrupt this fight/flight response process by completing the alarm reaction such as by moving our muscles (e.g., simulating a fight or flight behavior) before continuing with slower breathing or other self-soothing strategies. Many people have experienced their body tension is reduced and they feel calmer when they do vigorous exercise after being upset, frustrated or angry. Similarly, athletes often have reported that they experience reduced frequency and/or intensity of negative thoughts after an exhausting workout (Thayer, 2003; Liao et al., 2015; Basso & Suzuki, 2017).
Becoming aware of the escalating cascades of physical, behavioral and psychological responses to a stressor is the first step in interrupting the escalating process. After becoming aware, reduce the body’s arousal and change the though patterns using any of the techniques described in this blog. The self-regulation skills presented in this blog are ideally over-learned and automated so that these skills can be rapidly implemented to shift from being stressed to being calm. Examples of skills that can shift from sympathetic neervous system overarousal to parasympathetic nervous system calm include techniques of autogenic traing (Schulz & Luthe, 1959), the quieting reflex developed by Charles Stroebel in 1985 or more recently rescue breathing developed by Richard Gevirtz (Stroebel, 1985; Gevirtz, 2014; Peper, Gibney & Holt, 2002; Peper & Gibney, 2003).
Concepts underlying the rescue techniques
- Psychophysiological principle: “Every change in the physiological state is accompanied by an appropriate change in the mental-emotional state, conscious or unconscious, and conversely, every change in the mental-emotional state, conscious or unconscious, is accompanied by an appropriate change in the physiological state” (Green et al. 1970, p. 3).
- Posture evokes memories and feelings associated with the position. When the body posture is erect and tall while looking slightly up. It is easier to evoke empowering, positive thoughts and feelings. When looking down it is easier to evoke hopeless, helpless and powerless thoughts and feelings (Peper et al., 2017).
- Healing occurs more easily when relaxed and feeling safe. Feeling safe and nurtured enhances the parasympathetic state and reduces the sympathetic state. Use memory recall to evoke those experiences when you felt safe (Peper, 2021).
- Interrupting thoughts is easier with somatic movement than by redirecting attention and thinking of something else without somatic movement.
- Focus on what you want to do not want to do. Attempting to stop thinking or ruminating about something tends to keeps it present (e.g., do not think of pink elephants. What color is the elephant? When you answer, “not pink,” you are still thinking pink). A general concept is to direct your attention (or have others guide you) to something else (Hilt & Pollak, 2012; Oded, 2018; Seo, 2023).
- Skill mastery takes practice and role rehearsal (Lally et al., 2010; Peper & Wilson, 2021).
- Use classical conditioning concepts to facilitate shifting states. Practice the skills and associate them with an aroma, memory, sounds or touch cues. Then when you the situation occurs, use these classical conditioned cues to facilitate the regeneration response (Peper & Wilson, 2021).
Rescue techniques
Coping When Highly Stressed and Agitated
- Complete the alarm/defense reaction with physical activity (Be careful when you do these physical exercises if you have back, hip, knee, or ankle problems).
- Acknowledge you have reacted and have chosen to interrupt your automatic response.
- Check whether the situation is actually a threat. If yes, then do anything to get out of immediate danger (yell, scream, fight, run away, or dial 911).
- If there is no actual physical threat, then leave the situation and perform vigorous physical activity to complete your alarm reaction, such as going for a run or walking quickly up and down stairs. As you do the exercise, push yourself so that the muscles in your thighs are aching, which focusses your attention on the sensations in your thighs. In our experience, an intensive run for 20 minutes quiets the brain while it often takes 40 minutes when walking somewhat quickly.
- After recovering from the exhaustive exercise, explore new options to resolve the conflict.
- Complete the alarm/defense reaction and evoke calmness with the S.O.S™ technique (Oded, 2023)
- Acknowledge you have reacted and have chosen to interrupt your automatic response.
- Squat against a wall (similar to the wall-sit many skiers practice). While tensing your arms and fists as shown in Figure 2, gaze upward because it is more difficult to engage in negative thinking while looking upwards. If you continue to ruminate, then scan the room for object of a certain color or feature to shift visual attention and be totally present on the visual object.
- Do this set of movements for 7 to 10 seconds or until you start shaking. Than stand up and relax hands and legs. While standing, bounce up and down loosely for 10 to 15 seconds as you become aware of the vibratory sensations in your arms and shoulders, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 2.Defense position wall-sit to tighten muscles in the protective defense posture (Oded, 2023). Figure 3. Bouncing up and down to loosen muscles ((Oded, 2023).
- Acknowledge you have reacted and have chosen to interrupt your automatic response. Swing your arms back and forth for 20 seconds. Allow the arms to swing freely as illustrated in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Swinging the arms to loosen the body and spine (Oded, 2023).
- Rest and ground. Lie on the floor and put your calves and feet on a chair seat so that the psoas muscle can relax, as illustrated in Figure 5. Allow yourself to be totally supported by the floor and chair. Be sure there is a small pillow under your head and put your hand on your abdomen so that you can focus on abdominal breathing.

Figure 5. Lying down to allow the psoas muscle to relax and feel grounded (Oded, 2023).
- While lying down, imagine a safe place or memory and make it as real as possible. It is often helpful to listen to a guided imagery or music. The experience can be enhanced if cues are present that are associated with the safe place, such as pictures, sounds, or smells. Continue to breathe effortlessly at about six breaths per minute. If your attention wanders, bring it back to the memory or to the breathing. Allow yourself to rest for 10 minutes.
In most cases, thoughts stop and the body’s parasympathetic activity becomes dominant as the person feels safe and calm. Usually, the hands warm and the blood volume pulse amplitude increases as an indicator of feeling safe, as shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6. Blood volume pulse increases as the person is relaxing, feels safe and calm.
Coping When You Can’t Get Away (adapted from Peper, Harvey & Faass, 2020)
In many cases, it is difficult or embarrassing to remove yourself from the situation when you are stressed out such as at work, in a business meeting or social gathering.
- Become aware that you have reacted.
- Excuse yourself for a moment and go to a private space, such as a restroom. Going to the bathroom is one of the only acceptable social behaviors to leave a meeting for a short time.
- In the bathroom stall, do the 5-minute Nyingma exercise, which was taught by Tarthang Tulku Rinpoche in the tradition of Tibetan Buddhism, as a strategy for thought stopping (see Figure 7). Stand on your toes with your heels touching each other. Lift your heels off the floor while bending your knees. Place your hands at your sides and look upward. Breathe slowly and deeply (e.g., belly breathing at six breaths a minute) and imagine the air circulating through your legs and arms. Do this slow breathing and visualization next to a wall so you can steady yourself if necessary to keep balance. Stay in this position for 5 minutes or longer. Do not straighten your legs—keep squatting despite the discomfort. In a very short time, your attention is captured by the burning sensation in your thighs. Continue. After 5 minutes, stop and shake your arms and legs.

Figure 7. Stressor squat Nyingma exercise (reproduced from Peper et al., 2020).
- Follow this practice with slow abdominal breathing to enhance the parasympathetic response. Be sure that the abdomen expands as the inhalation occurs. Breathe in and out through the nose at about six breaths per minute.
- Once you feel centered and peaceful, return to the room.
- After this exercise, your racing thoughts most likely will have stopped and you will be able to continue your day with greater calm.
What to do When Ruminating, Agitated, Anxious or Depressed
(adapted from Peper, Harvey, & Hamiel, 2019).
- Shift your position by sitting or standing erect in a power position with the back of the head reaching upward to the ceiling while slightly gazing upward. Then sniff quickly through nose, hold and again sniff quickly then very slowly exhale. Be sure as you exhale your abdomen constricts. Then sniff again as your abdomen gets bigger, hold, and sniff one more time letting the abdomen get even bigger. Then, very slow, exhale through the nose to the internal count of six (adapted from Balban et al., 2023). When you sniff or gasp, your racing thoughts will stop (Peper et al., 2016).
- Continue with box breathing (sometimes described as tactical breathing or battle breathing) by exhaling slowly through your nose for 4 seconds, holding your breath for 4 seconds, inhaling slowly for 4 seconds through your nose, holding your breath for 4 seconds and then repeating this cycle of breathing for a few minutes (Röttger et al., 2021; Balban et al., 2023). Focusing your attention on performing the box breathing makes it almost impossible to think of anything else. After a few minutes, follow this with slow effortless diaphragmatic breathing at about six breaths per minute. While exhaling slowly through your nose, look up and when you inhale imagine the air coming from above you. Then as you exhale, imagine and feel the air flowing down and through your arms and legs and out the hands and feet.
- While gazing upward, elicit a positive memory or a time when you felt safe, powerful, strong and/or grounded. Make the positive memory as real as possible.
- Implement cognitive strategies such as reframing the issue, sending goodwill to the person, seeing the problem from the other person’s point of view, and ask is this problem worth dying over (Peper, Harvey, & Hamiel, 2019).
What to Do When Thoughts Keep Interrupting
Practice humming or toning. When you are humming or toning, your focus is on making the sound and the thoughts tend to stop. Generally, breathing will slow down to about six breaths per minute (Peper, Pollack et al., 2019). Explore the following:
- Box breathing (Röttger et al., 2021; Balban et al., 2023)
- Humming also known as bee breath (Bhramari Pranayama) (Abishek et al., 2019; Yoga, 2023) – Allow the tongue to rest against the upper palate, sit tall and erect so that the back of the head is reaching upward to the ceiling, and inhale through your nose as the abdomen expands. Then begin humming while the air flows out through your nose, feel the vibration in the nose, face and throat. Let humming last for about 7 seconds and then allow the air to blow in through the nose and then hum again. Continue for about 5 minutes.
- Toning – Inhale through your nose and then vocalize a single sound such as Om. As you vocalize the lower sound, feel the vibration in your throat, chest and even going down to the abdomen. Let each toning exhalation last for about 6 to 7 seconds and then inhale through your nose. Continue for about 5 minutes (Peper, al., 2019).
Many people report that after practice these skills, they become aware that they are reacting and are able to reduce their automatic reaction. As a result, they experience a significant decrease in their stress levels, fewer symptoms such as neck and holder tension and high blood pressure, and they feel an increase in tranquility and the ability to communicate effectively.
Practicing these skills does not resolve the conflicts; they allow you to stop reacting automatically. This process allows you a time out and may give you the ability to be calmer, which allows you to think more clearly. When calmer, problem solving is usually more successful. As phrased in a popular meme, “You cannot see your reflection in boiling water. Similarly, you cannot see the truth in a state of anger. When the waters calm, clarity comes” (author unknown).

Boiling water (photo modified from: https://www.facebook.com/photo/?fbid=388991500314839&set=a.377199901493999)
Below are additional resources that describe the practices. Please share these resources with friends, family and co-workers.
Stressor squat instructions
Toning instructions
Diaphragmatic breathing instructions
Reduce stress with posture and breathing
Conditioning
References
Abishek, K., Bakshi, S. S., & Bhavanani, A. B. (2019). The efficacy of yogic breathing exercise bhramari pranayama in relieving symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Yoga, 12(2), 120–123. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijoy.IJOY_32_18
Balban, M. Y., Neri, E., Kogon, M. M., Weed, L., Nouriani, B., Jo, B., Holl, G., Zeitzer, J. M., Spiegel, D., Huberman, A. D. (2023). Brief structured respiration practices enhance mood and reduce physiological arousal. Cell Reports Medicine, 4(1), 10089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100895
Basso, J. C. & Suzuki, W. A. (2017). The effects of acute exercise on mood, cognition, neurophysiology, and neurochemical pathways: A review. Brain Plast, 2(2), 127–152. https://doi.org/10.3233/BPL-160040
Bernard, C. (1872). De la physiologie générale. Paris: Hachette livre. https://www.amazon.ca/PHYSIOLOGIE-GENERALE-BERNARD-C/dp/2012178596
Cannon, W. B. (1929). Organization for Physiological Homeostasis. Physiological Reviews, 9, 399–431. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1929.9.3.399
Cohen, L. & Lansing, A. H. (2021). The tend and befriend theory of stress: Understanding the biological, evolutionary, and psychosocial aspects of the female stress response. In: Hazlett-Stevens, H. (eds), Biopsychosocial Factors of Stress, and Mindfulness for Stress Reduction. pp. 67–81, Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81245-4_3
Gevirtz, R. (2014). HRV Training and its Importance – Richard Gevirtz, Ph.D., Pioneer in HRV Research & Training. Thought Technology. Accessed December 29, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9nwFUKuJSE0
Green, E. E., Green, A. M., & Walters, E. D. (1970). Voluntary control of internal states: Psychological and physiological. Journal of Transpersonal Psychology, 2, 1–26. https://atpweb.org/jtparchive/trps-02-70-01-001.pdf
Hilt, L. M., & Pollak, S. D. (2012). Getting out of rumination: comparison of three brief interventions in a sample of youth. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(7), 1157–1165.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9638-3
Lally, P., VanJaarsveld, C. H., Potts, H. W., & Wardle, J. (2010). How habits are formed: Modelling habit formation the real world. European Journal of Social Psychology, 40, 998–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.674
Liao, Y., Shonkoff, E. T., & Dunton, G. F. (2015). The acute relationships between affect, physical feeling states, and physical activity in daily life: A review of current evidence. Frontiers in Psychology. 6, 1975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01975
McEwen, B. S. (1998). Stress, adaptation, and disease: Allostasis and allostatic load. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 840(1), 33–44.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09546.x
Oded, Y. (2018). Integrating mindfulness and biofeedback in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Biofeedback, 46(2), 37-47. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-46.02.03
Oded, Y. (2023). Personal communication. S.O.S 1™ technique is part of the Sense Of Safety™ method. www.senseofsafety.co
Peper, E. (2021). Relive memory to create healing imagery. Somatics, XVIII(4), 32–35.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369114535_Relive_memory_to_create_healing_imagery
Peper, E., Gibney, K.H. & Holt. C. (2002). Make Health Happen: Training Yourself to Create Wellness. Dubuque, IA: Kendall-Hunt. https://he.kendallhunt.com/product/make-health-happen-training-yourself-create-wellness
Peper, E., & Gibney, K.H. (2003). A teaching strategy for successful hand warming. Somatics. XIV(1), 26–30. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/376954376_A_teaching_strategy_for_successful_hand_warming
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153–160. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.153
Peper, E., Lee, S., Harvey, R., & Lin, I-M. (2016). Breathing and math performance: Implication for performance and neurotherapy. NeuroRegulation, 3(4), 142–149. http://dx.doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.4.142
Peper, E., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback, 45(2), 36–41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E., Pollack, W., Harvey, R., Yoshino, A., Daubenmier, J. & Anziani, M. (2019). Which quiets the mind more quickly and increases HRV: Toning or mindfulness? NeuroRegulation, 6(3), 128–133. https://www.neuroregulation.org/article/view/19345/13263
Peper, E. & Wilson, V. (2021). Optimize the learning state: Techniques and habits. Biofeedback, 9(2), 46–49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-49-2-04
Porges, S. W. (1995). Orienting in a defensive world: Mammalian modifications of our evolutionary heritage. A polyvagal theory. Psychophysiology, 32(4), 301–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.1995.tb01213.x
Porges, S.W. (2021) Cardiac vagal tone: a neurophysiological mechanism that evolved in mammals to dampen threat reactions and promote sociality. World Psychiatry, 20(2),296-298. Porges SW. Cardiac vagal tone: a neurophysiological mechanism that evolved in mammals to dampen threat reactions and promote sociality. World Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;20(2):296-298. https://doi.org10.1002/wps.20871
Röttger, S., Theobald, D. A., Abendroth, J., & Jacobsen, T. (2021). The effectiveness of combat tactical breathing as compared with prolonged exhalation. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 46, 19–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-020-09485-w
Sapolsky, R. (2004). Why zebras don’t get ulcers (3rd ed.). New York:Holt. https://www.amazon.com/Why-Zebras-Dont-Ulcers-Third/dp/0805073698/
Schultz, J. H., & Luthe, W. (1959). Autogenic training: A psychophysiologic approach to psychotherapy. Grune & Stratton. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Autogenic_Training/y8SwQgAACAAJ?hl=en
Selye, H. (1951). The general-adaptation-syndrome. Annual Review of Medicine, 2(1), 327–342. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.me.02.020151.001551
Seo, H. (2023). How to stop ruminating. The New York Times. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/02/01/well/mind/stop-rumination-worry.html
Stroebel, C. F. (1985). QR: The Quieting Reflex. Berkley. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-quieting-reflex-Charles-Stroebel/dp/0425085066
Taylor, S. E., Klein, L. C., Lewis, B. P., Gruenewald, T. L., Gurung, R. A. R., & Updegraff, J. A. (2000). Biobehavioral responses to stress in females: Tend-and-befriend, not fight-or-flight. Psychological Review, 107(3), 411–429. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.107.3.411
Thayer, R. E. (2003). Calm energy: How people regulate mood with food and exercise. Oxford University Press. https://www.amazon.com/Calm-Energy-People-Regulate-Exercise/dp/0195163397
Xin, Q., Bai, B., & Liu, W. (2017). The analgesic effects of oxytocin in the peripheral and central nervous system. Neurochemistry International, 103, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.12.021
Yoga, N. (2023). This simple breath practice is scientifically proven to calm your mind. The nomadic yogi. Accessed December 31, 2023. https://www.leahsugerman.com/blog/bhramari-pranayama-humming-bee-breath#
TechStress: Building Healthier Computer Habits
Posted: August 30, 2023 Filed under: ADHD, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, cognitive behavior therapy, computer, digital devices, education, emotions, ergonomics, Evolutionary perspective, Exercise/movement, health, laptops, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, screen fatigue, stress management, Uncategorized, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: cellphone, fatigue, gaming, mobile devices, screens 5 CommentsBy Erik Peper, PhD, BCB, Richard Harvey, PhD, and Nancy Faass, MSW, MPH
Adapted by the Well Being Journal, 32(4), 30-35. from the book, TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey, and Nancy Faass.

Every year, millions of office workers in the United States develop occupational injuries from poor computer habits—from carpal tunnel syndrome and tension headaches to repetitive strain injury, such as “mouse shoulder.” You’d think that an office job would be safer than factory work, but the truth is that many of these conditions are associated with a deskbound workstyle.
Back problems are not simply an issue for workers doing physical labor. Currently, the people at greatest risk of injury are those with a desk job earning over $70,000 annually. Globally, computer-related disorders continue to be on the rise. These conditions can affect people of all ages who spend long hours at a computer and digital devices.
In a large survey of high school students, eighty-five percent experienced tension or pain in their neck, shoulders, back, or wrists after working at the computer. We’re just not designed to sit at a computer all day.
Field of Ergonomics
For the past twenty years, teams of researchers all over the world have been evaluating workplace stress and computer injuries—and how to prevent them. As researchers in the fields of holistic health and ergonomics, we observe how people interact with technology. What makes our work unique is that we assess employees not only by interviewing them and observing behaviors, but also by monitoring physical responses.
Specifically, we measure muscle tension and breathing, in the moment, in real-time, while they work. To record shoulder pain, for example, we place small sensors over different muscles and painlessly measure the muscle tension using an EMG (electromyograph)—a device that is employed by physicians, physical therapists, and researchers. Using this device, we can also keep a record of their responses and compare their reactions over time to determine progress.
What we’ve learned is that people get into trouble if their muscles are held in tension for too long. Working at a computer, especially at a stationary desk, most people maintain low-level chronic tension for much of the day. Shallow, rapid breathing is also typical of fine motor tasks that require concentration, like data entry.
Muscle tension and breathing rate usually increase during data entry or typing without our awareness.
When these patterns are paired with psychological pressure due to office politics or job insecurity, the level of tension and the risk of fatigue, inflammation, pain, or injury increase. In most cases, people are totally unaware of the role that tension plays in injury. Of note, the absolute level of tension does not predict injury—rather, it is the absence of periodic rest breaks throughout the day that seems to correlate with future injuries.
Restbreaks
All of life is the alternation between movement and rest, inhaling and exhaling, sleeping and waking. Performing alternating tasks or different types of activities and movement is one way to interrupt the couch potato syndrome—honoring our evolutionary background.
Our research has confirmed what others have observed: that it’s important to be physically active, at least periodically, throughout the day. Alternating activity and rest recreate the pattern of our ancestors’ daily lives. When we alternate sedentary tasks with physical activity, and follow work with relaxation, we function much more efficiently. In short, move your body more.
Better Computer Habits: Alternate Periods of Rest and Activity
As mentioned earlier, our workstyle puts us out of sync with our genetic heritage. Whether hunting and gathering or building and harvesting, our ancestors alternated periods of inactivity with physical tasks that required walking, running, jumping, climbing, digging, lifting, and carrying, to name a few activities. In contrast, today many of us have a workstyle that is so immobile we may not even leave our desk for lunch.
As health researchers, we have had the chance to study workstyles all over the world. Back pain and strain injuries now affect a large proportion of office workers in the US and in high-tech firms worldwide. The vast majority of these jobs are sedentary, so one focus of the research is on how to achieve a more balanced way of working.
A recent study on exercise looked at blood flow to the brain. Researchers Carter and colleagues found that if people sit for four hours on the job, there’s a significant decrease in blood flow to the brain. However, if every thirty or forty minutes they get up and move around for just two minutes, then brain blood flow remains steady. The more often you interrupt sitting with movement, the better.
It may seem obvious that to stay healthy, it’s important to take breaks and be physically active from time to time throughout the day. Alternating activity and rest recreate the pattern of our ancestors’ daily lives. The goal is to alternate sedentary tasks with physical activity and follow work with relaxation. When we keep this type of balance going, most people find that they have more energy, are more productive, and can be more effective.
Genetics: We’re Hardwired Like Ancient Hunters

Despite a modern appearance, we carry the genes of our forebearers—for better and for worse. (Art courtesy of Peter Sis). Reproduced from Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books.
In the modern workplace, most of us find ourselves working indoors, in small office spaces, often sitting at a computer for hours at a time. In fact, the average Westerner spends more than nine hours per day sitting indoors, yet we’re still genetically programmed to be physically active and spend time outside in the sunlight most of the day, like the nomadic hunters and gatherers of forty thousand years ago.
Undeniably, we inherently conserve energy in order to heal and regenerate. This aspect of our genetic makeup also helps burn fewer calories when food is scarce. Hence the propensity for lack of movement and sedentary lifestyle (sitting disease).
In times of famine, the habit of sitting was essential because it reduced calorie expenditure, so it enabled our ancestors to survive. In a prehistoric world with a limited food supply, less movement meant fewer calories burned. Early humans became active when they needed to search for food or shelter. Today, in a world where food and shelter are abundant for most Westerners, there is no intrinsic drive to initiate movement.
It is also true that we have survived as a species by staying active. Chronic sitting is the opposite of our evolutionary pattern in which our ancestors alternated frequent movement while hunting or gathering food with periods of rest. Whether they were hunters or farmers, movement has always been an integral aspect of daily life. In contrast, working at the computer—maintaining static posture for hours on end—can increase fatigue, muscle tension, back strain, and poor circulation, putting us at risk of injury.
Quit a Sedentary Workstyle
Almost everyone is surprised by how quickly tension can build up in a muscle, and how painful it can become. For example, we tend to hover our hands over the keyboard without providing a chance for them to relax. Similarly, we may tighten some of the big muscles of our body, such as bracing or crossing our legs.
What’s needed is a chance to move a little every few minutes—we can achieve this right where we sit by developing the habit of microbreaks. Without regular movement, our muscles can become stiff and uncomfortable. When we don’t take breaks from static muscle tension, our muscles don’t have a chance to regenerate and circulate oxygen and necessary nutrients.
Build a variety of breaks into your workday:
- Vary work tasks
- Take microbreaks (brief breaks of less than thirty seconds)
- Take one-minute stretch breaks
- Fit in a moving break
Varying Work Tasks
You can boost physical activity at work by intentionally leaving your phone on the other side of the desk, situating the printer across the room, or using a sit-stand desk for part of the day. Even a few minutes away from the desk makes a difference, whether you are hand delivering documents, taking the long way to the bathroom, or pacing the room while on a call.
When you alternate the types of tasks and movement you do, using a different set of muscles, this interrupts the contractions of muscle fibers and allows them to relax and regenerate. Try any of these strategies:
- Alternate computer work with other activities, such as offering to do a coffee run
- Schedule walking meetings with coworkers
- Vary keyboarding and hand movements
Ultimately, vary your activities and movements as much as possible. By changing your posture and making sure you move, you’ll find that your circulation and your energy improve, and you’ll experience fewer aches and pains. In a short time, it usually becomes second nature to vary your activities throughout the day.
Experience It: “Mouse Shoulder” Test
You can test this simple mousing exercise at the computer or as a simulation. If you’re at the computer, sit erect with your hand on the mouse next to the keyboard. To simulate the exercise, sit with erect posture as if you were in front of your computer and hold a small object you can use to imitate mousing.
With the mouse (or a sham mouse), simulate drawing the letters of your name and your street address, right to left. Be sure each letter is very small (less than half an inch in height). After drawing each letter, click the mouse.
As part of the exercise, draw the letters and numbers as quickly as possible for ten to fifteen seconds. What did you observe? In almost all cases, you may note that you tightened your mousing shoulder and your neck, stiffened your trunk, and held your breath. All this occurred without awareness while performing the task. Over time, this type of muscle tension can contribute to discomfort, soreness, pain, or eventual injury.
Microbreaks
If you’ve developed an injury—or have chronic aches and pains—you’ll probably find split-second microbreaks invaluable. A microbreak means taking brief periods of time that last just a few seconds to relax the tension in your wrists, shoulders, and neck.
For example, when typing, simply letting your wrists drop to your lap for a few seconds will allow the circulation to return fully to help regenerate the muscles. The goal is to develop a habit that is part of your routine and becomes automatic, like driving a car. To make the habit of microbreaks practical, think about how you can build the breaks into your workstyle. That could mean a brief pause after you’ve completed a task, entered a column of data, or before starting typing out an assignment.
For frequent microbreaks, you don’t even need to get up—just drop your hands in your lap or shake them out, move your shoulders, and then resume work. Any type of shaking or wiggling movement is good for your circulation and kind of fun.
In general, a microbreak may be defined as lasting one to thirty seconds. A minibreak may last roughly thirty seconds to a few minutes, and longer large-movement breaks are usually greater than a few minutes. Popular microbreaks:
- Take a few deep breaths
- Pause to take a sip of water
- Rest your hands in your lap
- Stretch
- Let your arms drop to your sides
- Shake out your hands (wrists and fingers)
- Perform a quick shoulder or neck roll
Often, we don’t realize how much tension we’ve been carrying until we become more mindful of it. We can raise our awareness of excess tension—this is a learned skill—and train ourselves to let go of excess muscle tension. As we increase our awareness, we’re able to develop a new, more dynamic workstyle that better fits our goals and schedule.
One-Minute Stretch Breaks

We all benefit from a brief break, even with the best of posture (left). One approach is to totally release your muscles (middle). That release can be paired with a series of brief stretches (right). Reproduced from Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books.
The typical mini-stretch break lasts from thirty seconds to a few minutes, and ideally you want to take them several times per hour. Similar to microbreaks, mini-stretch breaks are especially important for people with an injury or those at risk of injury. Taking breaks is vital, especially if you have symptoms related to computer stress or whenever you’re working long hours at a sedentary job. To take a stretch break:
Begin with a big stretch, for example, by reaching high over your head then drop your hands in your lap or to your sides.
Look away from the monitor, staring at near and far objects, and blink several times. Straighten your back and stretch your entire backbone by lifting your head and neck gently, as if there were an invisible string attached to the crown of your head.
Stretch your mind and body. Sitting with your back straight and both feet flat on the floor, close your eyes and listen to the sounds around you, including the fan on the computer, footsteps in the hallway, or the sounds in the street.
Breathe in and out over ten seconds (breathe in for four or five seconds and breathe out for five or six seconds), making the exhale slightly longer than the inhale. Feel your jaw, mouth, and tongue muscles relax. Feel the back and bottom of the chair as your body breathes all around you. Envision someone in your mind’s eye who is kind and reassuring, who makes you feel safe and loved, and who can bring a smile to your face inwardly or outwardly.
Do a wiggling movement. When you take a one-minute break, wiggling exercises are fast and easy, and especially good for muscle tension or wrist pain. Wiggle all over—it feels good, and it’s also a great way to improve circulation.
Building Exercise and Movement into Every Day
Studies show that you get more benefit from exercising ten to twenty minutes, three times a day, than from exercising for thirty to sixty minutes once a day. The implication is that doing physical activities for even a few minutes can make a big difference.
Dunstan and colleagues have found that standing up three times an hour and then walking for just two minutes reduced blood sugar and insulin spikes by twenty-five percent.Fit in a Moving Break
Fit in a Moving Break
Once we become conscious of muscle tension, we may be able to reverse it simply by stepping away from the desk for a few minutes, and also by taking brief breaks more often. Explore ways to walk in the morning, during lunch break, or right after work. Ideally, you also want to get up and move around for about five minutes every hour.
Ultimately, research makes it clear that intermittent movement, such as brief, frequent stretching throughout the day or using the stairs rather than elevator, is more beneficial than cramming in a couple of hours at the gym on the weekend. This explains why small changes can have a big impact—it’s simply a matter of reminding yourself that it’s worth the effort.
Workstation Tips
Your ability to see the display and read the screen is key to reducing neck and eye strain. Here are a few strategic factors to remember:
Monitor height: Adjust the height of your monitor so the top is at eyebrow level, so you can look straight ahead at the screen.
Keyboard height: The keyboard height should be set so that your upper arms hang straight down while your elbows are bent at a 90-degree angle (like the letter L) with your forearms and wrists held horizontally.
Typeface and font size: For email, word processing, or web content, consider using a sans serif typeface. Fonts that have fewer curved lines and flourishes (serifs) tend to be more readable on screen.
Checking your vision: Many adults benefit from computer glasses to see the screen more clearly. Generally, we do not recommend reading glasses, bifocals, trifocals, and progressive lenses as they tend to allow clear vision at only one focal length. To see through the near-distance correction of the lens requires you to tilt your head back. Although progressive lenses allow you to see both close up and at a distance, the segment of the lens for each focal length is usually too narrow for working at the computer.
Wearing progressive lenses requires you to hold your head in a fixed position to be in focus. Yet you may be totally unaware that you are adapting your eye and head movements to sustain your focus. When that is the case, most people find that special computer glasses are a good solution.
Consider computer glasses if you must either bring your nose to the screen to read the text, wear reading glasses and find that their focal length is inappropriate for the monitor distance, wear bi- or trifocal glasses, or are older than forty.
Computer glasses correct for the appropriate focal distance to the computer. Typically, monitor distance is about twenty-three to twenty-eight inches, whereas reading glasses correct for a focal length of about fifteen inches. To determine your individual, specific focal length, ask a coworker to measure the distance from the monitor to your eyes. Provide this personal focal distance at the eye exam with your optometrist or ophthalmologist and request that your computer glasses be optimized for that distance.
Remembering to blink: As we focus on the screen, our blinking rate is significantly reduced. Develop the habit of blinking periodically: at the end of a paragraph, for example, or when sending an email.
Resting your eyes: Throughout the day, pause and focus on the far distance to relax your eyes. When looking at the screen, your eyes converge, which can cause eyestrain. Each time you look away and refocus, that allows your eyes to relax. It’s especially soothing to look at green objects such as a tree that can be seen through a window.
Minimizing glare: If the room is lit with artificial light, there may be glare from your light source if the light is right in front of you or right behind you, causing reflection on your screen. Reflection problems are minimized when light sources are at a 90-degree angle to the monitor (with the light coming from the side). The worst situations occur when the light source is either behind or in front of you.
An easy test is to turn off your monitor and look for reflections on the screen. Everything that you see on the monitor when it’s turned off is there when you’re working at the monitor. If there are bright reflections, they will interfere with your vision. Once you’ve identified the source of the glare, change the location of the reflected objects or light sources, or change the location of the monitor.
Contrast: Adjust the light contrast in the room so that it is neither too bright nor too dark. If the room is dark, turn on the lights. If it is too bright, close the blinds or turn off the lights. It is exhausting for your eyes to have to adapt from bright outdoor light to the lighting of your computer screen. You want the light intensity of the screen to be somewhat similar to that in the room where you’re working. You also do not want to look from your screen to a window lit by intense sunlight.
Don’t look down at phone: According to Kenneth Hansraj, MD, chief of spine surgery at New York Spine Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine, pressure on the spine increases from about ten pounds when you are holding your head erect, to sixty pounds of pressure when you are looking down. Bending forward to look at your phone, your head moves out of the line of gravity and is no longer balanced above your neck and spine. As the angle of the face-forward position increases, this intensifies strain on the neck muscles, nerves, and bones (the vertebrae).
The more you bend your neck, the greater the stress since the muscles must stretch farther and work harder to hold your head up against gravity. This same collapsed head-forward position when you are seated and using the phone repeats the neck and shoulder strain. Muscle strain, tension headaches, or neck pain can result from awkward posture with texting, craning over a tablet (sometimes referred to as the iPad neck), or spending long hours on a laptop.
A face-forward position puts as much as sixty pounds of pressure on the neck muscles and spine.
Repetitive strain of neck vertebrae (the cervical spine), in combination with poor posture, can trigger a neuromuscular syndrome sometimes diagnosed as thoracic outlet syndrome. According to researchers Sharan and colleagues, this syndrome can also result in chronic neck pain, depression, and anxiety.
When you notice negative changes in your mood or energy, or tension in your neck and shoulders, use that as a cue to arch your back and look upward. Think of a positive memory, take a mindful breath, wiggle, or shake out your shoulders if you’d like, and return to the task at hand.
Strengthen your core: If you find it difficult to maintain good posture, you may need to strengthen your core muscles. Fitness and sports that are beneficial for core strength include walking, sprinting, yoga, plank, swimming, and rowing. The most effective way to strengthen your core is through activities that you enjoy.
Final Thoughts
If these ideas resonate with you, consider lifestyle as the first step. We need to build dynamic physical activity into our lives, as well as the lives of our children. Being outside is usually an uplift, so choose to move your body in natural settings whenever possible, whatever form that takes. Being outside is the factor that adds an energetic dimension. Finally, share what you learn, and help others learn and grow from your experiences.
If you spend time in front of a computeror using a mobile device, read the book, TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. It provides practical, easy-to-use solutions for combating the stress and pain many of us experience due to technology use and overuse. The book offers extremely helpful tips for ergonomic use of technology, it
goes way beyond that, offering simple suggestions for improving muscle health that seem obvious once you read them, but would not have thought of yourself: “Why didn’t I think of that?” You will learn about the connection between posture and mood, reasons for and importance of movement breaks, specific movements you can easily perform at your desk, as well as healthier ways to utilize technology in your everyday life.
See the book, TechStress-How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey and Nancy Faass. Available from: https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X/

Additional resources
Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing
Posted: April 22, 2023 Filed under: behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, healing, health, meditation, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: dysmenorrhea, Imagery, menstrual cramps, stroking, visualization 6 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N., & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04; Republished in Townsend E-Letter – 18 November, 2023 https://www.townsendletter.com/e-letter-22-breath-affects-stress-and-menstrual-cramps/ Google NotebookLM generated podcast:

“I have always had extremely painful periods. They would get so painful that I would have to call in sick and take some time off from school. I have been to many doctors and medical professionals, and they told me there is nothing I could do. I am currently on birth control, and I still get some relief from the menstrual pain, but it would mess up my moods. I tried to do the diaphragmatic breathing so that I would be able to continue my life as a normal woman. And to my surprise it worked. I was simply blown away with how well it works. I have almost no menstrual pain, and I wouldn’t bloat so much after the diaphragmatic breathing.” -22 year old student
Each semester numerous students report that their cramps and dysmenorrhea symptoms decrease or disappear during the semester when they implement the relaxation and breathing practices that are taught in the semester long Holistic Health class. Given that so many young women suffer from dysmenorrhea, many young women could benefit by using this integrated approach as the first self-care intervention before relying on pain reducing medications or hormones to reduce pain or inhibit menstruation. Another 28-year-old student reported:
“Historically, my menstrual cramps have always required ibuprofen to avoid becoming distracting. After this class, I started using diaphragmatic breath after pain started for some relief. True benefit came when I started breathing at the first sign of discomfort. I have not had to use any pain medication since incorporating diaphragmatic breath work.”
This report describes students practicing self-regulation and effortless breathing to reduce stress symptoms, explores possible mechanisms of action, and suggests a protocol for reducing symptoms of menstrual cramps. Watch the short video how diaphragmatic breathing eliminated recurrent severe dysmenorrhea (pain and discomfort associated with menstruation).
Background: What is dysmenorrhea?
Dysmenorrhea is one of the most common conditions experienced by women during menstruation and affects more than half of all women who menstruate (Armour et al., 2019). Most commonly dysmenorrhea is defined by painful cramps in the lower abdomen often accompanied by pelvic pain that starts either a couple days before or at the start of menses. Symptoms also increase with stress (Wang et al., 2003) with pain symptoms usually decreasing in severity as women get older and, after pregnancy.
Economic cost of dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea can significantly interfere with a women’s ability to be productive in their occupation and/or their education. It is “one of the leading causes of absenteeism from school or work, translating to a loss of 600 million hours per year, with an annual loss of $2 billion in the United States” (Itani et al, 2022). For students, dysmenorrhea has a substantial detrimental influence on academic achievement in high school and college (Thakur & Pathania, 2022). Despite the frequent occurrence and negative impact in women’s lives, many young women struggle without seeking or having access to medical advice or, without exploring non-pharmacological self-care approaches (Itani et al, 2022).
Treatment
The most common pharmacological treatments for dysmenorrhea are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (e.g., Ibuprofen, Aspirin, and Naproxen Sodium) along with hormonal contraceptives. NSAIDs act by preventing the action of cyclooxygenase which prevents the production of prostaglandins. Itani et al (2022) suggested that prostaglandin production mechanisms may be responsible for the disorder. Hormonal contraceptives also prevent the production of prostaglandins by suppressing ovulation and endometrial proliferation.
The pharmacological approach is predominantly based upon the model that increased discomfort appears to be due to an increase in intrauterine secretion of prostaglandins F2α and E2 that may be responsible for the pain that defines this condition (Itani et al, 2022). Pharmaceuticals which influence the presence of prostaglandins do not cure the cause but mainly treat the symptoms.
Treatment with medications has drawbacks. For example, NSAIDs are associated with adverse gastrointestinal and neurological effects and also are not effective in preventing pain in everyone (Vonkeman & van de Laar, 2010). Hormonal contraceptives also have the possibility of adverse side effects (ASPH, 2023). Acetaminophen is another commonly used treatment; however, it is less effective than other NSAID treatments.
Self-regulation strategies to reduce stress and influence dysmenorrhea
Common non-pharmacological treatments include topical heat application and exercise. Both non-medication approaches can be effective in reducing the severity of pain. According to Itani et al. (2022), the success of integrative holistic health treatments can be attributed to “several mechanisms, including increasing pelvic blood supply, inhibiting uterine contractions, stimulating the release of endorphins and serotonin, and altering the ability to receive and perceive pain signals.”
Although less commonly used, self-regulation strategies can significantly reduce stress levels associated menstrual discomfort as well as reduce symptoms. More importantly, they do not have adverse side effects, but the effectiveness of the intervention varies depending on the individual.
- Autogenic Training (AT), is a hundred year old treatment approach developed by the German psychiatrist Johannes Heinrich Schultz that involves three 15 minute daily practice of sessions, resulted in a 40 to 70 percent decrease of symptoms in patient suffering from primary and secondary dysmenorrhea (Luthe & Schultz, 1969). In a well- controlled PhD dissertation, Heczey (1978) compared autogenic training taught individually, autogenic training taught in a group, autogenic training plus vaginal temperature training and a no treatment control in a randomized controlled study. All treatment groups except the control group reported a decrease in symptoms and the most success was with the combined autogenic training and vaginal temperature training in which the subjects’ vaginal temperature increased by .27 F degrees.
- Progressive muscle relaxation developed by Edmund Jacobson in the 1920s and imagery are effective treatments for dysmenorrhea (Aldinda et al., 2022; Chesney & Tasto, 1975; Çelik, 2021; Jacobson, 1938; Proctor et al., 2007).
- Rhythmic abdominal massage as compared to non-treatment reduces dysmenorrhea symptoms (Suryantini, 2022; Vagedes et al., 2019):
- Biofeedback strategies such as frontalis electromyography feedback (EMG) and peripheral temperature training (Hart, Mathisen, & Prater, 1981); trapezius EMG training (Balick et al, 1982); lower abdominal EMG feedback training and relaxation (Bennink, Hulst, & Benthem, 1982); and integrated temperature feedback and autogenic training (Dietvorts & Osborne, 1978) all successfully reduced the symptoms of dysmenorrhea.
- Breathing relaxation for 5 to 30 minutes resulted in a decrease in pain or the pain totally disappeared in adolescents (Hidayatunnafiah et al., 2022). While slow deep breathing in combination with abdominal massage is more effective than applying hot compresses (Ariani et al., 2020). Slow pranayama (Nadi Shodhan) breathing the quality of life and pain scores improved as compared to fast pranayama (Kapalbhati) breathing and improved quality of life and reduces absenteeism and stress levels (Ganesh et al. 2015). When students are taught slow diaphragmatic breathing, many report a reduction in symptoms compared to the controls (Bier et al., 2005).
Observations from Integrated stress management program
This study reports on changes in dysmenorrhea symptoms by students enrolled in a University Holistic Health class that included homework assignment for practicing stress awareness, dynamic relaxation, and breathing with imagery.
Respondents: 32 college women, average age 24.0 years (S.D. 4.5 years)
Procedure: Students were enrolled in a three-unit class in which they were assigned daily home practices which changed each week as described in the book, Make Health Happen (Peper, Gibney & Holt, 2002). The first five weeks consisted of the following sequence: Week 1 focused on monitoring one’s reactions to stressor; week 2 consisted of daily practice for 30 minutes of a modified progressive relaxation and becoming aware of bracing and reducing the bracing during the day; Week 3 consisted of practicing slow diaphragmatic breathing for 30 minutes a day and during the day becoming aware of either breath holding or shallow chest breath and then use that awareness as cue to shift to lower slower diaphragmatic breathing; week 4 focused on evoking a memory of wholeness and relaxing; and week 5 focused on learning peripheral hand warming.
During the class, students observed lectures about stress and holistic health and met in small groups to discuss their self-regulation experiences. During the class discussion, some women discussed postures and practices that were beneficial when experiencing menstrual discomfort, such as breathing slowly while lying on their back, focusing on slow abdominal awareness in which their abdomen expanded during inhalation and contracted during exhalation. While exhaling they focused on imagining a flow of air initially going through their arms and then through their abdomen, down their legs and out their feet. This kinesthetic feeling was enhanced by first massaging down the arm while exhaling and then massaging down their abdomen and down their thighs when exhaling. In most cases, the women also experienced that their hands and feet warmed. In addition, they were asked to shift to slower diaphragmatic breathing whenever they observed themselves gasping, shallow breathing or holding their breath. After five weeks, the students filled out a short assessment questionnaire in which they rated the change in dysmenorrhea symptoms since the beginning of the class.
Results.
About two-thirds of all respondents reported a decrease in overall discomfort symptoms. In addition to any ‘treatment as usual’ (TAU) strategies already being used (e.g. medications or other treatments such as NSAIDs or birth control pills), 91% (20 out 22 women) who reported experiencing dysmenorrhea reported a decrease in symptoms when they practiced the self-regulation and diaphragmatic breathing techniques as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Self-report in dysmenorrhea symptoms after 5 weeks.
Discussion
Many students reported that their symptoms were significantly reduced and they could be more productive. Generally, the more they practiced the relaxation and breathing self-regulation skills, the more they experienced a decrease in symptoms. The limitation of this report is that it is an observational study; however, the findings are similar to those reported by earlier self-care and biofeedback approaches. This suggests that women should be taught the following simple self-regulation strategies as the first intervention to prevent and when they experience dysmenorrhea symptoms.
Why would breathing reduce dysmenorrhea?
Many women respond by ‘curling up’ a natural protective defense response when they experience symptoms. This protective posture increases abdominal and pelvic muscle tension, inhibits lymph and blood flow circulation, increases shallow breathing rate, and decreases heart rate variability. Intentionally relaxing the abdomen with slow lower breathing when lying down with the legs extended is often the first step in reducing discomfort.
By focusing on diaphragmatic breathing with relaxing imagery, it is possible to restore abdominal expansion during inhalation and slight constriction during exhalation. This dynamic breathing while lying supine would enhance abdominal blood and lymph circulation as well as muscle relaxation (Peper et al., 2016). While practicing, participants were asked to wear looser clothing that did not constrict the waist to allow their abdomen to expand during inhalation; since, waist constriction by clothing (designer jean syndrome) interferes with abdominal expansion. Allowing the abdomen to fully extend also increased acceptance of self, that it was okay to let the abdomen expand instead of holding it in protectively. The symptoms were reduced most likley by a combination of the following factors.
- Abdominal movement is facilitated during the breathing cycle. This means reducing the factors that prevent the abdomen expanding during inhalation or constricting during exhalation (Peper et al., 2016).
- Eliminate‘Designer jean syndrome’ (the modern girdle). Increase the expansion of your abdomen by loosening the waist belt, tight pants or slimming underwear (MacHose & Peper, 1991).
- Accept yourself as you are. Allow your stomach to expand without pulling it in.
- Free up learned disuse: Allow the abdomen to expand and constrict instead of inhibiting movement to avoid pain that occurred following a prior abdominal injury/surgery (e.g., hernia surgery, appendectomy, or cesarean operation), abdominal pain (e.g., irritable bowel syndrome, recurrent abdominal pain, ulcers, or acid reflux), pelvic floor pain (e.g., pelvic floor pain, pelvic girdle pain, vulvodynia, or sexual abuse).
- The ‘defense response’ is reduced. Many students described that they often would curl up in a protective defense posture when experiencing menstrual cramps. This protective defense posture would maintain pelvic floor muscle contractions and inhibit blood and lymph flow in the abdomen, increase shallow rapid thoracic breathing and decrease pCO2 which would increase vasoconstriction and muscle constriction (Peper et al., 2015; Peper et al., 2016). By having the participant lie relaxed in a supine position with their legs extended while practicing slow abdominal breathing, the pelvic floor and abdominal wall muscles can relax and thereby increase abdominal blood and lymph circulation and parasympathetic activity. The posture of lying down implies feeling safe which is a state that facilitates healing.
- The pain/fear cycle is interrupted. The dysmenorrhea symptoms may trigger more symptoms because the person anticipates and reacts to the discomfort. The breathing and especially the kinesthetic imagery where the attention goes from the abdomen and area of discomfort to down the legs and out the feet acts as a distraction technique (not focusing on the discomfort).
- Support sympathetic-parasympathetic balance. The slow breathing and kinesthetic imagery usually increases heart rate variability and hand and feet temperature and supports sympathetic parasympathetic balance.
- Interrupt the classical conditioned response of the defense reaction. For some young girls, the first menstruation occurred unexpectedly. All of a sudden, they bled from down below without any understanding of what is going on which could be traumatic. For some this could be a defense reaction and a single trial condition response (somatic cues of the beginning of menstruation triggers the defense reaction). Thus, when the girl later experiences the initial sensations of menstruation, the automatic conditioned response causes her to tense and curl up which would amplify the discomfort. Informal interviews with women suggests that those who experienced their first menstruation experience as shameful, unexpected, or traumatic (“I thought I was dying”) thereafter framed their menstruation negatively. They also tended to report significantly more symptoms than those women who reported experiencing their first menstruation positively as a conformation that they have now entered womanhood.
How to integrate self-care to reduce dysmenorrhea
Be sure to consult your healthcare provider to rule out treatable underlying conditions before implementing learning effortless diaphragmatic breathing.
- Allow the abdomen to expand during inhalation and become smaller during exhalation. This often means, loosen belt and waist constriction, acceptance of allowing the stomach to be larger and reversing learned disuse and protective response caused by stress.
- Master diaphragmatic breathing (see: Peper & Tibbetts, 1994 and the blogs listed at the end of the article).
- Practice slow effortless diaphragmatic breathing lying down with warm water bottle on stomach in a place that feels safe.
- Include kinesthetic imagery as you breathe at about 6 breaths per minute (e.g. slowly inhale for 4 or 5 seconds and then exhale for 5 or 6 seconds, exhaling slightly longer than inhaling). Imaging that when you exhale you can sense healing energy flow through your abdomen, down the legs and out the feet.
- If possible, integrate actual touch with the exhalation can provide added benefit. Have a partner first stroke or massage down the arms from the shoulder to your fingertips as you exhale and, then on during next exhalation stroke gently from your abdomen down your legs and feet. Stroke in rhythm the exhalation.
- Exhale slowly and shift to slow and soft diaphragmatic breathing each time you become aware of neck and shoulder tension, breath holding, shallow breathing, or anticipating stressful situations. At the same time imagine /sense when exhaling a streaming going through the abdomen and out the feet when exhaling. Do this many times during the day.
- Practice and apply general stress reduction skills into daily life since stress can increase symptoms. Anticipate when stressful event could occur and implement stress reducing strategies.
- Be respectful of the biological changes that are part of the menstrual cycle. In some cases adjust your pace and slow down a bit during the week of the menstrual cycle; since, the body needs time to rest and regenerate. Be sure to get adequate amount of rest, hydration, and nutrition to optimize health.
- Use self-healing imagery and language to transform negative association with menstruation to positive associations (e.g., “curse” to confirmation “I am healthy”).
Conclusion
There are many ways to alleviate dysmenorrhea. Women can find ways to anticipate and empower themselves by practicing stress reduction, wearing more comfortable clothing, using heat compression, practicing daily diaphragmatic breathing techniques, visualizing relaxed muscles, and positive perception towards menstrual cycles to reduce the symptoms of dysmenorrhea. These self-regulation methods should be taught as a first level intervention to all young women starting in middle and junior high school so that they are better prepared for the changes that occur as they age.
“I have been practicing the breathing techniques for two weeks prior and I also noticed my muscles, in general, are more relaxed. Of course, I also avoided the skinny jeans that I like to wear and it definitely helped.
I have experienced a 90% improvement from my normal discomfort. I was still tired – and needed more rest and sleep but haven’t experienced any “terrible” physical discomfort. Still occasionally had some sharp pains or bloating but minor discomfort, unlike some days when I am bedridden and unable to move for half a day. – and this was a very positive experience for me “ — Singing Chen (Chen, 2023)
Useful blogs to learn diaphragmatic breathing
References
Aldinda, T. W., Sumarni, S., Mulyantoro, D. K., & Azam, M. (2022). Progressive muscle relaxation application (PURE App) for dysmenorrhea. Medisains Jurnal IlmiahLlmiah LLmu-LLmu Keshatan, 20(2), 52-57. https://doi.org/10.30595/medisains.v20i2.14351
Ariani, D., Hartiningsih, S.S., Sabarudin, U. Dane, S. (2020). The effectiveness of combination effleurage massage and slow deep breathing technique to decrease menstrual pain in university students. Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science, 8(3), 79-84. https://www.jrmds.in/articles/the-effectiveness-of-combination-effleurage-massage-and-slow-deep-breathing-technique-to-decrease-menstrual-pain-in-university-stu-53607.html
Armour, M., Parry, K., Manohar, N., Holmes, K., Ferfolja, T., Curry, C., MacMillan, F., & Smith, C. A. (2019). The prevalence and academic impact of dysmenorrhea in 21,573 young women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of women’s health, 28(8), 1161-1171.https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2018.7615
ASPH. (2023). Estrogen and Progestin (Oral Contraceptives). MedlinePlus. Assessed March 3, 2023. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a601050.html
Balick, L., Elfner, L., May. J., Moore, J.D. (1982). Biofeedback treatment of dysmenorrhea. Biofeedback Self Regul, 7(4), 499-520. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998890
Bennink, C.D., Hulst, L.L. & Benthem, J.A. (1982). The effects of EMG biofeedback and relaxation training on primary dysmenorrhea. J Behav Med, 5(3), 329-341.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846160
Bier, M., Kazarian, D. & Peper, E. (2005). Reducing PMS through biofeedback and breathing. Poster presentation at the 36th Annual Meeting of the Association for Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. Abstract published in: Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 30 (4), 411-412.
Çelik, A.S. & Apay, S.E. (2021). Effect of progressive relaxation exercises on primary dysmenorrhea in Turkish students: A randomized prospective controlled trial. Complement Ther Clin Pract, Feb 42,101280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101280
Chen, S. (2023). Diaphragmatic breathing reduces dysmenorrhea symptoms-a testimonial. YouTube. Accessed March 3, 2023. https://youtu.be/E45iGymVe3U
De Sanctis, V., Soliman, A., Bernasconi, S., Bianchin, L., Bona, G., Bozzola, M., Buzi, F., De Sanctis, C., Tonini, G., Rigon, F., & Perissinotto, E. (2015). Primary Dysmenorrhea in Adolescents: Prevalence, Impact and Recent Knowledge. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 13(2), 512-20. PMID: 26841639. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26841639/
De Sanctis, V., Soliman, A. T., Daar, S., Di Maio, S., Elalaily, R., Fiscina, B., & Kattamis, C. (2020). Prevalence, attitude and practice of self-medication among adolescents and the paradigm of dysmenorrhea self-care management in different countries. Acta Bio Medica: Atenei Parmensis, 91(1), 182. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i1.9242
Dietvorst, T.F. & Osborne, D. (1978). Biofeedback-Assisted Relaxation Training
for Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Case Study. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 3(3), 301-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999298
Chesney, M. A., & Tasto, D. L. (1975).The effectiveness of behavior modification with spasmodic and congestive dysmenorrhea. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 13, 245-253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(75)90029-7
Ganesh, B.R., Donde, M.P., & Hegde, A.R. (2015). Comparative study on effect of slow and fast phased pranayama on quality of life and pain in physiotherapy girls with primary dysmenorrhea: Randomize clinical trial. International Journal of Physiotherapy and Research, 3(2), 960-965. https://doi.org/10.16965/ijpr.2015.115
Hart, A.D., Mathisen, K.S. & Prater, J.S. A comparison of skin temperature and EMG training for primary dysmenorrhea. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation 6, 367–373 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000661
Heczey, M. D. (1978). Effects of biofeedback and autogenic training on menstrual experiences: relationship among anxiety, locus of control and dysmenorrhea. City University of New York ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 7805763. https://www.proquest.com/openview/088e0d68511b5b59de1fa92dec832cc8/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y
Hidayatunnafiah, F., Mualifah, L., Moebari, M., & Iswantiningsih, E. (2022). The Effect of Relaxation Techniques in Reducing Dysmenorrhea in Adolescents. The International Virtual Conference on Nursing. in The International Virtual Conference on Nursing, KnE Life Sciences, 473–480. https://doi.org/10.18502/kls.v7i2.10344
Itani, R., Soubra, L., Karout, S., Rahme, D., Karout, L., & Khojah, H.M.J. (2022). Primary Dysmenorrhea: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Updates. Korean J Fam Med, 43(2), 101-108. https://doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.21.0103
Jacobson, E. (1938). Progressive Relaxation: A Physiological and Clinical Investigation of Muscular States and Their Significance in Psychology and Medical Practice. Chicago: University of Chicago Press
Ju, H., Jones, M., & Mishra, G. (2014). The prevalence and risk factors of dysmenorrhea. Epidemiol Rev, 36, 104-13. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxt009
Karout, S., Soubra, L., Rahme, D. et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management practices of primary dysmenorrhea among young females. BMC Women’s Health 21, 392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-021-01532-w
Iacovides, S., Avidon,I, & Baker, F.C. (2015).What we know about primary dysmenorrhea today: a critical review, Human Reproduction Update, 21(6), 762–778. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmv039
Luthe, W. & Schultz, J.H. (1969). Autogenic Therapy, Volume II Medical Applications. New York: Grune & Stratton, pp144-148.
MacHose, M. & Peper, E. (1991). The effect of clothing on inhalation volume. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 16(3), 261–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000020
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Gibney, H. K. & Holt, C. (2002). Make Health Happen. Dubuque, Iowa: Kendall-Hunt. ISBN: 978-0787293314 https://he.kendallhunt.com/make-health-happen
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Peper, E. & Tibbetts, V. (1994). Effortless diaphragmatic breathing. Physical Therapy Products. 6(2), 67-71. Also in: Electromyography: Applications in Physical Therapy. Montreal: Thought Technology Ltd. https://biofeedbackhealth.files.wordpress.com/2011/01/peper-and-tibbets-effortless-diaphragmatic.pdf
Proctor, M. & Farquhar, C. (2006). Diagnosis and management of dysmenorrhoea. BMJ. 13, 332(7550), 1134-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.332.7550
Proctor, M.L, Murphy, P.A., Pattison, H.M., Suckling, J., & Farquhar, C.M. (2007). Behavioural interventions for primary and secondary dysmenorrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, (3):CD002248. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002248.pub3
Suryantini, N. P. (2022). Effleurage Massage: Alternative Non-Pharmacological Therapy in Decreasing Dysmenorrhea Pain. Women, Midwives and Midwifery, 2(3), 41-50. https://wmmjournal.org/index.php/wmm/article/view/71/45
Thakur, P. & Pathania, A.R. (2022). Relief of dysmenorrhea – A review of different types of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. MaterialsToday: Proceedings.18, Part 5, 1157-1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.207
Vagedes, J., Fazeli, A., Boening, A., Helmert, E., Berger, B. & Martin, D. (2019). Efficacy of rhythmical massage in comparison to heart rate variability biofeedback in patients with dysmenorrhea—A randomized, controlled trial. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 42, 438-444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2018.11.009
Vonkeman, H.E. & van de Laar, M,A. (2010). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: adverse effects and their prevention, Semin Arthritis Rheum, 39(4), 294-312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.08.001
Wang, L., Wand, X., Wang, W., Chen, C. Ronnennberg, A.G., Guang, W. Huang, A. Fang, Z. Zang, T., Wang, L. & Xu, X. (2003).Stress and dysmenorrhoea: a population based prospective study. Occupation and Environmental Medicine, 61(12). http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/oem.2003.012302
Thoughts Have the Power to Create or Eliminate Body Tension
Posted: January 31, 2023 Filed under: Breathing/respiration, CBT, cognitive behavior therapy, computer, emotions, ergonomics, healing, health, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: Alexander Technique, mind-body connection 3 CommentsBy Tami Bulmash republished from: Medium-Body Wisdom
Photo by Jonathan Borba on Unsplash
The mind and body have long been regarded and treated as separate entities, yet this distinction does little to promote holistic health. Understanding the direct relationship between thoughts and body tension can illustrate how the mind and body either work dysfunctionally through separation, or optimally as a unit.
Mental and physical aren’t separate entities
Stress and pain existed long before the coronavirus, though it was highlighted during this isolating era. In the height of the pandemic nearly eight in 10 American adults cited COVID-19 as a significant stressor. Though it may no longer be front page news, the aftermath of COVID still lingers. Its toll on mental health continues to impact children and adults alike. The shift to remote work was appealing at first, but later created a more pervasive sedentary lifestyle. Now the concern has shifted to an emerging pandemic of back pain.
Yet, there is nothing novel about body tension brought forth by stressful thinking. In 2014, the American Institute of Stress reported 77 percent of people regularly experience physical symptoms caused by stress. Moreover, the findings of a 2018 Gallup poll suggest 55 percent of Americans report feeling stressed for a large part of their day. This is compounded by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons finding one in two Americans have a musculoskeletal condition. Discerning between mental and physical stress is becoming increasingly obscure.
While the mind and body have long been regarded and treated as separate entities, this distinction does little to promote holistic health. Understanding the direct relationship between thoughts and tension can illustrate how the mind and body either work dysfunctionally through separation, or optimally as a unit. What’s more, viewing the body as a whole being — in thought and activity — can promote better habits which eliminate tension.
The link between stress and pain
Dividing the self into parts is common practice in the Western world. Expressions such as “I’m mentally exhausted” vs. “I’m physically exhausted” provoke differing self-reflections. However, the psycho-physical relationship is evident in the tension stimulated by either thought. For example, sitting in front of a computer necessitates both thought and action. Viewing content on a screen lends itself to a reaction from behind the screen. This response can be minimal and inconsequential, or it can be subtle, yet critical.
Repeatedly engaging in certain thinking habits like, “I have to get this done and fast” are often reflected in forms of body tension such as stiff fingers at the keyboard, a clenched jaw after a meeting, or tense neck at the end of the day. These unconscious responses are common and have a pervasive effect.
The prevalence of technology has led to a plethora of occupational ailments, now referred to as technology diseases. These include carpal tunnel syndrome, mouse shoulder, and cervical pain syndrome and occur because of excessive work at the computer — especially keyboard and mouse usage. According to the book, TechStress-How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping and Pragmatic Ergonomics, by Drs. Erik Peper, Richard Harvey and Nancy Faass, 45 million people suffer from tension headaches, carpal tunnel, and back injuries linked to computer use and more than 30 percent of North Americans who work at a computer develop a muscle strain injury every year.
Pushing through mental tasks is reflected in the physical
Dr. Peper, a biofeedback expert and Professor of Holistic Health at San Francisco State University, gives an illustration of the mind-body connection in relation to pain. His example requires the use of a computer mouse while trying to complete difficult mental tasks. He asks me to hold the mouse in my dominant hand and draw with it the last letter of an address. Then continue to go backward with each letter of the street name, making sure the letter height is only one-half of an inch. He tells me to perform the task as quickly as possible. As I’m drawing the address backwards trying to recall the letters and their order, Dr. Peper commands, “Do it quicker, quicker, quicker! Don’t make a mistake! Quicker, quicker, quicker!”
These commands reflect the endless to-do lists that pile up throughout the day and the stress associated with their efficacy and timely completion. While enacting this task, Dr. Peper asks me, “Are you tightening your shoulders? Are you tightening your trunk? Are you raising your shoulders possibly holding all this tension? If you are like most people who do this task, you did all of that and you were totally unaware. We are usually really unaware of our body posture.”
I have spent the past 20 years practicing the Alexander Technique, a method used to improve postural health. At its core the technique is about observation and utilizing psycho-physical awareness to stop repeating harmful habits. Dr. Peper’s words resonate because becoming aware of unconscious responses isn’t easy. Most people are completely unaware of the relationship between mind-body habits and how they contribute to stress-related pain.
Posture affects mood and energy levels
Posture is often thought of as a pose — most notably being associated with “sitting up straight”. Yet the health implications of good posture extend far beyond any held position. The agility and movement which are evident in good posture exemplify the mind-body connection.
It is well-known that feeling depressed has been linked to having less subjective energy. The American Psychiatric Association listed a variety of symptoms connected to depression including feeling sad or having a depressed mood, loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, and loss of energy or increased fatigue. While the treatment of depression hasn’t traditionally considered the role of posture in informing mood, researchers have started exploring this relationship.
A study by Dr. Peper and Dr. I-Mei Lin examined the subjective energy levels of university students and their corresponding expression of depression. Participants who walked in a slouched position reported lower energy levels and higher self-rated depression scores. In contrast, when those participants walked in a pattern of opposite arm and leg skipping, they experienced an increase in energy, allowing a positive mindset to ensue.
As mentioned in the study, the mind-body relationship is a two-way street: mind to body and body to mind. If thoughts are manifested in the way one holds their body, the inverse would also be true. Namely, changing the way one carries their body would also influence their thinking and subsequent mood. If stopping certain habits — such as walking in a slumped posture — could have a positive impact on mood and well-being, perhaps it’s worth exploring the mind-body relationship even further.
Supporting the mind-body connection
One of the best ways to improve the mind-body connection is through awareness. The more present you are in your activities, the more unified the relation becomes. Give yourself a couple of minutes to connect your thoughts with what you are doing at the moment.
Begin With Grounding
If you are sitting down, imagine coloring in the space of your whole body with an imaginary marker. Begin with your feet planted on the floor. Start to outline the footprints of your feet and then color in the bottom and top of each foot. Take your time. Fill in all the space. See if you discover new parts of your feet — like the spaces between your toes. Continue up through your ankles and toward your calves. Pay attention to the entire limb (front and back). Work your way upward through the knee and then the upper leg. See if you can find your sit bones along the way to the torso. Explore new joints — such as the hip joint.
Lengthen Your Body Through Thought
Continue up while circling the front and back of the torso. Extend the awareness of your thoughts through your shoulders. Allow for an exploration of the arms — noting the joints such as the elbows, wrists and fingers. Pay attention to their length and mobility. Come back up through the arms. Extend up through the shoulders again, this time noting the passage through the chest and neck. Observe the length and space within your entire being. Journey up to the head and travel around its circumference. Imagine filling your head space with air. Picture the wholeness of your head from top to bottom and side to side.
This two-minute mind-body meditation allows you to feel the full extent of the space your body takes up. It is a way to awaken the senses and include them in conscious thinking. This helps generate awareness in how to engage the mind-body relationship optimally. The next time you try it, use a visual aid like an anatomy diagram of the whole body. This can also introduce new parts and spaces of the body you may not have thought of before. However, don’t rely on the diagram each time, as it can pull away your attention from the mind-body meditation. Instead, use it as a reference or guide every once in a while.
Learn from other cultures
In Western cultures, it is common practice to divvy up musculoskeletal ailments into an array of categories such as tension headaches, tension neck syndrome, or mechanical back syndrome. For instance, in countries like the U.S., it is normal to seek a specialist for each area of concern — like a neurologist for a migraine, an orthopedist for neck strain, or chiropractors for back pain. In contrast, Eastern lifestyles have historically taken a more holistic approach to treating (and healing) their patients.
An article by Dr. Cecilia Chan, Professor of Social Sciences at the University of Hong Kong, explains how the Eastern philosophies of Buddhism, Taoism and traditional Chinese medicine adopt a holistic approach to the healing of an individual. Rather than diagnose and treat with medication, Chan and her colleagues explore health through the harmony and balance of the body-mind-spirit as a whole.
Because basic biology clearly delineates how the human head is attached to the body, it seems fitting that the entire being be regarded as a unit. By recognizing the relationship between thought stressors and their manifestation in the physical body, awareness is elevated. This, in turn, can prevent mindlessly engaging in harmful patterns that lead to stress and pain. Combating tension is possible through the realization of how thoughts — whether they are emotional or task oriented — directly impact the body as a whole.
This excerpt from Taro Gold’s book, Open Your Mind, Open Your Life: A Book of Eastern Wisdom, cites Mahatma Gandhi’s famous quote which beautifully elucidates the mind-body connection:
Keep your thoughts positive, because your thoughts become your words.
Keep your words positive, because your words become your behavior.
Keep your behavior positive, because your behavior becomes your habits.
Keep your habits positive, because your habits become your values.
Keep your values positive, because your values become your destiny.
Referring to the mind and body as separate entities perpetuates a disconnect in the being as a whole. This is why distinguishing the mental from the physical further exacerbates the notion that the two don’t work together as an indivisible unit. Understanding the relationship between stress and tension begins through the awareness of habits.
There are recurrent thinking habits like “I’ve got to get this done now” and their unconscious counterparts that become visible through posture. The unknown habits are the ones which accrue over time and often appear seemingly out of nowhere — in the form of tension or pain. Modern culture is quick to treat symptoms, such as those related to excessive technology use. However, a holistic approach to addressing the underlying issue would examine how stress and pain work hand in hand. Once the thoughts change, so will the tension.