Hope for dry eyes and eye strain
Posted: March 2, 2026 Filed under: attention, behavior, Breathing/respiration, computer, digital devices, emotions, health, Pain/discomfort, relaxation, screen fatigue, self-healing, stress management, techstress, Uncategorized, vision, zoom fatigue | Tags: behavioral optometry, blinking, digital eye strain, dry eyes, eyes, ophthalmology, optometry, prarasympathetic regulation 1 CommentAdapted from: Peper, E., Yoshino, A., & Harvey, R. Hope for Dry eyes and Eye Strain: How Breathing-Blinking Patterns Influence Dry Eye.
Many times during the day, I let my shoulders and face relax, and with each exhalation I feel the upper eyelids slightly dropping down at the same time as I am relaxing my jaw and mouth while sitting tall. I sense my tongue and throat sinking and feeling an increase in the space between my upper and lower molars. At the same time, I sense my eyes becoming soft and sinking down as my face muscle relax and are pulled down by gravity while sensing a gentle smile. My eyes are not trying to focus on anything. I continue to breathe slowly allowing a pause before inhaling and feel totally safe and at peace. While doing this, I sense moisture at the lower eyelids. After I have inhaled and as I exhale, I slowly open my eyes, and return to my work. My eyes feel slightly moist and as I blink, the eyelids glide smoothly over the corneal surface.
Background
Dry eyes and eye strain are far more common than most people realize. More than 50% of adults in the United States and Europe experience irritated or burning eyes, dryness, eye strain, headaches, tired or heavy eyes, sensitivity to bright light, and general eye discomfort (Wozniak et al., 2025). The prevalence increases with age and is higher among people who smoke, wear contact lenses, or spend excessive time looking at screens—typically more than six hours per day (Uchino et al,, 2013).
Prolonged, intense screen use—often referred to as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome—occurs when people focus and concentrate, and the muscles involved with near vision contract and do not relax (Chu et al., 2014). During near vision, the ciliary muscles tighten around the lens to allow near focus, and the medial rectus muscles contract to converge the eyes. These muscles stay contracted and only relax when looking into the distance. This ongoing tension and increased sympathetic activation combined with reduced blinking decrease tearing, and contribute to dry eye symptoms because the tears are not able to provide adequate moisture. As a result, the eyes may become irritated, red and inflamed, which increases eye discomfort (Sheppard & Wolffsohn, 2018; Portello et al., 2012; Sheedy et al., 2003).
When someone is vigilant, fearful, or anticipates a threat, sympathetic activation increases (Ranti et al., 2020) and “eye blink are inhibited at precise moments in time so as to minimize the loss of visual information that occurs during a blink. The more important the visual information is to the viewer, the more likely he or she will be to inhibit blinking” (Ranti et al., 2020).
Without being aware, many people are in a chronic state of vigilance and unknowingly are scanning the world for threats to which they must react. Clinically, I often observe this when guiding clients in relaxation. For example, when I give the instruction, “Let me lift your hand,” some clients immediately lift their hand towards me. This nonverbal response suggests that they are constantly vigilant and are monitoring the world around them—always ready to act instead of trusting that they do not have to act and that the world is safe. In most cases, their breathing pattern tends to be shallow and thoracic.
Would it be possible that this ongoing vigilance,which increases sympathetic arousal contributes to the experience of dry eye syndrome? It could be one factor explaining why women have a higher incidence of dry eye disease as well as anxiety than men since the world is often less safe for women, and they breathe more thoracically and less diaphragmatically (abdominally) than men. Shallow chest breathing is also associated with increased in anxiety (Fugl-Meyer, 1974; Mendes et al., 2020; Wilhelm et al., 2001; Banushi eat al., 2023; McLean et al., 2011; Jalnapurkar, et al., 2018).
Note: The risk of dry eye can also be further increased by a wide range of medical conditions and medications, such as diabetes; glaucoma and glaucoma medications; allergies; autoimmune diseases; arthritis; thyroid disease; high cholesterol; acne treatments; antihistamines; antidepressants; and a history of refractive surgery, conjunctival infections, or corneal abrasions. Dry eye also occurs more frequently in women (Mohamed et al., 2024).
What is usually recommended to resolve dry eyes
The primary and effective first-line treatment to reduce the symptoms of dry eye disease is the use of artificial tears (lubricating eye drops) to provide relief (Maity et al., 2025). Another recommendation to reduce eye strain associated with computer use is to implement the 20/20/20 rule developed by the American Optometric Association–take a 20-second break every 20 minutes and look at something 20 feet away (AOA, 2026). Although the 20/20/20 practice can reduce eye strain and momentarily reduce some of the symptoms associated with dry eye disease especially if the eyes are closed, how we orient, breathe and look may contribute to the experience of dry eye discomfort.
Experience how to evoke dry eyes
Sit comfortably, look around, and observe how your eyes feel. Close your eyes. Now imagine there is a threat. Take a very quick gasp through an open mouth by inhaling into your upper chest and keep breathing very shallowly and irregularly. At the same time, open your eyes wide while being vigilant and looking for danger. Simultaneously, tense your body, inclining it slightly backward as if trying to avoid something. Do not blink, as you may miss the potential threat approaching you (adapted from Lemeignan et al., 1990; Bloch, 2017). A sample physiological recording of this pattern is shown in Figure 1.
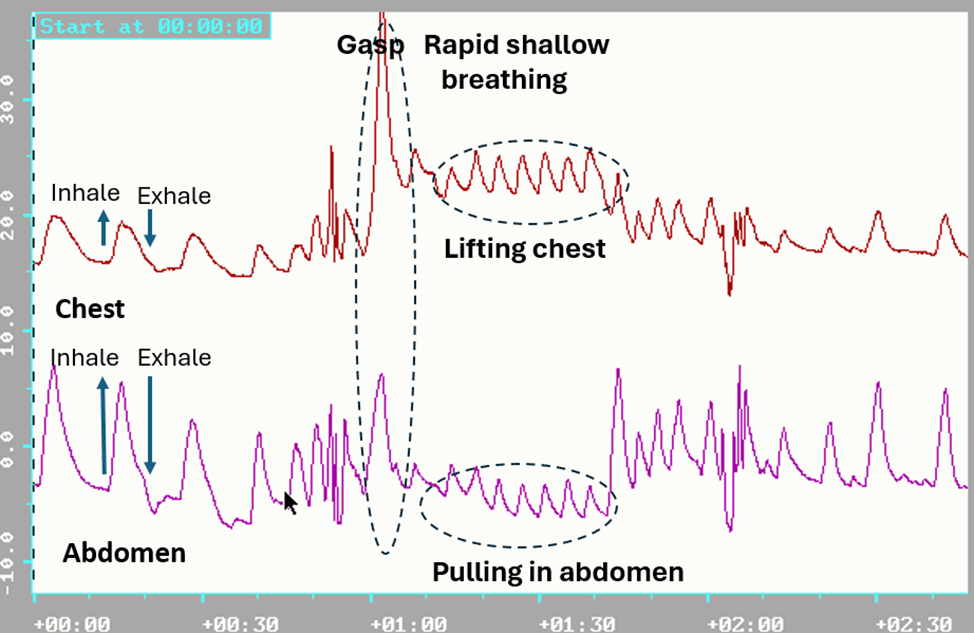
Figure 1. Breathing pattern in response to a threat; a rapid gasp into the chest and pulling the abdomen in to protect while breathing shallowly and rapidly.
Most participants report that almost immediately they feel their eyes getting cooler and after 15 seconds, drier. This facial, breathing, and posture pattern is an exaggeration of the somatic expression of fear that is evoked when we are vigilant and feel unsafe, and it increases sympathetic arousal (Kalawski, 2020).
In most cases, this pattern is automatic, and occurs without awareness, and increases sympathetic activity (Narkiewicz et al., 2006). On the other hand, slow diaphragmatic breathing tends to reduce sympathetic activity (Harada et al., 2014; Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014). Clinically, the vigilance pattern can often be observed as a person slightly lifts and expands their chest during inhalation and drops and constricts it during exhalation, while breathing shallowly and rapidly without any abdomen expansion or constriction. It is often punctuated with brief breath holding and a reduced blinking rate during concentration.
To investigate these observations more systematically, we compared the practice of gasping while opening the eyes with gentle exhalation while opening the eyes—a pattern that may reduce sympathetic activation and alter the subjective sensation of eye dryness.
Participants: 13 males and 13 females; average age, 39 years
Procedure: While sitting comfortably with their eyes closed, participants were guided through the following two practices:
1.Gasp while opening the eyes
Sit comfortably and look around and observe how your eyes feel. Now close your eyes. Now imagine there is a threat. Take a very quick gasp through an open mouth by inhaling into your upper chest and keep breathing very shallowly and irregularly. At the same time, open your eyes wide while being vigilant and looking for danger. Simultaneously, tense your body, inclining it slightly backward as if trying to avoid something. Do not blink, as you may miss the potential threat approaching you. Repeat three times.
2. Gentle exhalation while opening the eyes
Sit comfortably and look around and observe how your eyes feel. Now close your eyes. Breathe comfortably and inhale by allowing your abdomen to extend and widen while feeling your eyes sinking in their sockets and becoming softer as you gently start exhaling. While gently exhaling, begin to open your eyes very slowly, looking down through your eyelashes without caring what you see, allowing your jaw and face muscles to relax and feeling a slight smile. When you feel the urge to inhale, allow your eyes to close and let your abdomen expand as you inhale slowly. Repeat three times.
After these two practices, the participants filled out a short assessment questionnaire in which they rated how their eyes felt on a scale from -5 (dry), 0 (normal), to 5 (moist/tearing), and rated which eye-opening procedure allowed their eyes to be more relaxed and moist.
Results
92.3% of the participants reported that opening their eyes during exhalation significantly increased eye relaxation and moisture, as shown in Figure 2. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed a significant difference between the inhale condition (M = −0.19, n = 26) and the exhale condition (M = 1.00, n = 25), F(1, 49) = 9.65, p = .003. The experience of eye irritation was correlated (r = 0.64) with the self-rating of experiencing anxiety and fear during the last three months.
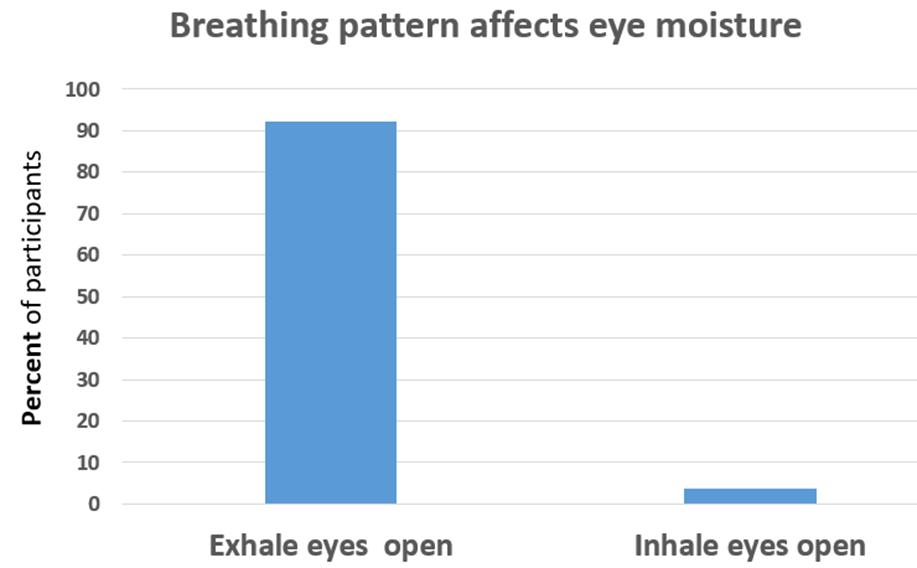
Figure 2. Gently opening the eyes during exhalation increases the experience of moisture and relaxation in the eyes.
Discussion
The results suggest that increased moisture and eye relaxation could be evoked by changing breathing-blinking patterns. Nearly all participants experienced an increase in tearing and eye relaxation; however, long-term benefits most likely occur if the person implements this practice many times during the day. By changing the breathingg-blink pattern and peacefully looking at the world with a smile, one would decrease sympathetic arousal and increase parasympathetic activity. This approach should be taught as the first self-care intervention to reduce eye irritation.
Recommendations to decrease dry eye and improve eye health
- Experience how the two different breathing and eye-opening practices described above affect your eye dryness or moistness.
- When you sense the first onset of minimal eye discomfort or when looking at screens on your computer or cellphone, implement the following practice for about 10 to 15 seconds. Allow your eyelids to close. Be aware of the sensations in your eyes, let your face and jaw relax as if they are being pulled down by gravity while sensing the eyes becoming soft and sinking into their sockets. Breathe diaphragmatically by allowing the abdomen to expand when you inhale. While gently exhaling, slowly open your eyes slightly while looking down with a gentle smile and sensing the moisture beginning to occur in the eyes. Repeat twice.
- During the day, implement the 20/20/20 vision-regeneration practice (every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and look at something 20 feet away without caring what you see), as shown in Figure 3.
- Read and incorporated the many practices described in the superb book, Vision for Life; Ten Steps to Natural Eye Improvement, by Meir Schneider (2012).

Figure 3. The 20/20/20 rule poster to prevent eye strain (AOA, 2026).
Do these practices many times and be aware of the sensations in your eyes and face. This passive awareness, in conjunction with slower breathing, tends to reduce sympathetic arousal and increase parasympathetic activity, which facilitates increased tearing. As one participant reported when she practiced this:
What a surprise it was when I closed my eyes and breathed slowly and diaphragmatically, and then, as I began to exhale, I very slowly began to open my eyes while looking down and through my eyelashes, while feeling my eyes sink into their sockets. Tearing occurred spontaneously, and my eyes felt lubricated. What a relief. It provided hope that I could help myself instead of only depending on lubricating eye drops whenever my eyes felt dry and irritated.
Two books to maintain and improve vision and reduce techstress
Vision for Life: Ten Steps to Natural Eye Improvement by Meir Schneider (2012) offers many strategies you can immediately incorporate into your daily life to improve and restore your vision. It provides guidelines on how to reverse developing vision issues before they cause damage and how to remedy existing problems, including near- and far-sightedness, lazy eye, as well as more serious conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, optic neuritis, detached retinas and retinal tears, macular degeneration, and retinitis pigmentosa.

TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics by Erik Peper, Richard Harvey, and Nancy Fsass (2020) offers practical tools to avoid the evolutionary traps that trip us up and address the problems associated with technological overuse. It includse effective strategies and practices that individuals can use to optimize their workspace, reduce physical strain, correct posture, and improve vision. It provides fresh insights on reducing stress and enhancing health.

Additional blogs that offer strategies to improve vision
References
AOA. (2026). 20/20/20/ to prevent digital eyes strain. American Optometric Association. https://www.aoa.org/AOA/Images/Patients/Eye%20Conditions/20-20-20-rule.pdf
Banushi, B., Brendle, M., Ragnhildstveit, A., Murphy, T., Moore, C., Egberts, J., & Robison, R. (2023). Breathwork interventions for adults with clinically diagnosed anxiety disorders: A scoping review. Brain Sciences, 13(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020256
Bloch, S. (2017). Alba Emoting: A scientific method for emotional induction. Scotts Valley, CA: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. https://www.amazon.com/Alba-Emoting-Scientific-Emotional-Induction/dp/154254884
Chu, C.A., Rosenfield, M., Portello, J.K. (2014). Blink patterns: reading from a computer screen versus hard copy. Optom Vis Sci., 91(3),297-302. https://doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000000157
Craig, J. P., Nichols, K. K., Akpek, E. K., et al. (2017). TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report. The Ocular Surface, 15(3), 276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2017.05.008
Dartt, D. A. (2009). Neural regulation of lacrimal gland secretory processes: Relevance in dry eye diseases. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 28(3), 155–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2009.04.003
Fugi-Meyer, A.R. (1974). Relative respiratory contribution of the rib cage and the abdomen in males and females with special regard to posture. Respiration, 31(3), 240–251. https://doi.org/10.1159/000193113
Harada, D., Asanoi, H., Takagawa, J., Ishise, H., Ueno, H., Oda, Y., Goso, Y., Joho, S., & Inoue, H. (2014). Slow and deep respiration suppresses steady-state sympathetic nerve activity in patients with chronic heart failure: from modeling to clinical application. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 307(8), H1159–H1168. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00109.2014
Jalnapurkar, I., Allen, M., & Pigott, T. (2018). Sex differences in anxiety disorders: A review. Journal of Psychiatry, Depression & Anxiety, 4, 011. https://doi.org/10.24966/PDA-0150/100011
Kalawski, J.P. (2020) The Alba Method and the Science of Emotions. Integr. Psych. Behav. 54, 903–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-020-09525-4
Lehrer, P. M., & Gevirtz, R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Frontiers in Psychology, 5, Article 756. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4104929/
Lemeignan, M., Guitart, L., & Bloch, S. (1990). Autonomic differentiation of emotional effector pattern of 6 basic emotions. Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Psychophysiology, Budapest, July 9–14, 199
Maity, M., Allay, M. B., Ali, M. H., Basu, S., & Singh, S. (2025). Effect of different artificial tears on tear film parameters in dry eye disease. Optometry and Vision Science, 102(1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000002206
McLean, C. P., Asnaani, A., Litz, B. T., & Hofmann, S. G. (2011). Gender differences in anxiety disorders: Prevalence, course of illness, comorbidity and burden of illness. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45(8), 1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.03.006
Mendes, L. P. S., Vieira, D. S. R., Gabriel, L. S., Ribeiro-Samora, G. A., Dornelas de Andrade, A., Brandão, D. C., Goes, M. C., Fregonezi, G. A. F., Britto, R. R., & Parreira, V. F. (2020). Influence of posture, sex, and age on breathing pattern and chest wall motion in healthy subjects. Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy, 24(3), 240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjpt.2019.02.007
Mohamed, Z., Alrasheed, S., Abdu, M., & Allinjawi, K. (2024). Dry eye disease prevalence and associated risk factors among the Middle East population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus, 16(9), e70522. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.70522
Narkiewicz, K., van de Borne, P., Montano, N., Hering, D., Kara, T., & Somers, V. K. (2006). Sympathetic neural outflow and chemoreflex sensitivity are related to spontaneous breathing rate in normal men. Hypertension, 47(1), 51–55. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000197613.47649.0
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics, North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X
Portello, J.K., Rosenfield, M., Bababekova, Y., et al. (2012). Computer-related visual symptoms in office workers. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 32, 375–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1313.2012.00925.x
Ranti, C., Jones, W., Klin, A. et al. Blink Rate Patterns Provide a Reliable Measure of Individual Engagement with Scene Content. Sci Rep 10, 8267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64999-x
Schneider, M. (2012). Vision for Life: Ten Steps to Natural Eye Improvement. North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Vision-Life-Natural-Eyesight-Improvement/dp/158394494X/
Sheedy, J.E., Hayes, J.N., & Engle, J.(2003). Is all asthenopia the same? Optom Vis Sci, 80, 732–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006324-200311000-00008
Sheppard, A. L., & Wolffsohn, J. S. (2018). Digital eye strain: prevalence, measurement and amelioration. BMJ open Ophthalmology, 3(1), e000146. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjophth-2018-000146
Stern, M. E., Gao, J., Siemasko, K. F., Beuerman, R. W., & Pflugfelder, S. C. (2004). The role of the lacrimal functional unit in the pathophysiology of dry eye. Experimental Eye Research, 78(3), 409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2003.09.003
Swamynathan, S. K., & Wells, A. (2020). Conjunctival goblet cells: Ocular surface functions, disorders that affect them, and the potential for their regeneration. The Ocular Surface, 18(1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2019.11.005
Uchino, M., Yokoi, N., Uchino, Y., Dogru, M., Kawashima, M., Komuro, A., Sonomura, Y., Kato, H., Kinoshita, S., Schaumberg, D.A., & Tsubota, K. (2013). Prevalence of Dry Eye Disease and its Risk Factors in Visual Display Terminal Users: The Osaka Study. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 156(4), 759-766.e1, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2013.05.040
The epidemiology of dry eye disease: report of the Epidemiology Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf. , 5(2), 93-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1542-0124(12)70082-4
Wilhelm, F. H., Gevirtz, R., & Roth, W. T. (2001). Respiratory dysregulation in anxiety, functional cardiac, and pain disorders: Assessment, phenomenology, and treatment. Behavior Modification, 25(4), 513–545. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445501254003
Wozniak, P., et al. (2025, September 12–16). Dry eye symptoms, severity, treatment and unmet needs: An analysis of the United States of America and a multinational snapshot (NESTS Study) [Poster presentation]. 43rd Congress of the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons (ESCRS), Copenhagen, Denmark. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/09/250914205829.htm
Ziemssen, F., & Ruprecht, K. W. (2005).Autonomic dysfunction in dry eye syndrome. Ophthalmologe, 102(8), 744–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00347-005-1169-1
Breathe Away Menstrual Pain- A Simple Practice That Brings Relief *
Posted: November 22, 2025 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, cognitive behavior therapy, education, emotions, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: dysmenorrhea, health, meditation, menstrual cramps, mental-health, mindfulness, wellness 2 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E. Harvey, R., Chen, & Heinz, N. (2025). Practicing diaphragmatic breathing reduces menstrual symptoms both during in-person and synchronous online teaching. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, Published online: 25 October 2025. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09745-7
“Once again, the pain starts—sharp, deep, and overwhelming—until all I can do is curl up and wait for it to pass. There’s no way I can function like this, so I call in sick. The meds take the edge off, but they don’t really fix anything—they just mask it for a little while. I usually don’t tell anyone it’s menstrual pain; I just say I’m not feeling well. For the next couple of days, I’m completely drained, struggling just to make it through.
Many women experience discomfort during menstruation, from mild cramps to intense, even disabling pain. When the pain becomes severe, the body instinctively responds by slowing down—encouraging rest, curling up to protect the abdomen, and often reaching for medication in hopes of relief. For most, the symptoms ease within a day or two, occasionally stretching into three, before the body gradually returns to balance.
Another helpful approach is to practice slow abdominal breathing, guided by a breathing app FlowMD. In our study led by Mattia Nesse, PhD, in Italy, the response of one 22-year-old woman illustrated the power of this simple practice.
“Last night my period started, so I was a bit discouraged because I knew I’d get stomach pain, etc. On the other hand, I said, “Okay, let’s see if the breathing works,” and it was like magic — incredible. I’ll need to try it more times to understand whether it consistently has the same effect, but right now it truly felt magical. Just 3 minutes of deep breathing with the app were enough, and I’m not saying I don’t feel any pain anymore, but it has decreased a lot, so thank you! Thank you again for this tool… I’m really happy!”
The Silent Burden of Menstrual Pain
Menstrual pain, or dysmenorrhea, affects most women at some point in their lives — often silently. For many, the monthly cycle brings not only physical discomfort but also shame, fatigue, and interruptions to work or school. It is one of the leading causes of absenteeism and reduced productivity worldwide (Itani et al., 2022; Thakur & Pathania, 2022). In addition, the estimated health cost ranged from US $1367 to US$ 7043 per year (Huang et al., 2021). Yet, despite its prevalence, most women are never taught how to use their own physiology to ease these symptoms.
The Study (Peper et al, 2025)
Seventy-five university women participated across two upper-division Holistic Health courses. Forty-nine practiced 30 minutes per day of breathing and relaxation over five weeks as well as practicing the moment they anticipated or felt discomfort; twenty-six served as a comparison group without a specific daily self-care routine. Students rated change in menstrual symptoms on a scale from –5 (“much worse”) to +5 (“much better”). For the detailed steps in training, see the blog: https://peperperspective.com/2023/04/22/hope-for-menstrual-cramps-dysmenorrhea-with-breathing/ (Peper et al., 2023).
What changed
The results were striking. Women who practiced breathing and relaxation showed significant decrease in menstrual symptoms compared to the non-intervention group (p = 0.0008) as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Decrease in menstrual symptoms as compared to the control group after implementing slow diaphragmatic breathing.
Why does breathing and posture change have a beneficial effect?
When you stay curled up, your abdomen becomes compressed, leaving little room for the lower belly to relax or for the diaphragm to move freely. The result? Tension builds, and pain often increases.
To reverse this, create space for relaxation. Gently loosen your waist and let your abdomen expand as you inhale. Uncurl your body—lengthen your spine and open your chest, as shown in Figure 2. With each easy breath, you invite calm and allow your body to shift from tension to ease.
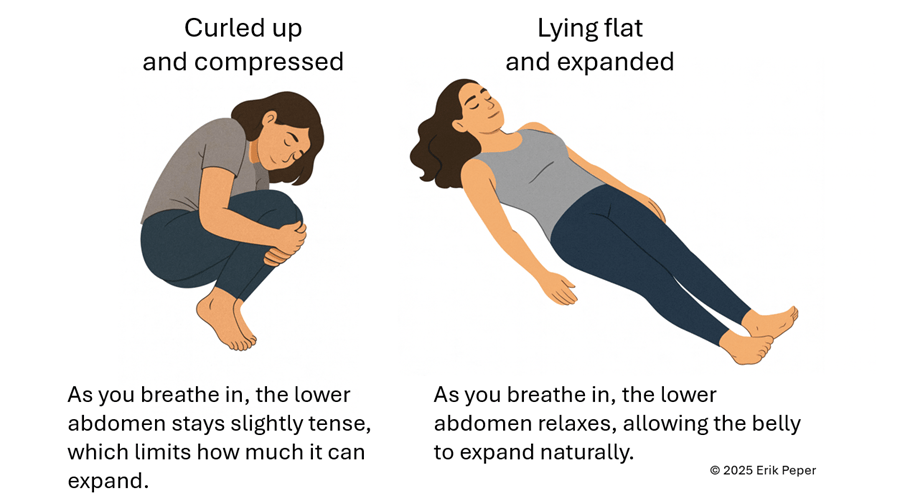
Figure 2. Curling up compresses the abdomen and prevents relaxation of the lower belly. In contrast, lying flat with the body gently expanded allows the abdomen to move freely with each breath, which can help reduce menstrual discomfort.
In contrast, slow abdominal or diaphragmatic breathing activates the body’s natural relaxation response. It quiets the stress-driven sympathetic nervous system, calms the mind, and improves circulation in the abdominal area. With each slow breath in, the abdomen gently expands while the pelvic floor and abdominal muscles relax. As you exhale, these muscles naturally tighten slightly, helping to massage and move blood and lymph through the abdominal region. This rhythmic movement supports healing and ease, as illustrated in Figure 3.
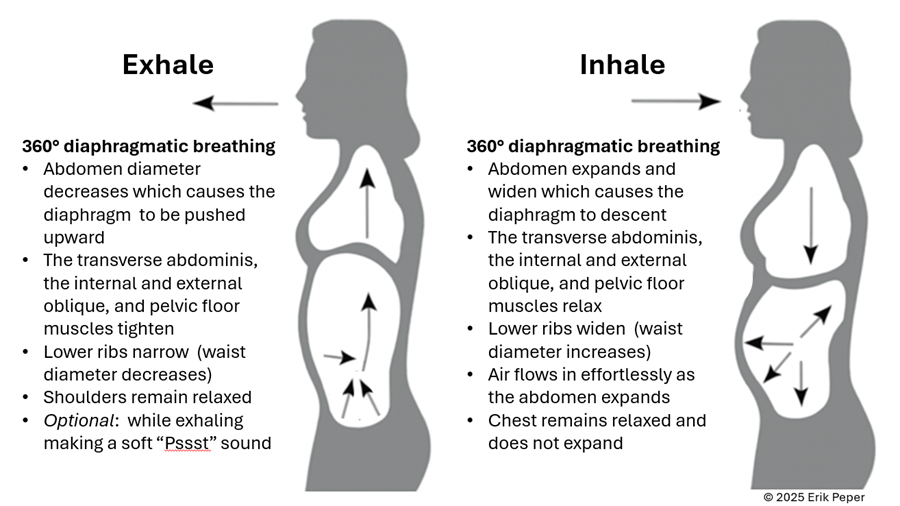
Figure 3. The dynamic process of diaphragmatic breathing.
The process of slower, lower diaphragmatic breathing
When lying down, rest comfortably on your back with your legs slightly apart. Allow your abdomen to rise naturally as you inhale and fall as you exhale. As you breathe out, imagine the air flowing through your abdomen, down your legs, and out through your feet. To deepen this sensation, you can ask a partner to gently stroke from your abdomen down your legs as you exhale—helping you sense the flow of release through your body.
Gently focus on slow, effortless diaphragmatic breathing. With each inhalation, your abdomen expands, and the lower belly softens. As you exhale, the abdomen gently goes down pushing the diaphragm upward and allowing the air to leave easily. Breathing slowly—about six breaths per minute—helps engage the body’s natural relaxation response.
If you notice that your breath is staying high in your chest instead of expanding through the abdomen, your symptoms may not improve and can even increase. One participant experienced this at first. After learning to let her abdomen expand with each inhalation while keeping her shoulders and chest relaxed, her next menstrual cycle was markedly easier and far less uncomfortable. The lesson is clear: technique matters.
“During times of pain, I practiced lying down and breathing through my stomach… and my cramps went away within ten minutes. It was awesome.” — 22-year-old college student
“Whenever I felt my cramps worsening, I practiced slow deep breathing for five to ten minutes. The pain became less debilitating, and I didn’t need as many painkillers.” — 18-year-old college student
These successes point out that it’s not just breathing — it’s how you breathe by providing space for the abdomen to expand during inhalation.
Practice: How to Do Diaphragmatic Breathing
- Find a quiet space. Lie on your back or sit comfortably erect with your shoulders relaxed.
- Place one hand on your chest and one on your abdomen.
- Inhale slowly through your nose for about 3–4 seconds. Let your abdomen expand as you breathe in — your chest should remain relaxed.
- Exhale gently through your mouth for 4—6 seconds, allowing the abdomen to fall or constrict naturally.
- As you exhale imagine the air moving down your arms, through your abdomen, down your legs, and out your feet
- Practice daily for 20 minutes and also for 5–10 minutes during the day when menstrual discomfort begins.
- Add warmth. Placing a warm towel or heating pad over your abdomen can enhance relaxation while lying on your back and breathing slowly.
With regular practice and implementing it during the day when stressed, this simple method can reduce cramps, promote calm, and reconnect you with your body’s natural rhythm.
Implement the ABCs during the day
The ABC sequence—adapted from the work of Dr. Charles Stroebel, who developed The Quieting Reflex (Stroebel, 1982)—teaches a simple way to interrupt stress reactions in real time. The moment you notice discomfort, pain, stress, or negative thoughts, interrupt the cycle with a simple ABC strategy:
A — Adjust your posture
Sit or stand tall, slightly arch your lower back and allowing the abdomen to expand while you inhale and look up. This immediately shifts your body out of the collapsed “defense posture’ and increases access to positive thoughts (Tsai et all, 2016; Peper et al., 2019)
B — Breathe
Allow your abdomen to expand as you inhale slowly and deeply. Let it get smaller as you exhale. Gently make a soft hissing sound as you exhale while helps the abdomen and pelvic floor to tighten. Then allow the abdomen to relax and widen which without effort draws the air in during inhalation. As you exhale, stay tall and imagine the air flowing through you and down your legs and out your feet.
C — Concentrate
Refocus your attention on what you want to do and add a gentle smile. This engages positive emotions, the smile helps downshift tension.
The video clip guides you through the ABCs process.
Integrate the breathing during the day by implementing your ABCs
When students practice relaxation technique and this method, they reported greater reductions in symptoms compared with a control group. By learning to notice tension and apply the ABC steps as soon as stress arises, they could shift their bodies and minds toward calm more quickly, as shown in Figure 4.
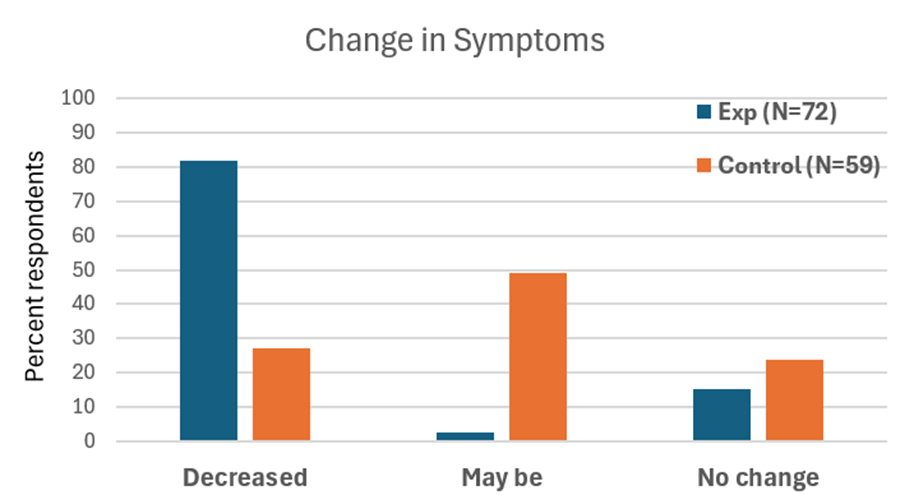
Figure 4. Change in symptoms after practicing a sequential relaxation and breathing techniques for four weeks.
Takeaway
Menstrual pain doesn’t have to be endured in silence or masked by medication alone. By practicing 30 minutes of slow diaphragmatic breathing daily and many times during the day, women may be able to reduce pain, stress, and discomfort — while building self-awareness and confidence in their body’s natural rhythms thereby having the opportunity to be more productive.
We recommend that schools and universities include self-care education—especially breathing and relaxation practices—as part of basic health curricula as this approach is scalable. Teaching young women to understand their bodies, manage stress, and talk openly about menstruation can profoundly improve well-being. It not only reduces physical discomfort but also helps dissolve the stigma that still surrounds this natural process,
Remember: Breathing is free—available anytime, anywhere and is helpful in reducing pain and discomfort. (Peper et al., 2025; Joseph et al., 2022)
See the following blogs for more in-depth information and practical tips on how to learn and apply diaphragmatic breathing:
REFERENCES
Itani, R., Soubra, L., Karout, S., Rahme, D., Karout, L., & Khojah, H.M.J. (2022). Primary Dysmenorrhea: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Updates. Korean J Fam Med, 43(2), 101-108. https://doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.21.0103
Huang, G., Le, A. L., Goddard, Y., James, D., Thavorn, K., Payne, M., & Chen, I. (2022). A systematic review of the cost of chronic pelvic pain in women. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada, 44(3), 286–293.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogc.2021.08.011
Joseph, A. E., Moman, R. N., Barman, R. A., Kleppel, D. J., Eberhart, N. D., Gerberi, D. J., Murad, M. H., & Hooten, W. M. (2022). Effects of slow deep breathing on acute clinical pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, 27, 2515690X221078006. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515690X221078006
Peper, E., Booiman, A. & Harvey, R. (2025). Pain-There is Hope. Biofeedback, 53(1), 1-9. http://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-53.01.16
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N., & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Chen, S., & Heinz, N. (2025). Practicing diaphragmatic breathing reduces menstrual symptoms both during in-person and synchronous online teaching. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. Published online: 25 October 2025. https://rdcu.be/eMJqt https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09745-7
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153-169. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.1533-1
Stroebel, C. (1982). The Quieting Reflex. New York: Putnam Pub Group. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-Quieting-Charles-M-D-Stroebel/dp/0399126570/
Thakur, P. & Pathania, A.R. (2022). Relief of dysmenorrhea – A review of different types of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. MaterialsToday: Proceedings.18, Part 5, 1157-1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.207
Tsai, H. Y., Peper, E., & Lin, I. M. (2016). EEG patterns under positive/negative body postures and emotion recall tasks. NeuroRegulation, 3(1), 23-27. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.1.23
*Edited with the help of ChatGPT 5
Compassionate Presence: Covert Training Invites Subtle Energies Insights
Posted: January 20, 2025 Filed under: attention, healing, meditation, mindfulness, relaxation, Uncategorized | Tags: being safe, compassion, energy, Energy healing, healing, reiki, spirituality, therapeutic touch Leave a commentAdapted from: Peper, E. (2015). Compassionate Presence: Covert Training Invites Subtle Energies Insights. Subtle Energies Magazine, 26(2), 22-25. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283123475_Compassionate_Presence_Covert_Training_Invites_Subtle_Energies_Insights
“Healing is best accomplished when art and science are conjoined, when body and spirit are probed together. Only when doctors can brood for the fate of a fellow human afflicted with fear and pain do they engage the unique individuality of a particular human being…a doctor thereby gains courage to deal with the pervasive uncertainties for which technical skill alone is inadequate. Patient and doctor then enter into a partnership as equals.
I return to my central thesis. Our health care system is breaking down because the medical profession has been shifting its focus away from healing, which begins with listening to the patient. The reasons for this shift include a romance with mindless technology.” Bernard Lown, MD, The Lost art of healing: Practicing Compassion in Medicine (1999)

Therapeutic Touch healing by Dora Kunz.
I wanted to study with the healer and she instructed me to sit and observe, nothing more. She did not explain what she was doing, and provided no further instructions. Just observe. I did not understand. Yet, I continued to observe because she knew something, she did something that seemed to be associated with improvement and healing of many patients. A few showed remarkable improvement – at times it seemed miraculous. I felt drawn to understand. It was an unique opportunity and I was prepared to follow her guidance.
The healer was remarkable. When she put her hands on the patient, I could see the patient’s defenses melt. At that moment, the patient seemed to feel safe, cared for, and totally nurtured. The patient felt accepted for just who she was and all the shame about the disease and past actions appeared to melt away. The healer continued to move her hands here and there and, every so often, she spoke to the client. Tears and slight sobbing erupted from the client. Then, the client became very peaceful and quiet. Eventually, the session was finished and the client expressed gratitude to the healer and reported that her lower back pain and the constriction around her heart had been released, as if a weight had been taken from her body.
How was this possible? I had so many questions to ask the healer: “What were you doing? What did you feel in your hands? What did you think? What did you say so softly to the client?”
Yet she did not help me understand how I could do this. The main instruction the healer kept giving me was to observe. Yes, she did teach me to be aware of the energy fields around the person and taught me how I could practice therapeutic touch (Kreiger, 1979; Peper, 1986; Kunz & Peper,1995; Kunz & Krieger, 2004; Denison, 2004; van Gelder & Chesley, F, 2015). But she was doing much more and I longed to understand more about the process.
Sitting at the foot of the healer, observing for months, I often felt frustrated as she continued to insist that I just observe. How could I ever learn from this healer if she did not explain what I should do! Does the learning occur by activating my mirror neurons (Acharya & Shukla, 2012).? Similar instructions are common in spiritual healing and martial arts traditions – the guru or mentor usually tells an apprentice to observe and be there. But how can one gain healing skills or spiritual healing abilities if you are only allowed to observe the process? Shouldn’t the healer be demonstrating actual practices and teaching skills?
After many sessions, I finally realized that the healer’s instruction to to learn was to observe and observe. I began to learn how to be present without judging, to be present with compassion, to be present with total awareness in all senses, and to be present without frustration. The many hours at the foot of this master were not just wasted time. It eventually became clear that those hours of observation were important training and screening strategies used to insure that only those students who were motivated enough to master the discipline of non-judgmental observation, the discipline to be present and open to any experience, would continue to participate in the training process. I finally understood. I was being taught a subtle energies skill of compassionate, and mindful awareness. Once I, the apprentice, achieved this state, I was ready to begin work with clients and master technical aspects of the healing practice – but not before.
A major component of the healing skill that relies on subtle energies is the ability to be totally present with the client without judgment (Peper, Gibney & Wilson, 2005). To be peaceful, caring, and present seems to create an energetic ambiance that sets stage, creates the space, for more subtle aspects of the healing interaction. This energetic ambiance is similar to feeling the love of a grandparent: feeling total acceptance from someone who just knows you are a remarkable human being. In the presence of a healer with such a compassionate presence, you feel safe, accepted, and engaged in a timeless state of mind, a state that promotes healing and regeneration as it dissolves long held defensiveness and fear-based habits of holding others at bay. This state of mind provides an opportunity for worries and unsettled emotions to dissipate. Feeling safe, accepted, and experiencing compassionate love supports the bological processes that nurture regeneration and growth.
How different this is from the more common experience with health care/medical practitioners who have little time to listen and to be with a patient. We might experience a medical provider as someone who sees us only as an illness (the cancer patient, the asthma patient) instead of recognizing us as a human spirit who happens to have an illness ( a person with cancer or asthma). At times we can feel as though we are seen only as a series of numbers in a medical chart – yet we know we are more than that. People long to be seen. Often the medical provider interrupts with unrelated questions instead of listening. It becomes clear that the computerized medical record is more important than the human being seated there. We can feel more fragmented, less safe, when we are not heard, not understood.
As one 23 year old student reported after being diagnosed with a serious medical condition,”/ cried immediately upon leaving the physician’s office. Even though he is an expert on the subject, I felt like I had no psychological support. I was on Gabapentin, and it made me very depressed. I thought to myself: Is my life, as I know it, over?” (Peper, Martinez Aranda, P., & Moss, 2015).
The healing connection is often blocked, the absence of a human connection is so obvious. The medical provider may be unaware of the effect of their rushed behavior and lack of presence. They can issue a diagnosis based on the scientific data without recognizing the emotional impact on the person receiving it.
What is missing is compassion and caring for the patient. Sitting at the foot of the master healer is not wasted time when the apprentice learns how to genuinely attend to another with non-judgmental, compassionate presence. However, this requires substantial personal work. Possibly all healthcare providers should be required, or at least invited, to learn how to attain the state of mind that can enhance healing. Perhaps the practice of medicine could change if, as Bernard Lown wrote, the focus were once again on healing, “…which begins with listening to the patient.”
References
Acharya, S., & Shukla, S. (2012). Mirror neurons: Enigma of the metaphysical modular brain. Journal of natural science, biology, and medicine, 3(2), 118–124. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-9668.101878
Denison, B. (2004). Touch the pain away: New research on therapeutic touch and persons with fibromyalgia syndrome. Holistic nursing practice, 18(3), 142-151. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004650-200405000-00006
Krieger, D. (1979). The therapeutic touch: How to use your hands to help or to heal. Vol. 15. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. https://www.amazon.com/Therapeutic-Touch-Your-Hands-Help/dp/067176537X
Kunz, D. & Krieger, D. (2004). The spiritual dimension of therapeutic touch. Rochester, VT: Inner Traditions/Bear & Co. https://www.amazon.com/Spiritual-Dimension-Therapeutic-Touch/dp/1591430259/
Kunz, D., & Peper, E. (1995). Fields and their clinical implications. In Kunz, D. Spiritual Aspects of the Healing Arts. Wheaton, ILL: Theosophical Pub House, 213-222. https://www.amazon.com/Spiritual-Aspects-Healing-Arts-Quest/dp/0835606015
Lown, B. (1999). The lost art of healing: Practicing compassion in medicine. New York, NY: Ballantine Books. https://www.amazon.com/Lost-Art-Healing-Practicing-Compassion/dp/0345425979
Peper, E. (1986). You are whole through touch: An energetic approach to give support to a breast cancer patient. Cooperative Connection. VII (3), 1-6. Also in: (1986/87). You are whole through touch: Dora Kunz and Therapeutic Touch. Somatics. VI (1), 14-19. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280884245_You_are_whole_through_touch_Dora_Kunz_and_therapeutic_touch
Peper, E. (2024). Reflections on Dora and the Healing Process, webinar presented to the Therapeutic Touch International Association, Saturday, December 14, 2024. https://youtu.be/skq9Chn-eME?si=HJNAhiUsgXSkqd_5
Peper, E., Gibney, K. H. & Wilson, V. E. (2005). Enhancing Therapeutic Success–Some Observations from Mr. Kawakami: Yogi, Teacher, Mentor and Healer. Somatics. XIV (4), 18-21. https://biofeedbackhealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/edited-enhancing-therapeutic-success-8-23-05.pdf
Peper, E., Martinez Aranda, P., & Moss, E. (2015). Vulvodynia treated successfully with breathing biofeedback and integrated stress reduction: A case report. Biofeedback, 43(2), 103-109. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.2.04
Van Gelder, K & Chesley, F. (2015). A Most Unusual Life. Wheaton Ill: Theosophical Publishing House. https://www.amazon.com/Most-Unusual-Life-Clairvoyant-Theosophist/dp/0835609367
[1] I thank Peter Parks for his superb editorial support.
Pragmatic techniques for monitoring and coaching breathing
Posted: December 14, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, emotions, meditation, mindfulness, neurofeedback, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, Uncategorized | Tags: art, books, Breathing rate, coaching, FlowMD app, nasal breathing, personal-development, self-monitoring, writing 4 CommentsDaniella Matto, MA, BCIA BCB-HRV , Erik Peper, PhD, BCB, and Richard Harvey, PhD
Adapted from: Matto, D., Peper, E., & Harvey, R. (2025). Monitoring and coaching breathing patterns and rate. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. https://townsendletter.com/monitoring-and-coaching-breathing-patterns-and-rate/
This blog aims to describe several practical strategies to observe and monitor breathing patterns to promote effortless diaphragmatic breathing. The goal of these strategies is to foster effortless, whole-body diaphragmatic breathing that promote health.
Breathing is usually covert and people are not usually aware of their breathing rate (breaths per minute) or pattern (abdominal or thoracic, breath holding or shallow breathing) unless they have an illness such as asthma, emphysema or are performing physical activity (Boulding et al, 2015)). Observing breathing is challenging; awareness of respiration often leads to unaware changes in the breath pattern or to an attempt to breathe perfectly (van Dixhoorn, 2021). Ideally breathing patterns should be observed/monitored when the person is unaware of their breathing pattern and the whole body participates (van Dixhoorn, 2008). A useful strategy is to have the person perform a task and then ask, “What happened to your breathing?”. For example, ask a person to simulate putting a thread through the eye of a needle or quickly look to the extreme right and left while keeping their head still. In almost all cases, the person holds their breath (Peper et al., 2002).
Teaching effortless slow diaphragmatic breathing is a precursor of Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback and is based on slow paced breathing (Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014; Steffen et al., 2017; Shaffer and Meehan, 2020). Mastering effortless diaphragmatic breathing is a powerful tool in the treatment of a variety of physical, behavioural, and cognitive conditions; however, to integrate this method into clinical or educational practice is easier said than done. Clients with dysfunctional breathing patterns often have difficulty following a breath pacer or mastering effortless breathing at a slower pace.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a few simple strategies that can be used to observe and monitor breathing patterns, provide economic strategies for observation and training, and suggestions to facilitate effortless diaphragmatic breathing.
Strategies to observe and monitor breathing pattern
Observation of the breathing patterns
- Is the breathing through the nose or mouth? Nose is usually better (Watso et al., 2023; Nestor, 2020).
- Does the abdomen expand during inhalation and constricts during exhalation or does the chest expand and rise during inhalation and fall during exhalation? Abdominal movement is usually better.
- Is exhalation flow softly or explosively like a sigh? Slow flow exhalation is preferred.
- Is the breath held or continues during activities? In most cases continued breathing is usually better.
- Does the person gasp before speaking or allows to speak while normally exhaling?
- What is the breathing rate (breaths per minute)? When sitting peacefully less than 14 breaths/minute is usually better and about 6 breaths per minute to optimize HRV
Physiological monitoring.
- Monitoring breathing with strain gauges around the abdomen and chest, and heart rate is the most common approach to identify the location of breath, the breathing pattern and heart rate variability. The strain gauges are placed around the chest and abdomen and heart rate is monitored with a blood volume pulse amplitude sensor from the finger. representative recording shows the effect of thoughts on breathing, heartrate and pulse amplitude of which the participant is totally unaware as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Physiological recording of breathing patterns with strain gauges.
- Monitoring breathing with a thermistor placed at the entrance of the nostril that has the most airflow (nasal patency) (Jovanov et al., 2001; Lerman et al., 2016). When the person exhales through the nose, the thermistor temperature increases and decreases when they inhale. A representative recording of a person being calm, thinking a stressful thought. and being calm. Although there were significant changes as indicated by the change in breathing patterns, the person was unaware of the changes as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Use of a thermistor to monitor breathing from the dominant nostril compared to the abdominal expansion as monitored by a strain gauge around the abdomen.
- Additional physiological monitoring approaches. There are many other physiological measures can be monitored to such as end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2), a non-invasive measurement of the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhaled breath (Meuret et al., 2008; Meckley, 2013); scalene/trapezius EMG to identify thoracic breathing (Peper & Tibbett, 1992; Peper & Tibbets, 1994); low abdominal EMG to identify transfers and oblique tightening during exhalation and relaxation during inhalation (Peper et al., 2016; and heart rate to monitor cardiorespiratory synchrony (Shaffer & Meehan, 2020). Physiological monitoring is useful; since, the clinician and the participant can observe the actual breathing pattern in real time, how the pattern changes in response the cognitive and physical tasks, and used for feedback training. The recorded data can document breathing problems and evidence of mastery.
The challenges of using physiological monitoring arethat the equipment may be expensive, takes skill to operate and interpret the data, and is usually located in the office and not at home.
Economic strategies for observation and training breathing
To complement the physiological monitoring and allow observations outside the office and at home, some of the following strategies may be used to observe breathing pattern (rate and expansion of the breath in the body), and suggestion to facilitate effortless diaphragmatic breathing. These exercises make excellent homework for the client. Practicing awareness and internal self-regulation by the client outside the clinic contributes enormously to the effect of biofeedback training (Wilson et al., 2023),
Observe breathing rate: Draw the breathing pattern
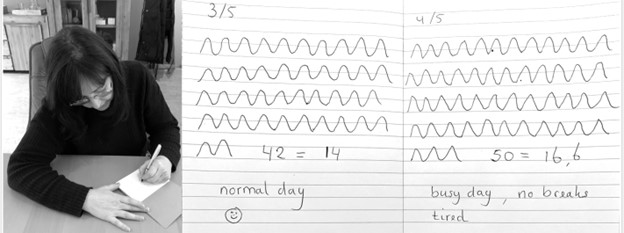
Take a piece of paper, a pen and a timer, set to 3 minutes. Start the timer. Upon inhalation draw the line up and upon exhalation draw the line down, creating a wave. When the timer stops, after 3 minutes, calculate the breathing rate per minute by dividing the number of waves by 3 as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Drawing the breathing pattern for three minutes during two different days.
From these drawings, the breathing rate become evident. Many individuals are often surprised to discover that their breathing rate increased during periods of stress, such as a busy day with no breaks, compared to their normal days.
Monitoring and training diaphragmatic breathing
The scarf technique for abdominal feedback
Many participants are unaware that they are predominantly breathing in their chest and their abdomen expansion is very limited during inhalation. Before beginning, have participant loosen their belt and or stand upright since sitting collapsed/slouched or having the waist constriction such as a belt of tight constrictive clothing that inhibits abdominal expansion during inhalation.
Place the middle part of a long scarf or shawl on your lower back, take the ends in both hands and cross the ends: your left hand is holding the right part of the scarf, and the right hand is holding the left end of the scarf. Give a bit of a pull, so you can feel any movement of the scarf. When breathing more abdominally you will feel a pull at the ends of the scarf as you lower back, and flanks will expand as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Using a scarf as feedback.
FlowMD app
A recent cellphone app, FlowMD, is unique because it uses the cellphone camera to detect the subtle movements of the chest and abdomen (FlowMD, 2024). It provides real time feedback of the persons breathing pattern. Using this app, the person sits in front of their cellphone camera and after calibration, the breathing pattern is displayed as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5. Training breathing with FlowMD,.
Suggestions to optimize abdominal breathing that may lead to a slower breath rate when the client practices the technique
Beach pose
By locking the upper chest and sitting up straight it is often easier to breathe so that the abdomen can expand and constrict. Place your hands behind your head and Interlock your finger of both hands, pull your elbows back and up. The person can practice this either laying down on their back or sitting straight up at the edge of the chair as shown in Figure 6.
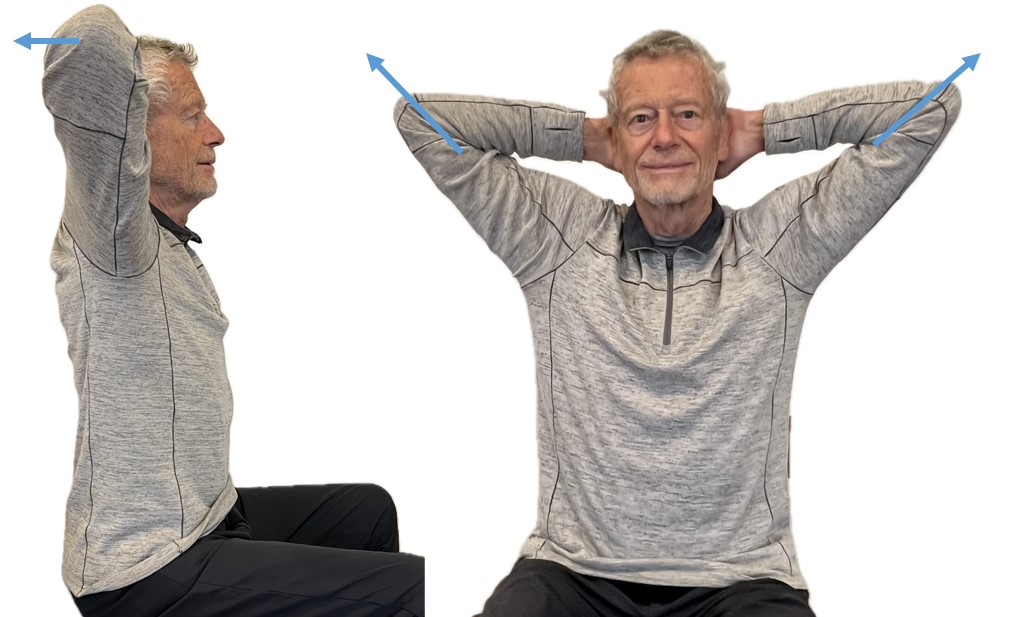

Figure 6. Sitting erect with the shoulders pulled back and up to allow abdominal expansion and constriction as the breathing pattern.
Observe the effect of posture on breathing
Have the person sit slouched/collapsed like a letter C and take a few slow breath, then have them sit up in a tall and erect position and take a few slow breaths. Usually they will observe that it is easier to breathe slower and lower and tall and erect.
Using your hands for feedback to guide natural breathing
Holding your hands with index fingers and thumbs touching the lower abdomen. When inhaling the fingers and thumbs separate and when exhaling they touch again (ensuring a full exhale and avoiding over breathing). The slight increase in lower abdominal muscle tension during the exhalation and relaxation during inhalation and the abdominal wall expands can also be felt with fingertips as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Using your hands and finger for feedback to guide the natural breathing of expansion and constriction of the abdomen. Reproduced by permission from Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49.
Coaching suggestions
There are many strategies to observe, teach and implement effortless breathing (Peper et al., 2024).. Even though breathing is natural and babies and young children breathe diaphragmatically as their large belly expands and constricts. Yet, in many cases the natural breathing shifts to dysfunctional breathing for multiple reasons such as chronic triggering defense reactions to avoiding pain following abdominal surgery (Peper et al, 2015). When participants initially attempt to relearn this natural pattern, it can be challenging especially, if the person habitually breathes shallowly, rapidly and predominantly in their chest.
When initially teaching effortless breathing, have the person exhale more air than normal without the upper chest compressing down and instead allow the abdomen comes in and up thereby exhaling all the air. If the person is upright then allow inhalation to occur without effort by letting the abdominal wall relaxes and expands. Initially inhale more than normal by expanding the abdomen without lifting the chest. Then exhale very slowly and continue to breathe so that the abdomen expands in 360 degrees during inhalation and constricts during exhalation. Let the breathing go slower with less and less effort. Usually, the person can feel the anus dropping and relaxing during inhalation.
Another technique is to ask the person to breathe in more air than normal and then breathe in a little extra air to completely fill the lungs, before exhaling fully. Clients often report that it teaches them to use the full capacity of the lungs.
The goal is to breath without effort. Indirectly this can be monitored by finger temperature. If the finger temperature decreases, the participant most likely is over-breathing or breathing with too much effort, creating sympathetic activity; if the finger temperature increases, breathing occurs slower and usually with less effort indicating that the person’s sympathetic activation is reduced.
Conclusion
There are many strategies to monitor and coach breathing. Relearning diaphragmatic breathing can be difficult due to habitual shallow chest breathing or post-surgical adaptations. Initial coaching may involve extended exhalations, conscious abdominal expansion, and gentle inhalation without chest movement. Progress can be monitored through indirect physiological markers like finger temperature, which reflects changes in sympathetic activity. The integration of these techniques into clinical or educational practice enhances self-regulation, contributing significantly to therapeutic outcomes. In this article we provided a few strategies which may be useful for some clients.
Additional blogs on breathing
https://peperperspective.com/2015/09/25/resolving-pelvic-floor-pain-a-case-report/
REFERENCES
Boulding, R., Stacey, R., & Niven, N. (2016). Dysfunctional breathing: a review of the literature and proposal for classification. European Respiratory Review, 25(141),: 287-294. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0088-2015
FlowMD. (2024). FlowMD app. Accessed December 13, 2024. https://desktop.flowmd.co/
Jovanov, E., Raskovic, D., & Hormigo, R. (2001). Thermistor-based breathing sensor for circadian rhythm evaluation. Biomedical sciences instrumentation, 37, 493–497. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11347441/
Lehrer, P. & Gevirtz R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work? Front Psychol, 5,756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
Lerman, J., Feldman, D., Feldman, R. et al. Linshom respiratory monitoring device: a novel temperature-based respiratory monitor. (2016). Can J Anesth/J Can Anesth, 63, 1154–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-016-0694-y
Meckley, A. (2013). Balancing Unbalanced Breathing: The Clinical Use of Capnographic Biofeedback. Biofeedback, 41(4), 183–187. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-41.4.02
Meuret, A. E., Wilhelm, F. H., Ritz, T., & Roth, W. T. (2008). Feedback of end-tidal pCO2 as a therapeutic approach for panic disorder. Journal of psychiatric research, 42(7), 560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.06.005
Nestor, J. (2020). Breath: The New Science of a Lost Art. New York: Riverhead Books. https://www.amazon.com/Breath-New-Science-Lost-Art/dp/0735213615/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Peper, E., Gibney, K.H., & Holt, C.F. (2002). Make Health Happen. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. https://he.kendallhunt.com/product/make-health-happen-training-yourself-create-wellness
Peper, E., Oded, Y., Harvey, R., Hughes, P., Ingram, H., & Martinez, E. (2024). Breathing for health: Mastering and generalizing breathing skills. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. November 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/suggestions-for-mastering-and-generalizing-breathing-skills/
Peper, E., & Tibbetts, V. (1992). Fifteen-month follow-up with asthmatics utilizing EMG/incentive inspirometer feedback. Biofeedback and self-regulation, 17(2), 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000104
Peper, E. & Tibbetts, V. (1994). Effortless diaphragmatic breathing. Physical Therapy Products. 6(2), 67-71. https://biofeedbackhealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/peper-and-tibbets-effortless-diaphragmatic.pdf
Shaffer, F. and Meehan, Z.M. (2020). A Practical Guide to Resonance Frequency Assessment for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.570400
Steffen, P.R., Austin, T., DeBarros, A., and Brown, T. (2017). The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood. Front Public Health, 5, 222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2017.00222
van Dixhoorn, J.V. (2008). Whole-body breathing. Biofeedback, 36,54–58. https://www.euronet.nl/users/dixhoorn/L.513.pdf
van Dixhoorn, J.V. (2021). Functioneel ademen-Adem-en ontspannings oefeningen voor gevorderden. Amersfoort: Uiteveriy Van Dixhoorn. https://www.bol.com/nl/nl/p/functioneel-ademen/9300000132165255/
Watso, J. C., Cuba, J.N., Boutwell, S.L, Moss, J…(2023). Acute nasal breathing lowers diastolic blood pressure and increases parasympathetic contributions to heart rate variability in young adults. American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology.
325I(6), R797-R80. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00148.2023
Wilson, V., Somers, K. & Peper, E. (2023). Differentiating Successful from Less Successful Males and Females in a Group Relaxation/Biofeedback Stress Management Program. Biofeedback, 51(3), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.5298/608570
[1] Correspondence should be addressed to:
Erik Peper, Ph.D., Institute for Holistic Health Studies, San Francisco State University, 1600 Holloway Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94132 Tel: 415 338 7683 Email: epeper@sfsu.edu web: www.biofeedbackhealth.org blog: www.peperperspective.com
Suggestions for mastering and generalizing breathing skills
Posted: October 30, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, CBT, cellphone, cognitive behavior therapy, emotions, ergonomics, healing, health, mindfulness, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, posture, relaxation, self-healing, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: abdominal beathing, anxiety, diaphragmatic braething, health, hyperventilation, meditation, mental-health, mindfulness, mouth breathing, Toning 3 CommentsAdapted from: Peper, E., Oded, Y., Harvey, R., Hughes, P., Ingram, H., & Martinez, E. (2024). Breathing for health: Mastering and generalizing breathing skills. Townsend Letter-Innovative Health Perspectives. November 15, 2024. https://townsendletter.com/suggestions-for-mastering-and-generalizing-breathing-skills/

Breathing techniques are commonly employed with complimentary treatments, biofeedback, neurofeedback or adjunctive therapeutic strategies to reduce stress and symptoms associated with excessive sympathetic arousal such as anxiety, high blood pressure, insomnia, or gastrointestinal discomfort. Even though it seems so simple, some participants experience difficulty in mastering effortless breathing and/or transferring slow breathing skills into daily life. The purpose of this article is to describe: 1) factors that may interfere with learning slow diaphragmatic breathing (also called cadence or paced breathing, HRV or resonant frequency breathing along with other names), 2) challenges that may occur when learning diaphragmatic breathing, and 3) strategies to generalize the effortless breathing into daily life.
Background
A simple two-item to-do list could be: ‘Breathe in, breathe out.’ Simple things are not always easy to master. Mastering and implementing effortless ‘diaphragmatic’ or ‘abdominal belly’ breathing may be simple, yet not easy. Breathing is a dynamic process that involves the diaphragm, abdominal, pelvic floor and intercostal muscles that can include synchronizing the functions of the heart and lungs and may result in cardio-respiratory synchrony or coupling, as well as ‘heart-rate variability breathing training (Codrons et al., 2014; Dick et al., 2014; Elstad et al., 2018; Maric et al., 2020; Matic et al., 2020). Improving heart-rate variability is a useful approach to reduce symptoms of stress and promotes health and reduce anxiety, asthma, blood pressure, insomnia, gastrointestinal discomfort and many other symptoms associated with excessive sympathetic activity (Lehrer & Gevirtz, 2014; Xiao et al., 2017; Jerath et al., 2019; Chung et al., 2021; Magnon et al., 2021; Peper et al., 2022).
Breathing can be effortful and In some cases people have dysfunctional breathing patterns such as breath holding, rapid breathing (hyperventilation), shallow breathing and lack of abdominal movement. This usually occurs without awareness and may contribute to illness onset and maintenance. When participants learn and implement effortless breathing, symptoms often are reduced. For example, when college students are asked to practice effortless diaphragmatic breathing twenty-minutes a day for one week, as well as transform during the day dysfunction breathing patterns into diaphragmatic breathing, they report a reduction in shallow breathing, breath holding,, and a decrease of symptoms as shown in Fig 1 (Peper et al, 2022).

Figure 1. Percent of people who reported that their initial symptoms improved after practicing slow diaphragmatic breathing for twenty minutes per day over the course of a week (reproduced from: Peper et al, 2022).
Most students became aware of their dysfunctional breathing and substituted slow, diaphragmatic breathing whenever they realized they were under stress; however, some students had difficulty mastering ‘effortless’ (e.g., automated, non-volitional) slow, diaphragmatic breathing that allowed abdominal expansion during inhalation.
Among those had more difficulty, they tended to have almost no abdominal movement (expansion during inhalation and abdominal constriction during exhalation). They tended to breathe shallowly as well as quickly in their chest using the accessory muscles of breathing (sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major and minor, serratus anterior, latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior superior).
The lack of abdominal movement during breathing reduced the movement of lymph as well as venous blood return in the abdomen; since; the movement of the diaphragm (the expansion and constriction of the abdomen) acts a pump. Breathing predominantly in the chest may increase the risk of anxiety, neck, back and shoulder pain as well as increase abdominal discomfort, acid reflux, irritable bowel, dysmenorrhea and pelvic floor pain (Banushi et al., 2023; Salah et al., 2023; Peper & Cohen, 2017; Peper et al., 2017; Peper et al., 2020, Peper et al., 2023). Learning slow, diaphragmatic or effortless breathing at about six breaths per minute (resonant frequency ) is also an ‘active ingredient’ in heartrate variability (HRV) training (Steffen et al., 2017; Shaffer & Meehan, 2020).
1. Factors that interfere with slow, diaphragmatic breathing
Difficulty allowing the skeletal and visceral muscles in the abdomen to expand or constrict in ‘three-dimensions’ (e.g., all around you in 360 degrees) during inhalation or exhalation. Whereas internal factors under volitional control and will mediate breathing practices, external factors can restrict and moderate the movement of the muscles. For example:
Clothing restrictions (designer jeans syndrome). The clothing is too tight around the abdomen; thereby, the abdomen cannot expand (MacHose & Peper, 1991; Peper et al., 2016). An extreme example were the corsets worn in the late 19th century that was correlated with numerous illnesses.
Suggested solutions and recommendations: Explain the physiology of breathing and how breathing occurs by the diaphragmatic movement. Discuss how babies and dogs breathe when they are relaxed; namely, the predominant movement is in the abdomen while the chest is relaxed. This would also be true when a person is sitting or standing tall. Discuss what happens when the person is eating and feels full and how they feel better when they loosen their waist constriction. When their belt is loosened or the waist button of their pants is undone, they usually feel better.
Experiential practice. If the person is wearing a belt, have the person purposely tighten their belt so that the circumference of the stomach is made much smaller. If the person is not wearing a belt, have them circle their waist with their hands and compress it so that the abdomen can not expand. Have them compare breathing with the constricted waist versus when the belt is loosened and then describe what they experienced.
Most participants will feel it is easier to breathe and much more comfortable when the abdomen is not constricted.
Previous abdominal injury. When a person has had abdominal surgery (e.g., Cesarean section, appendectomy, hernia repair, or episiotomy), they unknowingly may have learned to avoid pain by not moving (relaxing or tensing) the abdomen muscles (Peper et al., 2015; Peper et al., 2016). Each time the abdomen expands or constricts, it would have pulled on the injured area or stitches that would have cause pain. The body immediately learns to limit movement in the affected area to avoid pain. The reduction in abdominal movement becomes the new normal ‘feeling’ of abdominal muscle inactivity and is integrated in all daily activities. This is a process known as ‘learned disuse’ (Taub et al., 2006). In some cases, learned disuse may be combined with fear that abdominal movement may cause harm or injury such as after having a kidney transplant. The reduction in abdominal movement induces shallow thoracic breathing which could increase the risk of anxiety and would reduce abdominal venous and lymph circulation that my interfere with the healing.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss the concept of learned disuse and have participant practice abdominal movement and lower and slower breathing.
Experiential practices: Practicing abdominal movements
Sit straight up and purposely exhale while pulling the abdomen in and upward and inhale while expanding the abdomen. Even with these instructions, some people may continue to breathe in their chest. To limit chest movement, have the person interlock their hands and bring them up to the ceiling while going back as far as possible. This would lock the shoulders and allows the abdomen to elongate and thereby increase the diaphragmatic movement by allowing the abdomen to expand. If people initially have held their abdomen chronically tight then the initial expansion of abdomen by relaxing those muscle occurs with staccato movement. When the person becomes more skilled relaxing the abdominal muscles during inhalation the movement becomes smoother.
Make a “psssssst” sound while exhaling. Sit tall and erect and slightly pull in and up the abdominal wall and feel the anus tightening (pulling the pelvic floor up) while making the sound. Then allow inhalation to occur by relaxing the stomach and feeling the anus go down.
Use your hands as feedback. Sit up straight, placing one hand on the chest and another on the abdomen. While breathing feel the expansion of the abdomen and the contraction of the abdomen during exhalation. Use a mirror to monitor the chest-muscle movement to ensure there is limited rising and falling in this area.
Observe the effect of collapsed sitting. When sitting with the lower back curled, there is limited movement in the lower abdomen (between the pubic region and the umbilicus/belly button) and the breathing movement is shallower without any lower pelvic involvement (Kang et al., 2016). This is a common position of people who are working at their computer or looking at their cellphone.
Experiential practice: looking at your cellphone
Sit in a collapsed position and look down at your cellphone. Look at the screen and text as quickly as possible.
Compare this to sitting up and then lift the cell phone at eye level while looking straight ahead at the cellphone. Look at the screen and text as quickly as possible.
Observe how the position effected your breathing and peripheral awareness. Most likely, your experience is similar those reported by students. Close to 85%% of students who complete this activity reported that their breathing was shallower sitting slouched versus erect and about 85% of the students reported that their peripheral awareness and vision improved when sitting erect (Peper et al., 2024).
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Be aware how posture affect breathing. While sitting, place a rolled-up towel against the lower back so that the person sits more erect which would allow the abdomen to expand when inhaling.
Self-image, self-esteem, and confidence. Participants may hold their abdomen in because they want to look slim (sometimes labeled as the “hourglass syndrome” associate expanding the abdomen as unattractive (PTI, 2023). A flat abdomen is culturally reinforced by social media and fashion models and encouraged in some activities such as ballet. On the other hand, some people purposely puff up their chest to increase size and dominance (Cohen & Leung, 2009).
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss the benefits of diaphragmatic breathing including its ability to reduce anxiety in social settings that may enhance confidence. Similar to an earlier suggestion, have the person explore clothing with a looser waist that still supports feelings of attractiveness and power.
Feeling anxious, fearful or threatened. The normal physiological stress reaction is a slight gasp with the tightening of the abdomen muscles for protection when a stressor occurs (Gilbert, 1998; Ekerholt & Bergland., 2008). The stressor can be an actual physical event, social situation or thoughts and emotions. Shallow breathing is a natural self-protective response. This pattern is often maintained until one feels ‘safe’ enough to relax, which for many can have a duration of the entire day or until finding the relative safety of sleep.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss how the physiological stress reaction is a normal response pattern that the person most likely learned in early childhood for self-protection. This pattern is often observed in clients who are emotionally sensitive and/or react excessively to a variety of stimuli. Note that some people have learned not to show their reactivity on their face or in the overt behaviors, yet they continue to breathe shallowly as a telltale sign of ‘distress.’ People who breath shallowly may experience this response as burdensome. Discuss with them how to reframe their sensitivity as a gift; namely, they are more aware of other people’s reactions and emotions. They just need to learn how not to respond automatically. Encourage awareness of their breath-holding and shallow breathing. Follow this by teaching them to replace the dysfunctional breathing with slow, diaphragmatic breathing at 6-breaths-per-minute. A possible training sequence is the following:
- Teach slow, diaphragmatic breathing
- Practice evoking a stressor and the moment the client senses the stress response, shallow breaths or holds their breath have them shift to slow, diaphragmatic breathing.
- If the person slouches in response to stress, the moment they become aware of slouching, have then sit erect, look up and then breathe diaphragmatically. (Peper et al., 2019)
Experiential practice: Transform stressful thoughts by looking up, breathing, and changing thoughts.
Evoke a stressor and then attempt to reframe the experience (cognitive behavior therapy or CBT approach).
Compare this to evoking a stressor, then shift to an upright position while looking up, take a few slow, diaphragmatic breaths, and reframe the experience.
In almost all cases, when the client shifts position, looks up and then reframes, the stress reaction is significantly reduced and it is much easier to reframe the experiences positively compared to when only attempting to reframe the experience (Peper et al., 2019).
Diaphragmatic breathing feels abnormal. How you breathe habitually is what feels normal unless there is overt illness such as asthma or emphysema. Any new pattern usually feels abnormal. When the person shifts their breathing pattern, such as in a transition from habitual shallow chest breathing to slower diaphragmatic abdominal breathing, it feels strange and wrong.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Discuss the concept that habitual patterns are normal (e.g., a person who typically slouches when standing straight may experience that they are going to fall backwards). Emphasize the importance of making a shift in posture and leaning into the discomfort of the new experience. Often after practicing slow diaphragmatic breathing, the person may report feeling much more relaxed (e.g., sensing heaviness and warmth) with their fingers increasing in temperature.
2. Challenges that may occur when learning diaphragmatic breathing
Ideally, breathing is an effortless diaphragmatic process as described by the phrase, “it breathes me” (Luthe & Schultz, 1970; Luthe, 1979); however, some participants struggle to achieve this type of breathing. The following are common challenges and possible solutions:
Distraction and internal dialogue. Many people struggle with thoughts jumping from one area to another. Some people refer to this mental state as “monkey mind.”
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Validate that distraction and internal dialogue are normal and require continual managing and practice to overcome. Experimental Practice: Have the person train focus during diaphragmatic breathing techniques by focusing on 1 item in the room. Remind them that when thoughts arise, note them briefly instead of engaging with them and then refocus on the item. Start with increments of time and increase with practice.
Effect of gravity on breathing. In the vertical position, exhalation occurs when the abdomen constricts (slight tightening of the transverse and oblique abdominal muscles and the pelvic floor) pushes the diaphragm up, allowing the air to go out. It needs to push against gravity.
In the vertical position, inhalation occurs when the abdominal muscles and pelvic floor muscles relax and the abdomen widens in all directions (360 degrees) which causes the diaphragm to descend as it is being pulled down by gravity. This process allows effortless inhalation. The experience is the opposite when lying supine on one’s back. While lying down, gravity pulls on the abdomen that cause the diaphragm to go upward allowing the air to flow out during exhalation. Inhalation takes work because as the diaphragm descends it has to push the abdominal content upward against gravity.
Experiential practice: Erect versus supine
- Vertical position. Begin by exhaling completely by pulling the abdomen in and up while staying erect and not pressing/contracting the chest downward. At the end of exhalation, allow the abdomen to relax (pop out) and feel how the air is sucked in without trying to inhale
- Horizontal position. Begin by lying down, with the face pointing up. Inhale by expanding your abdomen and pushing your abdomen upward against gravity. Then let exhalation occur while totally relaxing as gravity pushes the abdomen downward, which pushes the diaphragm upward into the chest allowing the air to flow out. Optionally, place a small bag of rice/beans (e.g., approximately one to five pound or. One-half to two kilograms) on your lower abdomen while lying down. When you inhale, push the weight upward and away from you by allowing the stomach, but not the chest, to expand. Allow exhalation to occur as the weight pushes your abdomen down and upward into your chest. The weight is useful as it allows the mind to focus more easily on the task of feeling the movement of the abdomen.
Over breathing/hyperventilation. Even breathing at about six breaths per minute can cause hyperventilation can occur. Hyperventilation occurs when a person is breathing in excess of the metabolic needs of the body and thereby eliminating more carbon dioxide. The result is respiratory alkalosis and an elevated blood pH as the dissolved carbon dioxide (pCO2) in the blood is reduced (Folgering, 1999).
The most common symptoms of over breathing are colder sweaty hands and light-headedness. If this starts to occur, focus on decreasing the airflow during exhalation by exhaling through pursed lips making the sound, “Pssssssst.” While making this sound, make the sound softer with less airflow. Alternatively, have them imagine a holding a dandelion flower a few inches from their lips and blow so softly the seeds do not blow away. The blowing away of the seed is the feedback that you are blowing to hard as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Dandelion seeds as feedback when the person is blowing with too much effort. Alternatively, we recommend that the client imagine smelling the scent/fragrance of a flower that usually causes nose inhalation and then exhale gently through pursed lips ast if the air flows over a candle and, the flame does not move back and forth.
Mouth breathing. Mouth breathing contributes to disturbed sleep, snoring, sleep apnea, dry mouth upon waking, fatigue, allergies, ear infections, attention deficit disorders, crowded miss-aligned teeth, and poorer quality of life (Kahn & Ehrlich, 2018). Even the risk of ear infections in children is 2.4 time higher for mouth breathers than nasal breathers (van Bon et al, 1989) and nine and ten year old children who mouth breath have significantly poorer quality of life and have higher use of medications (Leal et al, 2016).
Breathing through the nose is associated with deeper and slower breathing rate than mouth breathing. Nose breathing reduces airway irritation since the nose filters, humidifies, warms/cools the inhaled air as well as reduces the air turbulence in the upper airways. The epithelial cells of the nasal cavities produce nitric oxide that are carried into the lungs when inhaling during nasal breathing (Lundberg & Weitzberg, 1999). The nitric oxide contributes to healthy respiratory function by promoting vasodilation, aiding in airway clearance, exerting antimicrobial effects, and regulating inflammation (McKeown, 2019; Allen, 2024). Note that alternate nostril breathing, such as breathing in one nostril for 5-seconds and out of the other for 5-seconds is another technique which some people find beneficial.
Slower breathing approaches also facilitates sympathetic parasympathetic balance and reduces airway irritation. If the person breathes habitually through their mouth, refer them to health care provider to explore factors that may contribute to mouth breathing such as enlarged tonsils and adenoids or deviated septum. In addition, explore environmental factors that could contribute nasal inflammation such as allergies or foods such as dairy (Al-Raby, 2016).
Performance anxiety. Many participants are concerned about their performance. The direct instructions such as “follow the graphic” causes the person to try hard to breathe with too much effort. Explore some of the following indirect strategies to interrupt ongoing cognitive judgements and self-talk.
- Toning or humming (Peper et al., 2019a). While exhaling, have the person hum a sound with their mouth closed. Let the sound go for about 6 seconds, relax, inhale and hum again. Toning is very similar except you verbalize a tone such as “Oammm.” (For detailed instructions on toning, see: Anziani & Peper (2021)).
- Stroking down arms and legs during exhalation. Have a partner gently stroke down your arms from your shoulder past your fingertips as you are exhaling. The downward stroking is in rhythm with the exhalation. As the arm is being stroked, attend to the sensations going down the arms. Be sure that the toucher exhales at the same time and the stroking down the arm takes about six seconds. After being stroked for a few times, have the person imagine that each time they exhale they feel a flow down through their arms and out their fingers.
- Repeat the same process while stroking down the legs from the side of their hips to their toes.
- Finally, have the person imagine/feel the sensation streaming down their legs with each exhalation.
- Many participants will report that they sense a steaming going down their arms, that they hands warm up, and their thought have stopped.
- Integrated body movement with breathing especially flexion and contraction (Meehan & Shaffer, 2023). Integrate the normal response of flexion that induces exhalation and extension evokes inhalation. Be careful that the flexion movement does not encourage participants to compress their chest during exhalation, which tends to encourage chest breathing. Have the person focus on their head staying tall and erect. Have the person sit straight up with their feet slight apart and their hands palm down on their lap. Allow inhaling to initiate as the person simultaneously arches their lower back expanding the stomach, separating the knees and turning the hands palm up. Initiate exhalation while simultaneously bringing the knees together, turning the palms face down on the thighs and rolling the pelvic back slightly rounding the lower back. Do the movements smoothly while keeping the legs and shoulders relaxed.
Flooded by emotions. Although very rare, at times when the person allows the abdomen to relax, they may experience by the emotions from a past trauma as the habitual bracing patterns are relaxed.
Suggested solutions and recommendations. Validate these emotions for the person. Explain that this is a normal process that may occur if past trauma has occurred. Clients who have had past trauma often experience hypervigilance, which may interfere with the relaxation response that occurs during more optimal states of breathing. Transitioning to a more optimal rest state may be uncomfortable for a person who has experienced trauma because it reduces hypervigilance. This can feel uncomfortable as hypervigilance in these cases serves a protective role, even if it is an illusory feeling of protection from future harm. Since persistent hypervigilance can interfere with the relaxation response, the benefits of allowing a relaxation response to occur through slower breathing should be highlighted. Grounding techniques as described by Peper et al (2024a) can be useful to become centered.
3. Strategies to generalize the effortless breathing into daily life.
Generalizing the skill occurs after having mastered diaphragmatic breathing in different positions (sitting, standing, lying down, and while performing tasks). It is important to remember that our breathing patterns are conditioned with our behavior. Become aware how breathing affects cognitions and emotions and how emotions and cognitions affects breathing. The following are some strategies that may facilitate learning and generalizing the slower breathing skills.
Observing how our behavior affects our breathing: Anything that may evoke the alarm or defense reaction tends to cause the person gasp and/or hold their breath. For example, when a person is sitting peacefully, make an unexpected noise behind their back or movement in their periphery of vision. In most cases they will gasp or hold their breath. Usually, they are unaware of this process unless they are asked what happened to their breathing. The major reason for the breath holding is that the stimuli triggers an alarm/defense reaction and when we hold our breath our hearing is more acute (we can hear approaching danger earlier). The problem is that we give this response when there is no actual, immediate or present threat.
Experiential practice. Sit comfortably. Now as quickly as possible without rotating the head, look with your eyes to the extreme right and then left and back and forth as if trying to identify danger at the periphery. Do this for a few eye movements. Almost everyone holds their breath when doing this exercise. For generalizing the skill, ask the person to observe during the day situations in which they hold their breath, ask them if it was necessary and encourage them to start diaphragmatic breathing.
Observing how breathing affects our thoughts and emotions. Breathing patterns are intrinsically linked to our emotions and thoughts as illustrated in the many language phrases such as sigh of relief, full of hot air, waiting with bated breath. At the same time, our breathing patterns also affect our thoughts. For instance, when we breathe shallowly and more rapidly, we can induce feelings of fear or anxiety. If we gasp, we can experience thought stopping.
Experiential practices: Incomplete exhalation: Observe what happens when you exhale less than you inhale. Begin by exhaling only 70% of the air you inhaled, then inhale and exhale again only 70% of the air you just inhaled continue this for 30 seconds. Many people will experience the onset of anxiety symptoms, lightheadedness, dizziness, neck and shoulder tension, etc. (Peper & MacHose, 1993). If you experience symptoms during this exercise and you have experienced these symptoms in the past, it is likely that unknowingly breathing in a dysfunctional pattern could have evoked them. Therefore, practicing effortless breathing may interrupt and reduce the symptoms. Do this practice while observing the person carefully and immediately interrupt and distract the person if they start feeling dizzy, too anxious, or trigger the beginning of a panic attack or PTSD symptoms.
Experiential practice: Gasp or sniff-hold sniff. Observe what happens when you are performing a cognitive task and you rapidly gasp or do sniff-hold-sniff again before exhaling. Begin by sequentially subtracting mentally, the number 7 from 146 (e.g., 146, 139, 132….). Do this as rapidly as possible and do not make a mistake. While doing the subtracting, take a rapid gasp (such as one is triggered by surprise or fear), alternatively, take a quick sniff through your nose, hold your breath and take another sniff on top of the first one, then exhale. Whereas subtrating numbers is a skill most adults can perform, the ‘time pressure’ along with the direction to avoid mistakes may be the ‘immediate’ source of strain. Whether it was the time pressure, the direction to avoid mistakes or the direction to gasp, observe what happened to your thinking process. In almost all cases, your higher-order thoughts (doing the sequential subtraction under time pressure while gasping) have disappeared, replaced by the immediate thoughts of ‘performance anxiety.’
If you blank out on exams or experience anxiety, gasping and breath holding may be one of the factors that increases symptoms and affects your performance. If you are aware that you are holding your breath or gasped, use that as the cue to shift to slow diaphragmatic breathing and you may find that your performance improves. Therefore, observe when and where you were blanking out, gasping and/or holding your breathing then substitute slow, effortless diaphragmatic breathing.
How to develop awareness and interrupting of dysfunctional breathing response. Most participants are unaware of their somatic responses until symptoms occur. Being aware of the initiation of a somatic response may assist you in identifying triggers and interrupting the developing process. A significant component of the training is symptom prescription rehearsal.
Symptom prescription is a practice in which the participant simulates/acts out the psychophysiological pattern associated with their symptoms. They amplify the body pattern until they feel the onset of the actual symptoms. The moment the person feels the beginning of the symptom, they stop the practice and initiate slow breathing and relaxation. After practicing the symptom rehearsal, they are instructed to become aware of the onset of the symptom and then use that signal to trigger the effortless breathing while looking up and shifting the body into an upright sitting position (Peper et al., 2019). Gasping and breath holding are normal responses to unexpected stimuli; however, they may trigger sympathetic activation even when there is no actual danger.
Experiential practice: Developing awareness on neck and shoulder tension:
Sit comfortably and practice effortless breathing for a minute. Take a fearful gasp and observe what happens in your body (e.g., slight neck and upper chest tension, light headedness, slight radiating pain into the eye, etc.). Shift back to effortless breathing until all symptoms /sensations have disappeared.
- Now gasp with less effort and observe the first sensations, use the awareness of first sensations to trigger the effortless breathing and continue to breathe until symptoms have disappeared
- Continue this practice. Reduce the gasping effort each time.
- After having developed the initial somatic sensation then during the day observe what triggers this response and immediately shift to slower diaphragmatic breathing. After you have shifted to effortless breathing, reflect on the trigger. Was it necessary to react? If yes, explore strategies to resolve the issue.
The same process can be done to assist with desensitization to painful memories or stressful events. Each time the person becomes aware of their somatic reaction to an evoked memory or stressful event, they shift to effortless diaphragmatic breathing. If they find that it is difficult to interrupt the emotional memories and it triggers more and more negative thoughts and associations, use the sniff-hold-sniff technique and follow that with box-breathing or any of the other quick somatic rescue techniques (Peper et al., 2024a). Box-breathing in this context could include a brief breath-holding. A typical box-breathing technique is to breath in for a count of four, hold for a count of four, breath out for a count of four, then breath in again for a count of four, continuing the figurative 4-4-4-4 count of breathing.
Practice slower diaphragmatic breathing during the day. Implement effortless diaphragmatic breathing through regeneration and interrupting the stress response.
- Support regeneration. Each day set aside 10 to 20 minutes to practice slow effortless diaphragmatic breathing at about 6-breaths-per-minute. In the beginning 10 to 20 minutes may be too long, thus in some cases have the person practice a few times a day for two minutes and slowly build up to 10 or more minutes. The practice is not just a mechanical process of breathing it includes mindfulness training. Namely, as you are breathing each time you exhale imagine a flow doing down your arms and legs and as you inhale an energy coming into you. Whenever your attention drifts bring it back to the breathing.
- Integrate breathing with daily activities. Practice slower breather before eating, after putting the seat belt on in the car, or whenever a notification pops up on the cell phone.
- Set reminders and alarms on your phone to check how you are feeling and breathing. Leave notes on nearby furniture such as a nightstand, on the shower door, and/or on the kitchen table as reminders to be mindful of your breath. If stressed or breathing shallowly, take a moment to breathe slowly.
- Interrupt the stress response. During the day when you are aware that you shallow breathe, are holding your breath, feel anxious, experience neck and shoulder tightness, or worry and use that as a cue to shift position by sitting or standing more erect, looking upward and take a few slow diaphragmatic breaths.
- Use cue condition to facilitate this process. Each time you begin the practice smell a specific aroma or do some behavioral movement and then do the breathing. After a while the aroma or behavioral movement will become the classically conditioned cue to trigger the effortless breathing.
- Use role rehearsal and conditioning to generalize the skill. Generalizing the skills often takes more time than what may be expected. In a culture where instant relief is expected— implied message associated with medication— self-mastery techniques are different and challenging as they take time to master the skill and implement them during daily life. The process of mastery is similar to learning to play a musical instrument or sports. Learning to play the violin requires practice as well as practice with failures along the way until one is ready for more challenging musical pieces, recitals, or performances.
A useful strategy to implement the learning is role rehearsal in the office, at home at work, and in real life. It is usually much easier to practice these skills in a safe space such as your own room or, with a therapist compared to with other people or, at work. To generalize the skill most efficiently, it can be helpful to practice in a safe environment while imagining being in the actual stressful location This process is illustrated by the strategy to reduce social anxiety and menstrual cramps.
Social anxiety when seeing my supervisor. Master effortless breathing in a safe environment. Role rehearsal in imagery. If you observed that you held your breath when your supervisor is around, begin with imagery when your supervisor is not present. Sit, comfortably. Let go of muscle tension and breathe effortlessly, evoking a scenario where your supervisor is walking by and continue to breathe slowly as you imagine the scene. Role rehearsal in action. Ask another person to role-play your supervisor. Sit, comfortably. Let go of muscle tension and breathe effortlessly. Have this person walk into the room in a similar way that your supervisor would. Imagine that person is your supervisor while practicing your effortless breathing. Repeat until the effortless breathing is more automatic. Practice many times in real life. Whenever the rehearsed situation occurs, implement slower paced breathing.
Menstrual cramps that causes most women to curl up and breathe shallowly when experiencing menstrual cramps (Peper et al., 2023). Master effortless breathing in a safe environment. Practice breathing lying down. While lying down, breathe diaphragmatically by having a three-to-five-pound weight such as a bag of rice or hot water pad on your abdomen. If you have a partner, have the person stroke your legs from the abdomen to your toes while you exhale. Role rehearse experiencing pain and then practice lower diaphragmatic breathing. Namely, tighten your abdomen as if you have discomfort, then focus on relaxing the buttocks and sensing the air flowing down your legs and out your feet as you exhale. Practice in real life. A few days before you expected menstruation, practice slow diaphragmatic breathing several times for at least 5-10 minutes during the day. When your menstruation starts practice the slower and lower breathing while imagining the air flowing down the abdomen, through the legs and out the feet.
Summary/Conclusion
Breathing is the mind-body bridge. It usually occurs without awareness and breathing changes affect our thought, emotions and body. Mastering and implementing slower breathing during the day takes time and practice. By observing when breathing patterns change, participants may identify internal and external factors that affect breathing which provides an opportunity to implement effortless diaphragmatic breathing to optimize health as well as resolve some of the triggers. As one 20-year-old, female student reported,
The biggest benefit from learning diaphragmatic breathing was that it gave me the feeling of safety in many moments. My anxiety tended to make me feel unsafe in many situations but homing in and mastering diaphragmatic breathing helped tremendously. I shifted from constant chest breathing to acknowledging it and in turn, reminding myself to breathe with my diaphragm.
References
Allen, R. (2024). The health benefits of nose breathing. Nursing in General Practice. http://hdl.handle.net/10147/559021
Al-Rabia, M.W. (2016). Food-induced immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic rhinitis. J Microsc Ultrastruct, 4(2), 69-75. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1016/j.jmau.2015.11.004
Anziani, M. & Peper, E. (2021). Healing from paralysis-Music (toning) to activate health. Peperperspective –ideas on illness, health and well-being from Erik Peper. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://peperperspective.com/2021/11/22/healing-from-paralysis-music-toning-to-activate-health/
Banushi, B., Brendle, M., Ragnhildstveit, A., Murphy, T., Moore, C., Egberts, J., & Robison, R. (2023). Breathwork Interventions for Adults with Clinically Diagnosed Anxiety Disorders: A Scoping Review. Brain Sci. 13(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020256
Chung, A.H., Gevirtz, R.N., Gharbo, R.S. et al. (2021).Pilot Study on Reducing Symptoms of Anxiety with a Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Wearable and Remote Stress Management Coach. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 46, 347–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-021-09519-x
Cohen, D. & Leung, A.K.Y. (2009). The hard embodiment of culture. European Journal of Social Psychology, 9, 1278–1289 https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.671
Codrons, E., Bernardi, N. F., Vandoni, M., & Bernardi, L. (2014). Spontaneous group synchronization of movements and respiratory rhythms. PloS one, 9(9), e107538. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107538
Dick, T. E., Mims, J. R., Hsieh, Y. H., Morris, K. F., & Wehrwein, E. A. (2014). Increased cardio-respiratory coupling evoked by slow deep breathing can persist in normal humans. Respiratory physiology & neurobiology, 204, 99-111. https://doil.org/10.1016/j.resp.2014.09.013
Ekerholt, K. & Bergland, A. (2008). Breathing: A sign of life and a unique area for reflection and action. Physical therapy, 88(7), 832-840. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20070316
Elstad, M., O’Callaghan, E. L., Smith, A. J., Ben-Tal, A., & Ramchandra, R. (2018). Cardiorespiratory interactions in humans and animals: rhythms for life. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 315(1), H6-H17. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00701.2017
Folgering, H. (1999). The pathophysiology of hyperventilation syndrome. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis, 54(4), 365-72. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10546483/
Gilbert, C. (1998). Emotional sources of dysfunctional breathing. Journal of bodywork and movement therapies, 2(4), 224-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-8592(98)80019-3
Jerath, R., Beveridge, C., & Barnes, V.A. (2019). Self-Regulation of Breathing as an Adjunctive Treatment of Insomnia. Front Psychiatry, 9(780). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00780
Kahn, S. & Ehrlich, P.R. (2018). Jaws. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. https://www.amazon.com/Jaws-Hidden-Epidemic-Sandra-Kahn/dp/1503604136/ref=tmm_hrd_swatch_0?_encoding=UTF8&qid=1685135054&sr=1-1
Kang, K.W., Jung, S.I., Lee, do Y., Kim, K., & Lee, N.K. (2016) Effect of sitting posture on respiratory function while using a smartphone. J Phys Ther Sci, 28(5), 1496-8. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.1496
Leal, R.B., Gomes, M.C., Granville-Garcia, A.F., Goes, P.S.A., & de Menezes, V.A. (2016). Impact of Breathing Patterns on the Quality of Life of 9- to 10-year-old Schoolchildren. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 30(5):e147-e152. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4363
Lehrer, P.M. & Gevirtz, R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work? Front Psychol. 5, 756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
Lundberg, J.O. & Weitzberg, E. (1999). Nasal nitric oxide in man. Thorax. (10):947-52. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.54.10.947
Luthe, W. (1979). About the Methods of Autogenic Therapy. In: Peper, E., Ancoli, S., Quinn, M. (eds). Mind/Body Integration. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2898-8_12
Luthe, W. & Schultz, J. H. (1970). Autogenic therapy: Medical applications. New York: Grune and Stratton. https://www.amazon.com/Autogenic-Therapy-II-Medical-Applications/dp/B001J9W7L6
MacHose, M., & Peper, E. (1991). The effect of clothing on inhalation volume. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 16(3), 261–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000020
Magnon. V., Dutheil, F., & Vallet, G.T. (2021). Benefits from one session of deep and slow breathing on vagal tone and anxiety in young and older adults. Sci Rep. 11(1),19267. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98736-9
Maric, V., Ramanathan, D., & Mishra, J. (2020). Respiratory regulation & interactions with neuro-cognitive circuitry. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 112, 95-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.02.001
Matić, Z., Platiša, M. M., Kalauzi, A., & Bojić, T. (2020). Slow 0.1 Hz breathing and body posture induced perturbations of RRI and respiratory signal complexity and cardiorespiratory coupling. Frontiers in physiology, 11, 24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00024
McKeown, P. (2021). The Breathing Cure: Develop New Habits for a Healthier, Happier, and Longer Life. Boca Raton, Fl “Humanix Books. https://www.amazon.com/BREATHING-CURE-Develop-Healthier-Happier/dp/1630061972/
Meehan, Z.M. & Shaffer, F. (2023). Adding Core Muscle Contraction to Wrist-Ankle Rhythmical Skeletal Muscle Tension Increases Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia and Low-Frequency Power. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 48(1), 127-134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-022-09568-w
McKeown, P. (2021). The breathing cure: Develop new habits for a healthier, happier, and longer life. Humanix Books. https://www.amazon.com/BREATHING-CURE-Develop-Healthier-Happier/dp/1630061972/
Peper, E., Booiman, A., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Mitose, J. (2016). Abdominal SEMG Feedback for Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Methodological Note. Biofeedback. 44(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-44.1.03
Peper, E., Chen, S., Heinz, N. & Harvey, R. (2023). Hope for menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) with breathing. Biofeedback, 51(2), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.2.04
Peper, E. & Cohen, T. (2017). Inhale to Breathe Away Pelvic Floor Pain and Enjoy Intercourse. Biofeedback, 45 (1), 21–24. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.1.04
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Peper, E., Harvey, R., Cuellar, Y., & Membrila, C. (2022). Reduce anxiety. NeuroRegulation, 9(2), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.9.2.91
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153-169. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.153
Peper, E., Harvey, R. & Rosegard, E. (2024). Increase attention, concentration and school performance with posture feedback. Biofeedback, 52(2). https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-52.02.07 or https://www.researchgate.net/publication/383151816_WHAT_ABOUT_THIS_Increase_Attention_Concentration_and_School_Performance_with_Posture_Feedback
Peper, E. & MacHose, M. (1993). Symptom prescription: Inducing anxiety by 70% exhalation. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 18(3), 133-138. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999790
Peper, E., Mason, L., Harvey, R., Wolski, L, & Torres, J. (2020). Can acid reflux be reduced by breathing? Townsend Letters-The Examiner of Alternative Medicine, 445/446, 44-47. https://www.townsendletter.com/article/445-6-acid-reflux-reduced-by-breathing/
Peper, E., Mason, L., Huey, C. (2017). Healing irritable bowel syndrome with diaphragmatic breathing. Biofeedback. 45(4), 83–87. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.4.04
Peper, E., Oded, Y., & Harvey, R. (2024a). Quick somatic rescue techniques when stressed. Biofeedback, 52(1), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.5298/982312
Peper, E., Pollack, W., Harvey, R., Yoshino, A., Daubenmier, J. & Anziani, M. (2019a). Which quiets the mind more quickly and increases HRV: Toning or mindfulness? NeuroRegulation, 6(3), 128-133. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.12
Peper, E., Swatzyna, R., & Ong, K. (2023). Mouth breathing and tongue position: a risk factor for health. Biofeedback. 51(3), 74–78 https://doi.org/10.5298/912512
PTI. (2023 August 3). Often suck your stomach in to look slimmer in pictures? It can lead to ‘hourglass syndrome.’ The Economic Times Panache. Accessed March 26, 2024. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/magazines/panache/often-suck-your-stomach-in-to-look-slimmer-in-pictures-it-can-lead-to-hourglass-syndrome/articleshow/102392681.cms?from=mdr
Salah, H.M., Goldberg, L.R., Molinger, J., Felker, G.M., Applefeld, W., Rassaf, T., Tedford, R.J., Mirro, M., Cleland, J.GF., & Fudim, M. (2022). Diaphragmatic Function in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 80(17), 1647-1659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.08.760
Shaffer, F. & Meehan, Z.M. (2020). A Practical Guide to Resonance Frequency Assessment for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback. Frontiers in Neuroscience,14. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.570400
Steffen, P.R., Austin, T., DeBarros, A., & Brown, T. (2017). The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood. Front Public Health, 5, 222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2017.00222
Taub, E., Uswatte, G., Mark, V. W., Morris, D. M. (2006). The learned nonuse phenomenon: Implications for rehabilitation. Europa Medicophysica, 42(3), 241-256. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17039223/
van Bon, M.J., Zielhuis, G.A., Rach, G.H., & van den Broek, P. (1989). Otitis media with effusion and habitual mouth breathing in Dutch preschool children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, (2), 119-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-5876(89)90087-6
Xiao, M., Zi-Qi, Y., Gong, Z.Q., Zhang, H., Duan, N.Y., Shi, Y.T,, Wei, G.X., Li, Y.F. (2017).The Effect of Diaphragmatic Breathing on Attention, Negative Affect and Stress in Healthy Adults. Front Psychol. 8(874). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00874
Grandmother Therapy: A Common-Sense Approach to Health and Wellness
Posted: July 24, 2024 Filed under: ADHD, attention, behavior, education, Evolutionary perspective, Exercise/movement, Nutrition/diet, Pain/discomfort, relaxation, self-healing | Tags: anxiety, depression, epilepsy, exhaustion, grandmother therapy, health, insomnia, life style change, mental-health, therapy 1 CommentErik Peper, PhD and Angelika Sadar, MA

In today’s fast-paced world, college students and young adults often struggle with various health issues. From anxiety and depression to ADHD and epilepsy, these challenges can significantly impact their daily lives. But what if the solution to many of these problems lies in something as simple as “Grandmother Therapy”?
What is Grandmother Therapy? Grandmother Therapy is all about going back to basics and establishing healthy lifestyle habits. It’s the common-sense approach that our grandmothers might have suggested: regular sleep patterns, balanced nutrition, increased social connections, and regular physical activity.
The Problem: Many college students:
- Skip breakfast before their first class
- Rely on fast food and sugary stimulants
- Have irregular sleep schedules
- Spend excessive time on gaming and social media
The Medical Approach: Often, the quick solution is medication:
- Depression? Take antidepressants.
- Insomnia? Use sleeping pills.
- Anxiety? Try anti-anxiety medication.
- ADHD? Prescribe Ritalin or similar drugs.
While these treatments may help manage symptoms, they often overlook the underlying lifestyle factors contributing to these issues.
The Grandmother Therapy Approach:
- Establish regular sleep patterns
- Adopt healthy eating habits
- Increase social connections
- Incorporate regular physical activity
- Reduce gaming and social media use
Case Study #1: The Power of Sleep
This illustrates the simple intervention of having a bedtime routine. A college student in a holistic health class complained that she was tired most of the time and had difficulty focusing her attention and continuously drifted off in class.
Here is her reported sleep schedule:
- last night I went to bed at 3am and woke up 7;
- the day before, I went to bed at 1pm and woke up at 6,
- two nights before, I went to bed at 4pm and woke up at 10 am.
Holistic treatment approach:
Set a sleep schedule: she was provided with information about the importance of having a regular pattern of sleep and waking. Namely, go to bed at the same time and get up 8 hours later. She agreed to do an experiment for a week to go to bed at 12 and wake up at 8m. To her surprise, she felt so much more energized and could pay attention in class during the week of the experiment.
Case Study #2: Beyond Seizures: A Holistic Approach to Treating Psychogenic Nonepileptic Seizures
This case study highlights the importance of a comprehensive, lifestyle-based approach to treating psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES). It follows a 24-year-old male student initially diagnosed with intractable epilepsy, experiencing over 10 seizures per week that didn’t respond to medication.
Key points:
1. Initial misdiagnosis: Despite normal MRI and EEG results, the client was initially treated for epilepsy.
2. Limited assessment: Traditional medical evaluations focused solely on seizure descriptions and diagnostics, overlooking crucial lifestyle factors.
3. Comprehensive evaluation: A psychophysiological assessment revealed high sympathetic arousal, including rapid breathing, sweaty palms, and muscle tension.
4. Lifestyle factors: The client’s diet consisted of high-glycemic fast foods, excessive caffeine, alcohol, and daily marijuana use. He also had significant student debt and a history of abdominal surgery.
Holistic treatment approach:
– Dietary changes: Switching to unprocessed, low-glycemic foods and increasing vegetable and fruit intake
– Breathing techniques: Learning and practicing slow diaphragmatic breathing
– Stress management: Addressing underlying stressors and practicing relaxation techniques
– Supplements: Adding omega-3 and multivitamins to support brain health
Remarkable results: Within four months, the patient became seizure-free, reduced marijuana use significantly, and decreased medication dosage.
Summary
These cases underscore the potential of integrating lifestyle modifications and stress management techniques in treating attention, anxiety and even psychogenic nonepileptic seizures; offering hope for patients who don’t respond to traditional treatments alone. Before turning to medication or complex treatments, consider the power of Grandmother Therapy. By addressing fundamental lifestyle factors, we can often improve our health and well-being significantly. Remember, sometimes the most effective solutions are the simplest ones.
The Challenges of Simplicity: While Grandmother Therapy may seem straightforward, its simplicity can make it challenging to implement. It requires commitment and a willingness to change long-standing habits.
Implement many Life Style Changes at once: Recommending one change at the time is logical; however, participants will more likely experience rapid benefits and are more motivated to continue when they change multiple lifestyle factors at once.
Call to Action: Are you struggling with health issues? Try implementing some aspects of Grandmother Therapy in your life. Implement changes and see how they impact your overall well-being.
Please let us know your experience with implementing Grandmother Therapy.
See the following blogs for more background information
360-Degree Belly Breathing with Jamie McHugh
Posted: April 26, 2024 Filed under: attention, Breathing/respiration, emotions, healing, health, meditation, mindfulness, Pain/discomfort, relaxation, self-healing | Tags: abdominal braething, belly breathing, daiphragm, effortless breathing, passive attention, self-acceptance, somatic awreness 4 Comments
Breathing is a whole mind-body experience and reflects our physical, cognitive and emotional well-being. By allowing the breath to occur effortlessly, we provide ourselves the opportunity to regenerate. Although there are many directed breathing practices that specifically directs us to inhale or exhale at specific rhythms or depth to achieve certain goals, healthy breathing is whole body experience. Many focus on being paced at a specific rhythm such as 5.5 breath per minute; however, effortless breathing is dynamic and constantly changing. It is contstantly adapting to the body’s needs: sometimes the breath is slightly slower, sometimes slightly faster, sometimes slightly deeper, sometimes slightly more shallower. The breathing process is effortless. This process can be described by the Autogenic training phrase, “It breathes me” (Luthe, 1969; Luthe, 1979; Luthe & de Rivera, 2015). Read the essay by Jamie McHugh, Registered Master Somatic Movement Therapist and then let yourself be guided in this non-striving somatic approach to allow effortless 360 degree belly breathing for regeneration.
The 360 degree belly breathing by Jamie McHugh, MSMT, is a somatic exploration to experience that breathing is not just abdominal breathing by letting the belly expand forward, but a rhythmic 360 degree increase and decrease in abdominal volume without effort. This effortless breathing pattern can often be observed in toddlers when they sit peacefully erect on the floor. This pattern of breathing not only enhances gas exchange, more importantly, it enhances abdominal blood and lymph circulation.
“The usual psychodynamic foundation for the self-experience is that of hunger, not breath. The body is experienced as an alien entity that has to be kept satisfied; the way an anxious mother might experience a new baby. When awareness is shifted from appetite to breath, the anxieties about not being enough are automatically attenuated. It requires a settling down or relaxing into one’s own body. When this fluidity moves to the forefront of awareness…there is a relaxation of the tensed self…and the emergence of a simpler, breath-based self that is capable of surrender to the moment.” – Mark Epstein (2013).
The intention behind 360 Degree Belly Breathing is to access and express the movement of the breath in all three dimensions. This is the basis for all subsequent somatic explorations within the Embodied Mindfulness protocol, a body-based approach to traditional meditation practices I have developed over the past 20 years (McHugh, 2016). Embodied Mindfulness explores the inner landscape of the body with the essential somatic technologies of breath, vocalization, self-contact, stillness and subtle movement. We focus and sustain mental attention while pleasurably cultivating bodily calm and clarity as a daily practice for survival in these turbulent times. Coupled with individual variations and experimentation, this practice becomes a reliable sanctuary from overwhelm, scattered attention, and emotional turmoil.
The Central Diaphragm

The central diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscular sheath that divides the thorax (chest) and the abdomen (belly), is the primary mechanism for breathing. It is the floor for your heart and lungs and the ceiling for your belly. The central diaphragm is a mostly impenetrable divide, with a few openings through it for the aorta, vena cava and the esophagus. Each time you inhale, the diaphragm contracts and flattens out a bit as it presses down towards your pelvis. Each time you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and floats back up towards your heart. The motion of the diaphragm impacts the barometric pressure in your chest: the downward movement of the diaphragm on the inhale pulls oxygen into your lungs, and the subsequent exhale expels carbon dioxide into the world as the diaphragm releases upwards.
The movement of the diaphragm is twofold: involuntary and voluntary. Involuntary, ordinary breathing is a homebase and a point of return. Breathing just automatically happens – you don’t have to think about it. Breathing is also voluntary; you can choose to change the tempo (quick or slow), the duration (short or long) and quality (smooth or sharp) of this movement to “charge up and chill out” at will. Knowing how to collaborate with your diaphragm, discovering your own rhythm of diaphragmatic action, and undulating between the automatic and the chosen is a foundation for physiological equilibrium and emotional “self-soothing”.
Watch these two brief videos to get a visual image of your diaphragm in motion:
Beginning Sitting Practice
“When your back becomes straight, your mind will become quiet.” – Shunryu Suzuki
What does it mean to have a “straight back”? What are the inner coordinates and outer parameters of this position in space? And what kind of environment is needed to support this uprightness? This simple orientation to sitting can create more comfort, ease and support in your structure, which will stimulate more fluidity in your breathing and your thinking.
As you sit on a chair, consider two points of focus: body and environment. Can I sit upright with ease and comfort on this chair? If not, what changes can I make with my body and how can I adapt the environment of this chair to meet my needs? Since we are all various heights, it is not surprising a one-size-fits-all chair would need adaptation. Don’t be content with your first solution – experiment until you find just the right configuration. Valuing and seeking bodily comfort and ease are simple yet profound acts of self-kindness.
Do you need to move your pelvis forward on the chair or back? If you move your pelvis back, do you get the necessary support from the back of the chair for your pelvic bowl? If the back of the chair is too far away and/or makes you lean back into space, place a small cushion or two between the back of the chair and the base of your spine. With your back supported, are your feet on the floor? If not, place a folded blanket or a cushion under them.
With pelvis and feet in place, take a few full breaths to stabilize your pelvis and let your weight drop down through your sitz bones into the chair. The upper body receives more support from the core muscles of the lower body when your center of gravity drops – you don’t have to work so hard to maintain uprightness. Finally, rock on your sitz bones forward, backward, and side-to-side. Movement awakens bodily feedback so you can feel where center is in this moment. That sense of center will continue to change throughout the duration of the practice period so feel free to periodically adjust your position.
After this initial structural orientation, the next step is attending to the combination of breath and self-contact to fill out our self-perception. Self-contact is like using a magnifying glass – focusing the mind by feeling the substance of the belly’s movement in our hands. Since the diaphragm is a 360-degree phenomenon that generates movement in our sides and our back as well as our front, spreading awareness out not only creates different patterns of muscular activation – it also changes the brain’s map of the body and how we perceive ourselves. This change of orientation over time recalibrates our alignment and how we settle in ourselves, with awareness of our back in equal proportion to our front and sides.
360-Degree Belly Breath
“To stop your mind does not mean to stop the activities of the mind. It means your mind pervades your whole body.” – Shunryu Suzuki
Read text below or be guided by the audio file or YouTube video. http://somaticexpression.com/classes/360DegreeBreathingwithJamieMcHugh.mp3
Sit comfortably and place your hands on the front of your belly. With each inhale, become aware of the forward movement of your belly swelling. Then, with each exhale, notice the release of your belly and the settling back to center. Give this action and each subsequent action at least 5-7 breath cycles. Intersperse this way of breathing with ordinary, effortless breathing by letting the body breathe automatically. Return time and again to ordinary breathing, letting go of the focus and the effort to rest in the aftermath.
Now, slide your hands to the sides of your belly. Notice with each breath cycle how your belly moves laterally out to the sides on the inhale and then settles back to center again on the exhale.
Now, slide your hands to the back of your belly. You may wish to make contact with the back of your hands instead of your palms if it is more comfortable. With each inhale, focus on the movement into the backspace – this will be much smaller than the movement to the front; and with each exhale, the movement settling back to center.
Finally, connect all three directions: your belly radiates out 360 degrees on the horizon with each inhale, simultaneously moving forward, backward, and out to both sides, and then settles inward with each exhale.
Finish with open awareness – scanning your whole inner landscape from feet to head, back to front, and center to extremities, and letting your body breathe itself, as you notice what is alive in you now.
Inhale – Belly Radiates Outwards; Exhale – Belly Settles Inwards
“The belly is an extraordinary diagnostic instrument. It displays the armoring of the heart as a tension in the belly. Trying tightens the belly. Trying stimulates judgment. Hard belly is often judging belly. Observing the relative openness or closedness of the belly gives insight into when and how we are holding (on) to our pain. The deeper our relationship to the belly, the sooner we discover if we are holding in the mind or opening into the heart.” – Steven Levine (1991)
The contact of your hands on your belly helps the mind pay attention to the subtle movement created by the inhale-exhale cycle of the diaphragm. The combination of tactility and interoceptive awareness focusing on the belly shifts attention into our “second brain” (the enteric nervous system) and signals the mind it can rest and soften. More pleasurable sensation is often accompanied by an emergent feeling of safety as you settle into sensing the rhythm of a slower, more even breath, creating a feedback loop between bodily/somatic ease and mental calm. Giving yourself some daily “breathing room” in this way can help you build the calm muscle!
Naturally, there can be hiccups along the way so it is not all unicorns and rainbows! By giving the mind bodily tasks to accomplish, particularly in relationship to deepening and expanding the movement of the breath, we ease the self into a slower, more receptive state of being. Yet, in this receptive state of ease, whatever is in the background of awareness can arise and slip through the “border control”, sometimes taking us by surprise and causing distress. Depending upon the nature of the information, there are layers of action strategies that can be progressively taken to modulate and buffer what arises:
Tether your awareness to the breath rhythm with hands on your belly to stay present as a witness. Next step up: open your eyes softly and look around to orient in your present environment. Further step up: breath flow, hands-on belly, eyes open a wee bit looking around, and adding simple movement, like rocking a bit in all directions or expressing an exhale as a sigh, a yawn or a hum.
Note: If you find your personal resources are insufficient, find a guide to work with one-on-one to discover your own individual path for increasing the “window of capacity”. Above all, be gentle with yourself – take your time – cultivate your garden – and enjoy your breath!
References
Epstein, M. (2013) Thoughts without a Thinker: Psychotherapy from a Buddhist Perspective. New York: Basic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Thoughts-Without-Thinker-Psychotherapy-Perspective/dp/0465050948
Levine, S. (1991). Guided Meditations, Explorations and Healings. New York: Anchor. https://www.amazon.com/Guided-Meditations-Explorations-Healings-Stephen/dp/0385417373
Luthe, W. (1969). Autogenic Therapy Volume 1 Autogenic Methods. New York: Grune and Stratton. https://www.amazon.com/Autogenic-Therapy-1-Methods/dp/B0013457B4/
Luthe, W. (1979). About the Methods of Autogenic Therapy. In: Peper, E., Ancoli, S., Quinn, M. (eds). Mind/Body Integration. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2898-8_12
Luthe, W. & de Rivera, L. (2015). Wolfgang Luthe Introductory workshop: Introduction to the Methods of Autogenic Training, Therapy and Psychotherapy (Autogenic Training & Psychotherapy). CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. https://www.amazon.com/WOLFGANG-LUTHE-INTRODUCTORY-WORKSHOP-Psychotherapy/dp/1506008038/
Quick Rescue Techniques When Stressed
Posted: February 4, 2024 Filed under: attention, behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, CBT, cognitive behavior therapy, education, emotions, Evolutionary perspective, Exercise/movement, health, mindfulness, Neck and shoulder discomfort, posture, relaxation, stress management, Uncategorized | Tags: alarm reaction, anxiety, box breathing, Breathing, conditioning, defense reaction, health, huming, Parasympathetic response, rumination, safety, sniff inhale, somatic practices, stress, sympathetic arousal, tactical breathing, Toning, yoga 9 CommentsErik Peper, PhD, Yuval Oded, PhD, and Richard Harvey, PhD
Adapted from Peper, E., Oded, Y, & Harvey, R. (2024). Quick somatic rescue techniques when stressed. Biofeedback, 52(1), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.5298/982312 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380481426

“If a problem is fixable, if a situation is such that you can do something about it, then there is no need to worry. If it’s not fixable, then there is no help in worrying. There is no benefit in worrying whatsoever.” ― Dalai Lama XIV
To implement the Dalai Lama’s quote is challenging. When caught up in an argument, being angry, extremely frustrated, or totally stressed, it is easy to ruminate, worry. It is much more challenging to remember to stay calm. When remembering the message of the Dalai Lama’s quote, it may be possible to shift perspective about the situation although a mindful attitude may not stop ruminating thoughts. The body typically continues to reacti to the torrents of thoughts that may occur when rehashing rage over injustices, fear over physical or psychological threats, or profound grief and sadness over the loss of a family member. Some people become even more agitated and less rational as illustrated in the following examples.
I had an argument with my ex and I am still pissed off. Each time I think of him or anticipate seeing them, my whole body tightened. I cannot stomach seeing him and I already see the anger in his face and voice. My thoughts kept rehashing the conflict and I am getting more and more upset.
A car cut right in front of me to squeeze into my lane. I had to slam on my brakes. What an idiot! My heart rate was racing and I wanted to punch the driver.
When threatened, we respond quickly in our thoughts and body with a defense reaction that may negatively affect those around us as well as ourselves. What can we do to interrupt negative stress reactions?
Background
Many approaches exist that allow us to become calmer and less reactive. General categories include techniques of cognitive reappraisal (seeing the situation from the other person’s point of view and labeling your own feelings and emotions) and stress management techniques. Practices that are beneficial include mindfulness meditation, benign humor (versus gallows humor), listening to music, taking a time out while implementing a variety of self-soothing practices, or incorporating slow breathing (e.g., heart rate variability and/or box breathing) throughout the day.
No technique fits all as we respond differently to our stressful life circumstances. For example, some people during stress react with a “tend and befriend stress response” (Cohen & Lansing, 2021; Taylor et al., 2000). This response appears to be mostly mediated by the hormone oxytocin acting in ways that sooth or calm the nervous system as an analgesic. These neurophysiological mechanisms of the soothing with the calming analgesic effects of oxytocin have been characterized in detail by Xin, et al. (2017).
The most common response is a fight/flight/freeze stress response that is mediated by excitatory hormones such as adrenalin and inhibitory neurotransmitters such as gamma amino butyric acid (GABA). There is a long history of fight/flight/freeze stress response research, which is beyond the scope of this blog with major theories and terms such as interior milleau (Bernard, 1872); homeostasis and fight/flight (Cannon, 1929); general adaptation syndrome (Selye, 1951); polyvagal theory (Porges, 1995); and, allostatic load (McEwen, 1998). A simplified way to start a discussion about stress reactions begins with the fight/flight stress response. When stressed our defense reactions are triggered. Our sympathetic nervous system becomes activated our mind and body stereotypically responds as illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1. An intense confrontation tends to evoke a stress response (reproduced from Peper et al., 2020).
The flight/fight response triggers a cascade of stress hormones or neurotransmitters (e.g., hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal cascade) and produces body changes such as the heart pounding, quicker breathing, an increase in muscle tension and sweating. Our body mobilizes itself to protect itself from danger. Our focus is on immediate survival and not what will occur in the future (Porges, 2021; Sapolsky, 2004). It is as if we are facing an angry lion—a life-threatening situation—and we feel threatened and unsafe.
Rather than sitting still, a quick effective strategy is to interrupt this fight/flight response process by completing the alarm reaction such as by moving our muscles (e.g., simulating a fight or flight behavior) before continuing with slower breathing or other self-soothing strategies. Many people have experienced their body tension is reduced and they feel calmer when they do vigorous exercise after being upset, frustrated or angry. Similarly, athletes often have reported that they experience reduced frequency and/or intensity of negative thoughts after an exhausting workout (Thayer, 2003; Liao et al., 2015; Basso & Suzuki, 2017).
Becoming aware of the escalating cascades of physical, behavioral and psychological responses to a stressor is the first step in interrupting the escalating process. After becoming aware, reduce the body’s arousal and change the though patterns using any of the techniques described in this blog. The self-regulation skills presented in this blog are ideally over-learned and automated so that these skills can be rapidly implemented to shift from being stressed to being calm. Examples of skills that can shift from sympathetic neervous system overarousal to parasympathetic nervous system calm include techniques of autogenic traing (Schulz & Luthe, 1959), the quieting reflex developed by Charles Stroebel in 1985 or more recently rescue breathing developed by Richard Gevirtz (Stroebel, 1985; Gevirtz, 2014; Peper, Gibney & Holt, 2002; Peper & Gibney, 2003).
Concepts underlying the rescue techniques
- Psychophysiological principle: “Every change in the physiological state is accompanied by an appropriate change in the mental-emotional state, conscious or unconscious, and conversely, every change in the mental-emotional state, conscious or unconscious, is accompanied by an appropriate change in the physiological state” (Green et al. 1970, p. 3).
- Posture evokes memories and feelings associated with the position. When the body posture is erect and tall while looking slightly up. It is easier to evoke empowering, positive thoughts and feelings. When looking down it is easier to evoke hopeless, helpless and powerless thoughts and feelings (Peper et al., 2017).
- Healing occurs more easily when relaxed and feeling safe. Feeling safe and nurtured enhances the parasympathetic state and reduces the sympathetic state. Use memory recall to evoke those experiences when you felt safe (Peper, 2021).
- Interrupting thoughts is easier with somatic movement than by redirecting attention and thinking of something else without somatic movement.
- Focus on what you want to do not want to do. Attempting to stop thinking or ruminating about something tends to keeps it present (e.g., do not think of pink elephants. What color is the elephant? When you answer, “not pink,” you are still thinking pink). A general concept is to direct your attention (or have others guide you) to something else (Hilt & Pollak, 2012; Oded, 2018; Seo, 2023).
- Skill mastery takes practice and role rehearsal (Lally et al., 2010; Peper & Wilson, 2021).
- Use classical conditioning concepts to facilitate shifting states. Practice the skills and associate them with an aroma, memory, sounds or touch cues. Then when you the situation occurs, use these classical conditioned cues to facilitate the regeneration response (Peper & Wilson, 2021).
Rescue techniques
Coping When Highly Stressed and Agitated
- Complete the alarm/defense reaction with physical activity (Be careful when you do these physical exercises if you have back, hip, knee, or ankle problems).
- Acknowledge you have reacted and have chosen to interrupt your automatic response.
- Check whether the situation is actually a threat. If yes, then do anything to get out of immediate danger (yell, scream, fight, run away, or dial 911).
- If there is no actual physical threat, then leave the situation and perform vigorous physical activity to complete your alarm reaction, such as going for a run or walking quickly up and down stairs. As you do the exercise, push yourself so that the muscles in your thighs are aching, which focusses your attention on the sensations in your thighs. In our experience, an intensive run for 20 minutes quiets the brain while it often takes 40 minutes when walking somewhat quickly.
- After recovering from the exhaustive exercise, explore new options to resolve the conflict.
- Complete the alarm/defense reaction and evoke calmness with the S.O.S™ technique (Oded, 2023)
- Acknowledge you have reacted and have chosen to interrupt your automatic response.
- Squat against a wall (similar to the wall-sit many skiers practice). While tensing your arms and fists as shown in Figure 2, gaze upward because it is more difficult to engage in negative thinking while looking upwards. If you continue to ruminate, then scan the room for object of a certain color or feature to shift visual attention and be totally present on the visual object.
- Do this set of movements for 7 to 10 seconds or until you start shaking. Than stand up and relax hands and legs. While standing, bounce up and down loosely for 10 to 15 seconds as you become aware of the vibratory sensations in your arms and shoulders, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 2.Defense position wall-sit to tighten muscles in the protective defense posture (Oded, 2023). Figure 3. Bouncing up and down to loosen muscles ((Oded, 2023).
- Acknowledge you have reacted and have chosen to interrupt your automatic response. Swing your arms back and forth for 20 seconds. Allow the arms to swing freely as illustrated in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Swinging the arms to loosen the body and spine (Oded, 2023).
- Rest and ground. Lie on the floor and put your calves and feet on a chair seat so that the psoas muscle can relax, as illustrated in Figure 5. Allow yourself to be totally supported by the floor and chair. Be sure there is a small pillow under your head and put your hand on your abdomen so that you can focus on abdominal breathing.

Figure 5. Lying down to allow the psoas muscle to relax and feel grounded (Oded, 2023).
- While lying down, imagine a safe place or memory and make it as real as possible. It is often helpful to listen to a guided imagery or music. The experience can be enhanced if cues are present that are associated with the safe place, such as pictures, sounds, or smells. Continue to breathe effortlessly at about six breaths per minute. If your attention wanders, bring it back to the memory or to the breathing. Allow yourself to rest for 10 minutes.
In most cases, thoughts stop and the body’s parasympathetic activity becomes dominant as the person feels safe and calm. Usually, the hands warm and the blood volume pulse amplitude increases as an indicator of feeling safe, as shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6. Blood volume pulse increases as the person is relaxing, feels safe and calm.
Coping When You Can’t Get Away (adapted from Peper, Harvey & Faass, 2020)
In many cases, it is difficult or embarrassing to remove yourself from the situation when you are stressed out such as at work, in a business meeting or social gathering.
- Become aware that you have reacted.
- Excuse yourself for a moment and go to a private space, such as a restroom. Going to the bathroom is one of the only acceptable social behaviors to leave a meeting for a short time.
- In the bathroom stall, do the 5-minute Nyingma exercise, which was taught by Tarthang Tulku Rinpoche in the tradition of Tibetan Buddhism, as a strategy for thought stopping (see Figure 7). Stand on your toes with your heels touching each other. Lift your heels off the floor while bending your knees. Place your hands at your sides and look upward. Breathe slowly and deeply (e.g., belly breathing at six breaths a minute) and imagine the air circulating through your legs and arms. Do this slow breathing and visualization next to a wall so you can steady yourself if necessary to keep balance. Stay in this position for 5 minutes or longer. Do not straighten your legs—keep squatting despite the discomfort. In a very short time, your attention is captured by the burning sensation in your thighs. Continue. After 5 minutes, stop and shake your arms and legs.

Figure 7. Stressor squat Nyingma exercise (reproduced from Peper et al., 2020).
- Follow this practice with slow abdominal breathing to enhance the parasympathetic response. Be sure that the abdomen expands as the inhalation occurs. Breathe in and out through the nose at about six breaths per minute.
- Once you feel centered and peaceful, return to the room.
- After this exercise, your racing thoughts most likely will have stopped and you will be able to continue your day with greater calm.
What to do When Ruminating, Agitated, Anxious or Depressed
(adapted from Peper, Harvey, & Hamiel, 2019).
- Shift your position by sitting or standing erect in a power position with the back of the head reaching upward to the ceiling while slightly gazing upward. Then sniff quickly through nose, hold and again sniff quickly then very slowly exhale. Be sure as you exhale your abdomen constricts. Then sniff again as your abdomen gets bigger, hold, and sniff one more time letting the abdomen get even bigger. Then, very slow, exhale through the nose to the internal count of six (adapted from Balban et al., 2023). When you sniff or gasp, your racing thoughts will stop (Peper et al., 2016).
- Continue with box breathing (sometimes described as tactical breathing or battle breathing) by exhaling slowly through your nose for 4 seconds, holding your breath for 4 seconds, inhaling slowly for 4 seconds through your nose, holding your breath for 4 seconds and then repeating this cycle of breathing for a few minutes (Röttger et al., 2021; Balban et al., 2023). Focusing your attention on performing the box breathing makes it almost impossible to think of anything else. After a few minutes, follow this with slow effortless diaphragmatic breathing at about six breaths per minute. While exhaling slowly through your nose, look up and when you inhale imagine the air coming from above you. Then as you exhale, imagine and feel the air flowing down and through your arms and legs and out the hands and feet.
- While gazing upward, elicit a positive memory or a time when you felt safe, powerful, strong and/or grounded. Make the positive memory as real as possible.
- Implement cognitive strategies such as reframing the issue, sending goodwill to the person, seeing the problem from the other person’s point of view, and ask is this problem worth dying over (Peper, Harvey, & Hamiel, 2019).
What to Do When Thoughts Keep Interrupting
Practice humming or toning. When you are humming or toning, your focus is on making the sound and the thoughts tend to stop. Generally, breathing will slow down to about six breaths per minute (Peper, Pollack et al., 2019). Explore the following:
- Box breathing (Röttger et al., 2021; Balban et al., 2023)
- Humming also known as bee breath (Bhramari Pranayama) (Abishek et al., 2019; Yoga, 2023) – Allow the tongue to rest against the upper palate, sit tall and erect so that the back of the head is reaching upward to the ceiling, and inhale through your nose as the abdomen expands. Then begin humming while the air flows out through your nose, feel the vibration in the nose, face and throat. Let humming last for about 7 seconds and then allow the air to blow in through the nose and then hum again. Continue for about 5 minutes.
- Toning – Inhale through your nose and then vocalize a single sound such as Om. As you vocalize the lower sound, feel the vibration in your throat, chest and even going down to the abdomen. Let each toning exhalation last for about 6 to 7 seconds and then inhale through your nose. Continue for about 5 minutes (Peper, al., 2019).
Many people report that after practice these skills, they become aware that they are reacting and are able to reduce their automatic reaction. As a result, they experience a significant decrease in their stress levels, fewer symptoms such as neck and holder tension and high blood pressure, and they feel an increase in tranquility and the ability to communicate effectively.
Practicing these skills does not resolve the conflicts; they allow you to stop reacting automatically. This process allows you a time out and may give you the ability to be calmer, which allows you to think more clearly. When calmer, problem solving is usually more successful. As phrased in a popular meme, “You cannot see your reflection in boiling water. Similarly, you cannot see the truth in a state of anger. When the waters calm, clarity comes” (author unknown).

Boiling water (photo modified from: https://www.facebook.com/photo/?fbid=388991500314839&set=a.377199901493999)
Below are additional resources that describe the practices. Please share these resources with friends, family and co-workers.
Stressor squat instructions
Toning instructions
Diaphragmatic breathing instructions
Reduce stress with posture and breathing
Conditioning
References
Abishek, K., Bakshi, S. S., & Bhavanani, A. B. (2019). The efficacy of yogic breathing exercise bhramari pranayama in relieving symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Yoga, 12(2), 120–123. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijoy.IJOY_32_18
Balban, M. Y., Neri, E., Kogon, M. M., Weed, L., Nouriani, B., Jo, B., Holl, G., Zeitzer, J. M., Spiegel, D., Huberman, A. D. (2023). Brief structured respiration practices enhance mood and reduce physiological arousal. Cell Reports Medicine, 4(1), 10089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100895
Basso, J. C. & Suzuki, W. A. (2017). The effects of acute exercise on mood, cognition, neurophysiology, and neurochemical pathways: A review. Brain Plast, 2(2), 127–152. https://doi.org/10.3233/BPL-160040
Bernard, C. (1872). De la physiologie générale. Paris: Hachette livre. https://www.amazon.ca/PHYSIOLOGIE-GENERALE-BERNARD-C/dp/2012178596
Cannon, W. B. (1929). Organization for Physiological Homeostasis. Physiological Reviews, 9, 399–431. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1929.9.3.399
Cohen, L. & Lansing, A. H. (2021). The tend and befriend theory of stress: Understanding the biological, evolutionary, and psychosocial aspects of the female stress response. In: Hazlett-Stevens, H. (eds), Biopsychosocial Factors of Stress, and Mindfulness for Stress Reduction. pp. 67–81, Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81245-4_3
Gevirtz, R. (2014). HRV Training and its Importance – Richard Gevirtz, Ph.D., Pioneer in HRV Research & Training. Thought Technology. Accessed December 29, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9nwFUKuJSE0
Green, E. E., Green, A. M., & Walters, E. D. (1970). Voluntary control of internal states: Psychological and physiological. Journal of Transpersonal Psychology, 2, 1–26. https://atpweb.org/jtparchive/trps-02-70-01-001.pdf
Hilt, L. M., & Pollak, S. D. (2012). Getting out of rumination: comparison of three brief interventions in a sample of youth. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(7), 1157–1165.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9638-3
Lally, P., VanJaarsveld, C. H., Potts, H. W., & Wardle, J. (2010). How habits are formed: Modelling habit formation the real world. European Journal of Social Psychology, 40, 998–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.674
Liao, Y., Shonkoff, E. T., & Dunton, G. F. (2015). The acute relationships between affect, physical feeling states, and physical activity in daily life: A review of current evidence. Frontiers in Psychology. 6, 1975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01975
McEwen, B. S. (1998). Stress, adaptation, and disease: Allostasis and allostatic load. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 840(1), 33–44.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09546.x
Oded, Y. (2018). Integrating mindfulness and biofeedback in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Biofeedback, 46(2), 37-47. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-46.02.03
Oded, Y. (2023). Personal communication. S.O.S 1™ technique is part of the Sense Of Safety™ method. www.senseofsafety.co
Peper, E. (2021). Relive memory to create healing imagery. Somatics, XVIII(4), 32–35.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369114535_Relive_memory_to_create_healing_imagery
Peper, E., Gibney, K.H. & Holt. C. (2002). Make Health Happen: Training Yourself to Create Wellness. Dubuque, IA: Kendall-Hunt. https://he.kendallhunt.com/product/make-health-happen-training-yourself-create-wellness
Peper, E., & Gibney, K.H. (2003). A teaching strategy for successful hand warming. Somatics. XIV(1), 26–30. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/376954376_A_teaching_strategy_for_successful_hand_warming
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Faass, N. (2020). TechStress: How Technology is Hijacking Our Lives, Strategies for Coping, and Pragmatic Ergonomics. North Atlantic Books. https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Ergonomics-Prevent-Fatigue-Burnout/dp/158394768X
Peper, E., Harvey, R., & Hamiel, D. (2019). Transforming thoughts with postural awareness to increase therapeutic and teaching efficacy. NeuroRegulation, 6(3),153–160. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.6.3.153
Peper, E., Lee, S., Harvey, R., & Lin, I-M. (2016). Breathing and math performance: Implication for performance and neurotherapy. NeuroRegulation, 3(4), 142–149. http://dx.doi.org/10.15540/nr.3.4.142
Peper, E., Lin, I-M, Harvey, R., & Perez, J. (2017). How posture affects memory recall and mood. Biofeedback, 45(2), 36–41. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-45.2.01
Peper, E., Pollack, W., Harvey, R., Yoshino, A., Daubenmier, J. & Anziani, M. (2019). Which quiets the mind more quickly and increases HRV: Toning or mindfulness? NeuroRegulation, 6(3), 128–133. https://www.neuroregulation.org/article/view/19345/13263
Peper, E. & Wilson, V. (2021). Optimize the learning state: Techniques and habits. Biofeedback, 9(2), 46–49. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-49-2-04
Porges, S. W. (1995). Orienting in a defensive world: Mammalian modifications of our evolutionary heritage. A polyvagal theory. Psychophysiology, 32(4), 301–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.1995.tb01213.x
Porges, S.W. (2021) Cardiac vagal tone: a neurophysiological mechanism that evolved in mammals to dampen threat reactions and promote sociality. World Psychiatry, 20(2),296-298. Porges SW. Cardiac vagal tone: a neurophysiological mechanism that evolved in mammals to dampen threat reactions and promote sociality. World Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;20(2):296-298. https://doi.org10.1002/wps.20871
Röttger, S., Theobald, D. A., Abendroth, J., & Jacobsen, T. (2021). The effectiveness of combat tactical breathing as compared with prolonged exhalation. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 46, 19–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-020-09485-w
Sapolsky, R. (2004). Why zebras don’t get ulcers (3rd ed.). New York:Holt. https://www.amazon.com/Why-Zebras-Dont-Ulcers-Third/dp/0805073698/
Schultz, J. H., & Luthe, W. (1959). Autogenic training: A psychophysiologic approach to psychotherapy. Grune & Stratton. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Autogenic_Training/y8SwQgAACAAJ?hl=en
Selye, H. (1951). The general-adaptation-syndrome. Annual Review of Medicine, 2(1), 327–342. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.me.02.020151.001551
Seo, H. (2023). How to stop ruminating. The New York Times. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/02/01/well/mind/stop-rumination-worry.html
Stroebel, C. F. (1985). QR: The Quieting Reflex. Berkley. https://www.amazon.com/Qr-quieting-reflex-Charles-Stroebel/dp/0425085066
Taylor, S. E., Klein, L. C., Lewis, B. P., Gruenewald, T. L., Gurung, R. A. R., & Updegraff, J. A. (2000). Biobehavioral responses to stress in females: Tend-and-befriend, not fight-or-flight. Psychological Review, 107(3), 411–429. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.107.3.411
Thayer, R. E. (2003). Calm energy: How people regulate mood with food and exercise. Oxford University Press. https://www.amazon.com/Calm-Energy-People-Regulate-Exercise/dp/0195163397
Xin, Q., Bai, B., & Liu, W. (2017). The analgesic effects of oxytocin in the peripheral and central nervous system. Neurochemistry International, 103, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.12.021
Yoga, N. (2023). This simple breath practice is scientifically proven to calm your mind. The nomadic yogi. Accessed December 31, 2023. https://www.leahsugerman.com/blog/bhramari-pranayama-humming-bee-breath#
Healing a Shoulder/Chest Injury
Posted: August 14, 2023 Filed under: behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, emotions, Exercise/movement, healing, Neck and shoulder discomfort, Pain/discomfort, relaxation, self-healing, Uncategorized | Tags: electromyograph, guided imagery, shoulder pain Leave a commentAdapted from Peper, E. & Fuhs, M. (2004). Applied psychophysiology for therapeutic use: Healing a shoulder injury, Biofeedback, 32(2), 11-18.

“It has been an occurrence of the third dimension for me! How come my pain — that lasted for more than 10 days and was still so strong that I really had difficulties in breathing, couldn’t laugh without pain nor move my arm not even to fulfil my daily routines such as dressing and eating — disappeared within one single session of 20 minutes? And not only that, I was able to freely rotate my arm as if it had never been injured before.” —23 year old woman
The participant T., aged 23, was a psychology student who participated in an educational workshop for Healthy Computing. She volunteered to be a subject for a surface electromyographic (SEMG) monitoring and feedback demonstration. Ten days prior to this workshop, she had a severe skiing accident. She described the accident as follows:
I went skiing and may be I had too much snow in my ski-binding and while turning, I slipped out of my binding and fell head first down into the hill. As I fell, I landed on my ski pole which hit my left upper chest and breast area. Afterwards, my head was humming and I assumed that I had a light concussion. I stopped skiing and stayed in bed for a while. The next day it started hurting and I couldn’t turn my head or put my shoulders back (they were rotated forward). Also, I couldn’t ski as I was not able to look down to my feet–my muscles were too contracted and I felt searing pain whenever I moved. I hoped that it would go away however, the pain and left forward shoulder rotation stayed.
Assessment
Observation and Palpation
T.´s left shoulder was rolled forward (adducted and in internal rotation). She was not able to breathe or laugh without pain or move her arm freely. All movements in vertical and horizontal directions and rotations were restricted by at least 50 % as compared to her right arm (limitations in shoulder extension, flexion and external rotation). Also, her hands were ice-cold and she breathed very shallowly and rapidly in her chest. She was not able to stand in an upright position or sit in a comfortable position without maintaining her left upper extremity in a protected position. Her left shoulder blade (scapula) was winging.
After visually observing her, the instructor placed his left hand on her left shoulder and pectoralis muscles and his right hand on the back of her shoulder. Using palpation and anchoring her back with his leg so that she could not rotate her trunk, he explored the existing range of shoulder movement. He also attempted to rotate the left shoulder outward and back–not by forcing or pulling—but by very gentle traction. No change in mobility was observed and the pectoralis muscle felt tight (SEMG monitoring is helpful to the therapist during such a diagnostic assessment by helping to identify the person’s reactivity and avoiding to evoke and condition even more bracing). T. reported afterwards that she was very scared by this assessment because there was one point in the back which was highly reactive to touch. T. appeared to tighten automatically out of fear and trigger a general flexor contraction pattern—a process that commonly occurs if a person is guarding an area.
Often a traumatic injury first induces a general shock that triggers an automatic freeze and fear reaction. Therefore, an intervention needed to be developed that did not trigger vigilance or fear and thereby allowed the muscle to relax. If pain is experienced or increased, it is another negative reinforcement for generalizing guarding and bracing and tightening the muscles. This guarding decreases mobility – a common reaction that may occur when health professionals in the process of assessment increase the client’s discomfort. T.’s vigilance was also “telegraphed” to the therapist by her ice-cold hands and very shallow chest breathing. Therefore, it was important to increase her comfort level and to not induce any further pain. We hypothesized that only if she felt safe it would be possible for her muscle tension to decrease and thereby increase her mobility.
Underlying concept: The very cold hands and shallow breathing probably indicated excessive vigilance and arousal—a possible indicator of a catabolic state that could limit regeneration. The chronic cold hands most likely implied that she was very sensitive to other people’s emotions and continuously searches/scans the environment for threats. In addition, she indicated that she liked to do/perform her best which induced more anxiety and fear of judgement.
Single Channel Surface Electromyographic (SEMG)Assessment
The triode electrode with sensor was placed over the left pectoralis muscle area as shown in Figure 1. The equipment was a MyoTrac™ produced by Thought Technology Ltd. which is a small portable SEMG with the preamplifiers at the triode sensor to eliminate electrode lead and movement artefacts (Peper & Gibney, 2006). Such a device is an inexpensive option for people who may use biofeedback for demonstrating and teaching awareness and control over muscle tension from a single electrode location.

Figure 1. Location of the Triode electrode placement on the left pectoralis muscle area of another participant.
The MyoTrac was placed on a table within view, so that the therapist and the subject could simultaneously see the visual feedback signal and observe what was going on as well as demonstrate expected changes. The feedback was used for T. as a tool to see if she could reduce her SEMG activity. It was also used by the therapist to guide his interventions: To keep the SEMG activity low and to stop any intervention that would increase the SEMG activity as this would prevent bracing as a possible reaction to, or anticipation of, pain.
1. Assessment of Muscle Reactivity. After the electrode was attached on her pectoralis muscle and with her arm resting on her lap, she was asked to roll her left shoulder slightly more forward, hold the tension for the count of 10 and then let go and relax. Even with feedback, the muscle activity stayed high and did not relax and return to a lower level of activity as shown in Figure 2. This lack of return to baseline is often a diagnostic indicator of muscle irritability or injury (Sella, 1998; Sella, 2006). If the muscle does not relax immediately after contraction, movement or exercise should not be prescribed, since it may aggravate the injury. Instead, the person first needs to learn how to relax and then learn how to relax between activation and tensing of the muscle. The general observation of T. was that at the initiation of any movement (active or passive) muscle tension increased and did not return to baseline for more than two minutes.

Figure 2. Simulation of the effect on the pectoralis sEMG (this is a recording from another subject who showed a similar response pattern that was visually observed from T. with the Myotrac). After the muscle is contracted it takes a long time to return to baseline level
2. Exploration. Self-exploration with feedback was encouraged. T. was instructed to let go of muscle tension in her left shoulder girdle. In addition the therapist tried to induce her letting go by gently and passively rocking her left arm. The increased SEMG activity and the protective bracing in her shoulder showed that she couldn’t reduce the muscle tension. Each time her arm was moved, however slightly, she helped with the movement and kept control. In addition, T. was asked to reduce the muscle tension using the biofeedback signal; again she was not able to reduce her muscle tension with feedback.
3. Passive Stretch and Movements. The next step was to passively stretch the pectoralis muscle by holding the shoulder between both hands and very gently externally rotate the shoulder — a process derived from the Alexander technique (Barlow, 1991). Each time the instructor attempted to rotate her shoulder, the SEMG increased and T. reported an increased fear of pain. T.’s SEMG response most likely consisted of the following components:
- Movement induced pain
- Increased splinting and guarding
- Increased arousal/vigilance to perform well
These three assessment and self-regulation procedures were unsuccessful in reducing muscle tension or increasing shoulder movement. This suggested that another therapeutic intervention would need to be developed to allow the left pectoralis area to relax. The SEMG could be used as an indicator whether the intervention was successful as indicated by a reduction in SEMG activity. Finally, the inability to relax after tightening (bracing and splinting) probably aggravated her discomfort.
Multiple levels of injury: The obvious injury and discomfort was due to her left chest wall being hit by the ski pole. She then guarded the area by bracing the muscles to protect it which limited movement. The guarding tightened the muscles and limited blood circulation and lymphatic flow which increased local ischemia, irritation and pain. This led to a self-perpetuating cycle: Pain triggers guarding and guarding increases pain and impedes self-healing.
As the SEMG and passive stretching assessment were performed, the therapist concurrently discussed the pain process. Namely, from this perspective, there were at least two types of pains:
- Pain caused by the physiological injury
- Pain as the result of guarding
The pain from the guarding is similar to having exercised for a long time after not having exercised. The next day you feel sore. However, if you feel sore, you know that it was due to the exercise therefore it is defined as a good pain. In T.’s case, the pain indicated that something was wrong and did not heal and therefore she would need to protect it. We discussed this process as a way to use cognitive reframing to change her attitude toward guarding and pain.
Rationale: The intention was to interrupt her negative image of pain that acted as a post hypnotic suggestion. The objective was to change her image and thoughts from “pain indicates the muscle is damaged” to “pain indicates the muscle has worked too hard and long and needs time to regenerate.”
Treatment interventions
The initial intervention focused upon shifting shallow thoracic breathing to diaphragmatic breathing. Generally, when people breathe rapidly and predominantly in their chest, they usually tighten their neck and shoulder muscles during inhalation. One of the reasons T. breathed in her chest was that her clothing–very tight jeans–constricted her waist (MacHose & Peper, 1991; Peper et al., 2015). This breathing pattern probably contributed to sub-clinical hyperventilation and was part of a fear or flexor response pattern. When she loosened the upper buttons of her jeans and allowed her stomach to expand her pectoralis muscle relaxed as she breathed as shown in Figure 3. As she began to breathe in this pattern, each time she exhaled her pectoralis muscle tension decreased.

Figure 3. Illustration of the effect of loosening tight waist constriction (eliminating designer’s jean syndrome) on blood flow and pectoralis sEMG. Abdominal breathing became possible and finger temerature increased (this recording is from another subject whose physiological responses were similar to that was observed with the Myotrac from T.)
Following the demonstration that breathing significantly lowered her chest muscle tension, the discussion focussed on the importance of effortless diaphragmatic breathing for health and reduction of vigilance. Being awkward and uncomfortable at loosening her pants, she struggled with allowing her abdomen to expand and her pants to be looser because she thought that she looked much more attractive in tight clothing. Yet, she agreed that her boy friend would love her regardless whether she wore loose or tight clothing. To encourage an acceptance for wearing looser clothing and thereby permit diaphragmatic breathing during the day, an informal discussion focused on “designer jeans syndrome” (chest breathing induced by tight clothing) with humorous examples such as discussing the name of the room that is located on top of the stairs in the Victorian houses in San Francisco. It is called the fainting room–in the 19th century women who wore corsets and had to climb the stairs would have to breathe rapidly and then would faint when they reached the top of the stairs (Peper, 1990).
Rationale: Rapid shallow chest breathing can induce a catabolic state that inhibits healing while diaphragmatic breathing may induce an anabolic state that promotes regeneration. Moreover, effortless diaphragmatic breathing would increase respiratory sinus arhythmia (RSA)–heart rate variability linked to breathing– and thereby facilitate sympathetic-parasympathetic balance that would promote self-healing.
The discussion included the use of the YES set which meant asking a person questions in such a way that she/he answers the question with YES. When a person answers YES at least three times in a row rapport is often facilitated (Erikson, 1983, pp. 237-238). Questions were framed in such a way that the client would answer with YES. For example, if the therapist thought the person did not do their homework, a yes question could be framed as, “It must have been difficult to find time to do the homework this week?” In T.’s case, the therapist said, “I see, you would rather wear tight clothing than allow your shoulder to heal.” She answered, “Yes.” This was the expected answer, however, the question was framed in an intuitive guess on the therapist’s part. Nevertheless, the strategy would have been successful either way because if she had answered “No,” it would have broken the “Yes: set, but she would then be committed to change her clothing.
Throughout this discussion, the therapist placed his left hand on her abdomen over her belly button and overtly and covertly guided her breathing movement. As she exhaled, he pressed gently on her abdomen; as she inhaled he drew his hand away–as if her abdomen was like a balloon that inflated during inhalation and deflated during exhalation. To enhance learning diaphragmatic breathing and slower exhalation, the therapist covertly breathed at the same rhythm and gently exhaled as she exhaled while allowing the breathing movement to be mainly in his abdomen. In this process, learning occurred without demand for performance and she could imitate the breathing process that was covertly modelled by the therapist.
The Change
The central observation was that each time she tried to relax or do something, she would slight brace which increased her pectoralis SEMG activity. The chronic tension from guarding probably induced localized ischemia, inhibited lymphatic flow and drainage, and reduced blood circulation which would increase tissue irritation. Whenever the therapist began to move her arm, she would anticipate and try to help with the movement. Overall she was vigilant (also indicated by her very cold hands) and wanted to perform very well (a possible need for approval). Her muscle bracing and helping with movement was reframed as a combined activity that consisted of guarding to prevent further injury and as a compliment that she would like to perform well.
Labelling her activity as a “compliment” was part of a continuing YES set approach. The therapist was deliberately framing whatever happened as adaptive behaviour, with positive intent. Further, if one tries and does something with too much effort while being vigilant, the arousal would probably induce hand cooling. If the activity can be performed with passive attention, then increased blood flow and warmth may occur. The therapeutic challenge was how to reduce vigilance, perfectionism and guarding so that the muscles that were guarding the traumatized area would relax.
Therapeutic concept: If a direct approach does not work, an indirect approach needs to be employed. Through an indirect approach, the person experiences a change without trying to focus on doing or achieving it. Underlying this approach is the guideline: If something does not work, try it once more and then if it does not work, do something completely different. This is analogous to sexual arousal: If you demand from a male to have an erection: The more performance you demand the less likely will there be success. On the other hand, if you remove the demand for performance and allow the person to become interested and thereby feel an erotic experience an erection may occur without effort.
The shift to an indirect intervention was done through active somatic visualization. T. was encouraged to visualize and remember a positive image or memory from her past. She chose a memory of a time when she was in Paris with her grandmother. While T. visualized being with her grandmother, the therapist asked another older women participant to help and hold T’s right hand in a grandmother-like way as if she was her grandmother. The “grandmother” then moved T.’s hand in a playful way as if dancing with T.’s right arm. Through this kinesthetic experience, T. became more and more absorbed in her memory experience. At the same time, T´s left hand was being held and gently rocked by the therapist. During this gentle rocking, the SEMG activity decreased completely in her left pectoralis area. The therapist used the SEMG feedback to guide him in the gentle rocking motion of T.’s left arm and very slowly increased the range of her arm and shoulder motion. Gentle movement was done only as long as the SEMG activity did not increase. It allowed the muscle to stay relaxed and facilitated the experience of trust. The following is T. report two days later of what happened.
“Initially it was very difficult for me to let go of control because I found this idea somewhat strange and I was puzzled. I expected the therapist to intervene and I felt frightened. The therapist’s soft and gentle touch and his very soft voice in this kind of meditation helped me to let go of control and I was surprised about my own courage to give myself into the process without knowing what would happen next.”
Rationale: Every corresponding thought and emotion has an associated body response and every body response has an associated mental/emotional response (Green & Green, 1977; Green, 1999). Therefore, an image and experience of a happy and safe past memory will allow the body to evoke the same state and vigilance can be abated. The intensity of the experience is increased when multi-sensory cues are included such as actual handholding. The more senses are involved, the more the experience can become real. In addition, the tactile sensation of feeling the grandmother’s hand diverted her attention away from her shoulder into her hand and thereby reduced her active efforts of trying to relax the shoulder and pectoralis area. Doing something she did not expect to happen also helped her loose control – an implicit confusion approach.
SEMG feedback was used as the guide for controlling the movement. The therapist gently increased the range of the movements in abduction and external rotation directions while continuously rocking her arm until her injured arm was able to move unrestricted in full range of motion. The arm and shoulder relaxation and continuous subtle movement without evoking any SEMG activation facilitated blood flow and lymphatic drainage which probably reduced congestion. After a few minutes, the therapist gently dropped her arm on her lap. After her arm was resting on her lap, she reported that it felt very heavy and relaxed and that she didn’t feel any pain. However, she initially didn’t really realize that her mobility had increased dramatically.
Rationale: When previous movements that had been associated with pain are linked to an experience of pleasure, the movement is often easier. The conditioned muscle bracing patterns associated with anticipation of pain and/or concern for improvement/results are reduced.
Process to deepen and generalize the relaxation and breathing. She was asked to imagine breathing the air down and through her arms and legs–a strategy that she could then do at home with her boyfriend. We wanted to involve another person because it is often difficult to do homework practices without striving and concern for results and focussing on the area of discomfort. Her response to asking if her boyfriend would help was an automatic “naturally” (the continuation of the YES set). With her agreement, we role played how her boyfriend was to encourage diaphragmatic breathing. He was to gently stroke down her legs as she exhaled. She could then just focus on the sensations and allow the air to flow down her legs. Then, while she continued to breathe effortlessly, he would gently rock and move her arm.
To be sure that she knew how to give the instructions, the therapist role played her boyfriend and then asked her to rock his arm so that she would know how to teach her boy friend how to move her arm. The therapist sat on her left side, and, as she now held his right arm and gently rocked it with her left arm, the therapist gently moved backwards. This meant that she externally rotated her left arm and shoulder more and more. He moved in such a way that in the process of rocking his arm, she moved her “previously injured shoulder” in all directions (up, down, forward and backwards) and was unaware that she could move her arm and shoulder as she did not experience any discomfort. Afterwards, we shared our observations and she was asked to move her arm and shoulder. She moved it without any restrictions or discomfort.
Rationale: By focusing outside herself and not being concerned about herself, she did not think of herself or of trying to move her arm and shoulder. Hence, she did not evoke the anticipatory guarding and thus significantly increased her flexibility.
Process of acceptance. Often after an injury, we are frustrated with our bodies. This frustration may interfere with healing. Therefore, the session concluded by asking her to be appreciative of her shoulder and arm. She was asked to think of all the positive things her shoulder, chest and arm have done for her in the past instead of the many limitations and pains caused by the injury. Instead of being angry at her shoulder that it had not healed or restricted her movement, we suggested that she should appreciate her shoulder and pectoralis area for all it had done without her awareness such as: How the shoulder moved her arm during love-making, how without complaining her shoulder moved during walking, writing, skiing, eating, etc., and how many times in the past she had abused her shoulder without giving it proper respect and appreciation. This process reframes the way one symbolically relates to the injured area. Every thought of discomfort or negative judgement becomes the trigger and is transformed into breathing lower and slower and evokes an appreciation of the positive nice things her shoulder has done for her in the past.
Rationale: When injured we often evoke negative mental and emotional images which become post- hypnotic suggestions. Those negative thoughts, images and emotions interfere with healing while positive thoughts, images and emotions tend to promote healing. A possible energetic process that occurs when injured is that we withdraw awareness/ consciousness from the injured area which reduces blood and lymph circulation. Caring and positive feelings about an area tends to increase blood flow and warmth (a heart-warming experience) and promotes healing.
RESULTS
She left the initial session without any pain and with total range of motion. At the two week follow-up she reported continued pain relief and complete range of motion. T.s reflection of the experience was:
“I really was not aware that I could move my arm freely like before the accident, I was just feeling a kind of trance and was happy to not feel any pain and to feel much more upright than before. Then I watched the faces of the two other therapists who sat there with big eyes and a grin on their face and then become aware of my own arms position which was rotated backwards and up, a movement that was impossible to do before. I remember this evening that I left with this feeling of trance and that I often tried to go back to my collapsed posture but this was not possible anymore and I felt very tall and straight. Now two weeks later I still feel like that and know that I had an amazing experience which I will store in my brain!
My father who is an orthopedic surgeon tested me and found out, that I had hurt my rib. He said that I have a contusion and it will go away in a few weeks. Before this experience, I would say that he was not open to Biofeedback. However he was so captivated by my experiences that he spontaneously promised me to pay for my own biofeedback equipment and to support me with my educational program and even offered me a job in his practice to do this work!”
Psychophysiological Follow-up: 3 Weeks Later
The physiological assessment included monitoring thoracic and abdominal breathing patterns, blood volume pulse, heart rate and SEMG from her left pectoralis muscle while she was asked to roll her left shoulder forward (adducted and internally rotated) for the count of 10 and then relax. The physiological recording showed that she breathed more diaphragmatically and that her pectoralis muscle relaxed and returned directly to baseline after rotation as shown in Fig. 4.

Figure 4. Physiological profile during the rolling left shoulder forward (tense) and relaxing at thethree week follow-up. Note that the pectoralis sEMG activity returned rapidly to baseline after contracting and her breathing pattern is abdomninal and slower.
Summary
This case example demonstrates the usefulness of a simple one-channel SEMG biofeedback device to guide the interventions during assessment and treatment. It suggests that the therapist and client can use the SEMG activity as an indicator of guarding–a visual representation of the subjective experience of fear, pain and range of mobility–that can be evoked during assessment and therapeutic interventions. The anticipation of increased pain commonly occurs during diagnosis and treatment and often becomes an obstacle for healing because increased pain may increase anticipation of pain and trigger even more bracing. To avoid triggering this vicious circle of guarding/fear, the feedback signal allows the therapist and the client to explore strategies that reduce muscle activity by indirect interventions.
By using an indirect approach that the client may not expect, the interventions shift the focus of attention and striving and may allow increased freedom and relaxation. The biofeedback signal may guide the therapeutic process to reduce the patterns of fear, panic, and bracing that are commonly associated with injury and illnesses. Once this excessive sympathetic activity is reduced, the actual pathophysiology may become obvious (in most cases is much less then before) and the healing process may be accelerated. This case description may offer an approach in diagnosis and treatment for many therapists and open a door for a gentle, painless and yet successful way of treatment and encourage therapists to be creative and use both experience/technique and intuition.
For additional intervention approaches see the following two blogs.
References
Barlow, W. (1991). The Alexander technique: How to use your body without stress. Rochester, VT: Healing Arts Press https://www.amazon.com/Alexander-Technique-Your-without-Stress/dp/0892813857#:~:text=Barlow%2C%20the%20foremost%20exponent%20and,and%20movement%20in%20everyday%20activities.
Erikson, M. H. (1983). Healing in hypnosis, volume 1 (Edited by E. L. Rossi, M. O. Ryan, M. & F. A. Sharp). New York: Irvington Publishers, Inc.. https://www.amazon.com/Hypnosis-Seminars-Workshops-Lectures-Erickson/dp/0829007393/ref=sr_1_1?keywords=9780829007398&linkCode=qs&qid=1692038804&s=books&sr=1-1
Green, E. (1999). Psychophysical Principal. Accessed August 14, 2023 https://www.elmergreenfoundation.org/psychophysiological-principal/
Green, E., & Green, A. (1977). Beyond biofeedback. New York:
Delacorte Press/Seymour. https://elmergreenfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Beyond-Biofeedback-Green-Green-Searchable.pdf
MacHose, M., & Peper, E. (1991). The effect of clothing on inhalation volume. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation. 16(3), 261-265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000020
Peper, E. (1990). Breathing for health. Montreal: Thought Technology Ltd.
Peper, E. & Gibney, K.H. (2006). Muscle biofeedback at the computer-A manual to prevent repetitive strain injury (RSI) by taking the guesswwork out of assessment, monitoring and training. Biofeedback Foundation of Europe. https://thoughttechnology.com/muscle-biofeedback-at-the-computer-book-t2245/
Peper, E., Gilbert, C.D., Harvey, R. & Lin, I-M. (2015). Did you ask about abdominal surgery or injury? A learned disuse risk factor for breathing dysfunction. Biofeedback. 34(4), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.4.06
Sella, G. E. (2006). SEMG: Objective methodology in muscular dysfunction investigation and rehabilitation. Weiner’s pain management: A practical guide for clinicians, CRC Press, 645-662. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/b14253-45/semg-objective-methodology-muscular-dysfunction-investigation-rehabilitation-gabriel-sella
Sella, G. E. (1998). Towards an Integrated Approach of sEMG Utilization: Quantative Protocols of Assessment and Biofeedback. Electromyography: Applications in Physical Medicine. Thought Technology, 13. https://www.bfe.org/protocol/pro13eng.htm
[1] We thank Theresa Stockinger for her significant contribution and Candy Frobish for her helpful comments.
Healing from vulvodynia
Posted: May 4, 2023 Filed under: behavior, biofeedback, Breathing/respiration, emotions, healing, health, Pain/discomfort, relaxation, self-healing, Uncategorized | Tags: muscle tension, pelvic floor pain, therapeutic relationship, triggers for illness, vulvodynia 1 CommentPamela Jertberg and Erik Peper
Adapted from: Jertberg, P. & Peper, E. (2023). The healing of vulvodynia from the client’s perspective. Biofeedback, 51 (1), 18–21. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-51.01.02

This introspective report describes how a young woman who experienced a year-long struggle with vulvodynia, or vulvar vestibulitis, regained her health through biofeedback training and continues to be symptom-free 7 years after the intervention. This perspective may offer insight into factors that promote health and healing and provide an approach to reduce symptoms and promote health. The methodology of this case was described previously by Peper et al. (2015).
The Client’s Experience
I have been a healthy young woman my whole life. Growing up in a loving, dedicated family, I always ate home-cooked meals, went to bed at a reasonable time, and got plenty of exercise by playing with my family members and friends. I never once thought that at age 23 I might be at risk of undergoing vulvar surgery. There are many factors that contributed to the genesis of my vulvar pain, and many other factors that worsened this pain. Traditional medicine did not help me, and I did not find relief until I met my biofeedback practitioner, who taught me biofeedback. Through the many strategies I learned, such as visualization, diaphragmatic breathing techniques, diet tips, and skills to reframe my thoughts, I finally began to feel relief and hope. Practicing all these elements every day helped me overcome my physical pain and enjoy a normal life once again. Today, I do not have any vulvar discomfort. I am so grateful to my biofeedback practitioner for the many skills he taught me. I can enjoy my daily activities once again without experiencing pain. I have been given a second chance at loving life, and now I have learned the techniques that will help me sustain a more balanced path for the rest of my life. Seven years later, I am healthy and have no symptoms.
Triggers for Illness
Not Having a Positive Relationship with the Doctor
The first factor that aggravated my pain was having a doctor with whom I did not have a good relationship. Although the vulvar specialist I was referred to had treated hundreds of women with vulvar vestibulitis, his methods were very traditional: medicine, low oxalate diet, ointments, and surgery. Whenever I left his office, I would cry and feel like surgery was the only option. Vaginal surgery at 23 was one of the scariest and most unexpected thoughts my brain had ever considered. The doctor never thought of the impact that his words and treatment would have on my mental state.
Depression
Being depressed also triggered more pain. Whenever I would have feelings of hopelessness and create irrational beliefs in my mind (“I will never get better,” “I will never have sex again,” “I am not a woman anymore”), my physical pain would increase. Having depression only triggered more depression and pain, and this became a vicious cycle. The depression deeply affected my relationships with my boyfriend, friends, and family and my performance in my college classes.
Being Sedentary
Being sedentary and not exercising also increased my pain. At first, I believed that the mere act of sitting down hurt me due to the direct pressure on the area, but after a few months I came to realize that it was inactivity itself that triggered pain. Whenever I would sit for too long writing a paper or I would stay home all day because of my depression, my pain would increase, perhaps because I was inhibiting circulation. Still, when I am inactive most of the day, I feel lethargic and bloated. When I exercise, the pain goes away 100%. Exercise is almost magical.
Stress
Stress is the worst trigger for pain. Throughout my life, I always strived to be perfect in every way, meaning I was stressed about the way I looked, performed in school, drove, etc. Through the sessions with my biofeedback practitioner, I learned that my body was in a state of perpetual stress and tightness, which induced pain in certain areas. My body’s way of releasing such tension was to send pain signals to my vulvar area, perhaps because of a yeast infection a couple of months back. Still, if I become very stressed, I will feel pain or tightness in certain parts of my body, but now I have strategies for performing proper stress-relieving techniques.
Processed Foods
Junk food affects me instantly. When I eat processed foods for a week straight, I feel groggy, bloated, lethargic, and in pain. Processed sugar, white flour, and salt are a few of the foods that make the pain increase. I used to love sugar, so I would enjoy the occasional milkshake and cheeseburger and feel mostly okay. However, in times of stress it became crucial for me to learn to refrain from any junk food, because it would worsen my vulvar pain and increase my overall stress levels.
Menstruation
Menstruation is unavoidable, and unfortunately it would always worsen my vulvar pain. Right about the time of my period, my sensitivity and pain would massively increase. Sometimes as my pain would increase incredibly, I would question myself: “What am I doing wrong?” Then, I would remember: “Oh yes, I am getting my period in a few days.” The whole area became very sensitive and would get irritated easily. It became imperative to listen to my body and nurture myself especially around that time of the month.
Triggers for Healing
A Good Doctor
Just as I learned which factors triggered the pain, I also learned how to reduce it. The most important factor that helped me find true relief was meeting a good health professional (which could be a healer, nurse, or professor). The first time I met my biofeedback practitioner and told him about my issues, he really listened, gave me positive feedback, and even made jokes with me. To this day we still have a friendship, which has really aided me in getting better. In contrast to the vulvar specialist, I would leave the biofeedback practitioner’s office feeling powerful, able to defeat vulvodynia, and truly happy. Just having this support from a professional (or a friend, boyfriend, or relative) can make all the difference in the world. I don’t know where I would be right now if I hadn’t worked with him.
Positive Thoughts and Beliefs
Along with having a good support group, having positive thoughts and believing in a positive result helped me greatly. When I actually set my mind to feel “happy” and to believe that I was getting better, I began to really heal. After months of being depressed and feeling incomplete, when I began to practice mantras such as “I am healing,” “I am healthy,” and “I am happy,” my pain began to go away, and I was able to reclaim my life.
Journaling
One of the ways in which “happiness” became easier to achieve was to journal every day. I would write everything: from my secrets to what I ate, my pain levels, my goals for the day, and my symptoms. Writing down everything and knowing that no one would ever read it but me gave me relief, and my journal became my confidante. I still journal every day, and if I forget to write, the next day I will write twice as much. Now that writing has become a habit and a hobby, it is hard to imagine my life without that level of introspection.
Meditation
Although I would do yoga often, I would never sit and meditate. I began to use Dr. Peper’s guided meditations and Dr. Kabat-Zinn’s CD (Kabat-Zinn, 2006; Peper et al., 2002). The combination of these meditation techniques, whether on different days or on the same day, helped me focus on my breathing and relax my muscles and mind. Today, I meditate at least 20 min each day, and I feel that it helps me see life through a more willing and patient perspective. In addition, through meditation and deep breathing I have learned to control my pain levels, concentration, and awareness.
Imagery and Visualization
Imagery is a powerful tool that allowed me to heal faster. My biofeedback practitioner instructed me to visualize how I wanted to feel and look. In addition, he suggested that I draw and color how I was feeling at any given moment, my imagined healing process, and how I would look and feel after the healing process had traveled throughout my body (Peper et al., 2022). It is still amazing to me how much imagery helped me. Even visualizing here and there throughout the day helped. Now I envision how I want to feel as a healthy woman, I take a deep breath, and as a I breathe out I let my imagined healing process go through my body into all my tight areas along with the exhalation.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is the single strategy that helped me the most. During my first session with my biofeedback practitioner, he pointed out that my muscles were always contracted and stressed and that I was not breathing diaphragmatically. As I learned how to take deep belly breaths, I began to feel the tight areas in my body loosen up. I started to practice controlled breathing 20 min every day. Through biofeedback, my body and muscles became more relaxed, promoting circulation and ultimately reducing the vulvar pain.
Regular Exercise and Yoga
Exercising daily decreased my pain and improved the quality of my life greatly. When I first started experiencing significant vulvar pain, I stopped exercising because I felt that movement would aggravate the pain. To my surprise, the opposite was true. Being sedentary increased the feelings of discomfort, whereas exercising released the tension. The exercise I found most helpful was yoga because it is meditation in movement. I became so focused on my breathing and the poses that my brain did not have time to think about anything else. After attending every yoga class, I felt like I could take on anything. Swimming, Pilates, and gentle cardiovascular exercises have also helped me greatly in reducing stress and feeling great.
Sex
Although sex was impossible for almost a year due to the pain, it became possible and even enjoyable after implementing other relaxation strategies. When I first reintroduced sex back into my life, my partner at the time and I would go gently and stop if it hurt my vulvar area at all. Today, sex again is joyful. Being able to engage in intercourse has boosted my self-esteem and helped me feel sexy again, which empowers me to keep practicing the relaxation techniques.
Listening to the Mind-Body Connection
The mind-body connection is present in all of us, but I am fortunate to have a very strong connection. My thoughts influence my body almost instantly, which is why when I would get depressed my pain would increase, and when I would see my biofeedback practitioner or believe in a good outcome, my pain would decrease. Being aware of this connection is crucial because it can help me or hurt me greatly. After a few months of practicing the relaxation strategies, I saw a different gynecologist and one dermatologist. Both professionals said that there was nothing wrong with my vulvar area—that maybe I just felt some irritation due to the medicines I had previously taken and my current stress. They said that there was no way I needed surgery. When I heard these opinions, I began to feel instantly better—thus proving that my thoughts (and even others’ thoughts) affect my body in significant ways.
Although today I am 100% better, I still experience pain and tightness in my body when I experience the “illness factors” I mentioned above. I still have to remember that feeling healthy and good is a process, not a result, and that even if I feel better one day that does not mean I can stop all my new healthy habits. To completely cure vulvodynia, I needed to change my life habits, perspective, and attitude toward the illness and life. I needed to make significant changes, and now my biggest challenge is to stick to those changes. Biofeedback, imagery, meditation, good food, and exercise are not just treatments that I begin and end on a certain day, but rather they have become essential components of my life forever.
My life with vulvodynia was ultimately a journey of introspection, decision making, and life-changing habits. I struggled with vulvar pain for over a year, and during that year I experienced severe symptoms, depression, and the loss of several friendships and relationships. I felt old, hopeless, useless, and powerless. When I began to incorporate biofeedback, relaxation techniques, journaling, visualization, a proper diet, and regular exercise, life took a turn for the better. Not only did my vulvar pain begin to decrease, but the quality of my overall life improved and I regained the self-confidence I had lost. I became happy, hopeful, and proactive. Even though I practiced the relaxation strategies every day, the pain did not go away in a day or even a month. It took me several months of diligent practice to truly heal my vulvar pain. Even today, such practices have carried on to all areas of my life, and now there is not a day when I do not meditate, even for 5 min.
As paradoxical as it may seem, vulvodynia was a blessing in disguise. I believe that vulvodynia was my body’s way of signaling to me that many areas of my life were in perpetual stress: my pelvic floor, my thoracic breathing, my romantic relationship at the time, etc. When I learned to let go and truly embrace my life, I began to feel relief. I became less irritable and more patient and understanding, with both my body and the outside world. The best advice I can give a woman with vulvar symptoms or any person with otherwise inexplicable chronic pain is to apply the strategies that work for you and stick to them every day—even on the days when you want to go astray. When I started to focus on what my body needed to be nurtured and to live my life and do the things I truly wanted to do, I became free. Today, I live in a way that allows me to find peace, serenity, pride, and fun. I live exactly the way I want to, and I find the time to follow my passions. Vulvodynia, or any kind of chronic pain, does not define who we are. We define who we are.
Conclusion
This introspective account of the client’s personal experience with biofeedback suggests that healing is multidimensional. We suggest that practitioners use a holistic approach, which can provide hope and relief to clients who suffer from vulvodynia or other disorders that are often misunderstood and underreported.
Useful blogs
References
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2006). Coming to our senses: Healing ourselves and the world through mindfulness. Hachette Books
Peper, E., Cosby, J. & Almendras, M. (2022). Healing chronic back pain. NeuroRegulation, 9(3), 164–172. https://doi.org/10.15540/nr.9.3.164
Peper, E., Gibney, K.H, & Holt, C.F. (2002. Make health happen: Training yourself to create wellness. Kendall/Hunt.
Peper, E. Martinex, Aranda, P. & Moss, D. (2015). Vulvodynia treated successfully with breathing biofeedback and integrated stress reduction: A case report. Biofeedback, 43(2), 103–109. https://doi.org/10.5298/1081-5937-43.2.04